* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nolte – Chapter 2 (Development of the Nervous System)
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Binding problem wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Neurocomputational speech processing wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Artificial neural network wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Recurrent neural network wikipedia , lookup
Neural binding wikipedia , lookup
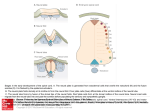
Nolte – Chapter 2 (Development of the Nervous System) and all Class-Notes tagged with Chapter 2. Gastrulation is what gives rise to three different germ layers by going from symmetrical to asymmetrical. o Ectoderm Leads to the nervous system, epidermis, and nervous system These cells all have an affinity to become neurons (since the express bone morphogenetic proteins) The organizer has a BMP inhibitor. o Endoderm Yields the gut o Mesoderm Muscle and tissues o A neural plate initially forms as a longitudinal band of ectoderm This neural plate, by way of the organizer begins to hold from the outside in to approach the dorsal midline. As cells come in an move under the ectoderm that got pinched, the cells on top get inhibited, while the other ones begin to express their calling of becoming neurons. The hinhibited ones become epidermis. The dorsal blastopore lip forms. o A full fusing results in the neural tube, that is separate from the ectoderm. o The segments of the plate that touched first will drop off and break below as the neural crest, which will sit on top of the tube. Neural crest cells will be used for many purposes, but mainly becoming parts of the PNS and Enteric nervous system. This process is known as primary neurulation If a new organizer is introduced, a new axis will be created. This neural tub develops into virtually the entire CNS The cavity becomes the ventricular system. o Concentration gradients cause the dorsal to become separated from ventral The ectoderm is responsible for dorsal and notochord for ventral. A groove will appear marking this sepeartion Its known as the sulcus limitans Formal name for dorsal is alar. Basal for ventral. Sensory in alar, motor with basal. The notochord remains in close proximity to the floor plate and motor neurons flank the floor plate. Sonic Hedghod protein is expressed here and directy ventral identity. Neural Tube has rostral to caudal enlargements in its cylinder. o Prosencephalon (fore) Develops into cerebrum Gives rise to the Telencephalon Becomes the cerebral hemisphere There is a thin membrane that connects the two swellings on either side of the neural tube known as the lamina terminalis o Become the anterior commissure and the CC. Basal part thickens and becomes the basal ganglia. The rest of telencephalon proliferates and hangs down (off of lamina terminalis?) and folds down to the diencephalon. o Where tel and dien meet is the insula. o The hanging creates the ventricular system. Gives rise to the Diencephelon Becomes the thalamus, hypothalamus, and retina. There is a bit of fusion to form the hypothalamic sulcus. o Mesencephelaon(mid) Becomes the midbrain Has a bending known as the cephalic flexure Ends up being the bend between the axes of the brainstem and cerebrum. o Rhombencephalon(hind) Rest of brainstem and cerebellum Gives rise to the metencephalon Becomes the Pons Gives rise to the Myelencephalon Becomes the medulla Between met and myelencephalon there is a pontine flexure This gives rise to the fourth ventricle (remember this looks like a rhombus rhombencephalon) This flexure shoves the dorsal (alar) to the side of the basal in this region. o So now its lateral medial relationship. So the lateral is more sensory and the medial is more motor. o The lateral portions of this alar plate thicken to form the rhombic lips which continue to enlarge, and fuse in the midline and form the cerebellum This seems a little strange since alar was sensory? o Spinal Cord Separated from Rhombencephalon by the cervical fissure. Defects o Complete failure to close the neural tube Craniorachischisis Just the caudal end Spina bifida (myelomeningocele) Just the rostral end Anencephaly o Most of cerebral hemisphere is lost. Sufficient levels of folic acid seem to help against neural tube closer problems We can detect problems by elevated levels of alpha fetoprotein that the open neural tub allows to leak out into maternal circulation. o Abnormal Development Disrupting the signaling molecules can cause holoprosencephaly (can be evoked by mutations in SHH) Failure of prosencephalon to separate into the diencephalon and telencephalon.