* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download November 13th Notes (Nervous System)
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
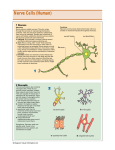
Part 1 Biology 12 http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=x4PPZCLnVkA An integral part of your body’s communication system. It plays an important role in the smooth functioning of the body. The nervous system is a complex network of cells which are specialized in function. The Nervous System allows the body to respond to changes in the internal and external environments. Communication comes in the form of electrochemical messages relayed to and from the brain, or a series of chemical messengers carried in the blood. Through a series of adjustments, all systems of the body are regulated to maintain the internal environment within safe limits (homeostasis). The nervous system has two main divisions: Central Nervous System (CNS) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Consists of the nerves of the brain and spinal cord. Brain is known as the “cerebrum” Acts as a coordinating centre for incoming and outgoing information. The brain consists of millions of nerve cells that cluster together and interact with each other through the process of neurotransmission. It controls most of the bodily functions like movements, thoughts, speech, sensations and memory. The spinal cord is a continuation of the brain and is surrounded by the vertebral bodies that form the spinal column. The spinal cord is divided into four main segments; reach transferring signals to different parts of the body. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vGxho71t ScM&NR=1 Consists of nerves that carry information between the organs of the body and the central nervous system. It can be further divided into: Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Information about your body is continuously relayed to your brain for processing and storage. The cells that transfer these messages to the brain and around the body are nerve cells. Nerve cells gather & transmits electrochemical signals. DID YOU KNOW???? Neurons cannot be repaired Some last a life time Approximately 1000 die each day!!! A nerve is a bundle of neurons attached by connective tissue Average number of neurons in the human brain = 100 billion Nerve “highway” in the human body contains 100 billion neurons 1000 impluses/sec SENSORY Carries signals FROM periphery (outside) TO central nervous system for processing Information FROM environment NOTE: detect external stimuli (light, sound, touch, heat, smell, & taste) or internal conditions (blood pressure, CO2 level & muscle tension) MOTOR Carries signals FROM central nervous system TO body part (e.g. muscles, skin, glands) Respond to sensory neurons Responsible for movement INTERNEURONS Connects sensory or motor neurons to central nervous system Carries messages in-between neurons Majority of neurons in the brain are interneurons Cell Body Contains all organelles, including a nucleus Dendrites Projections off cell bodies Make connections with other cells Dendrites Cell body Cell body Nucleus Figure 27.3 Axon Long cable like projection off cell body Sends messages (nerve impulses) Myelin Fatty protein that covers/insulates most nerves Increases speed of transmission Formed by Schwann cells Nodes Sheath of Ranvier Exposed axon between myelin sheath Dendrites Cell body Cell body Axon Nucleus Nodes of Ranvier Myelin sheath Figure 27.3 Synaptic knob End of axon branches Comes near dendrites of adjacent neurons Passes messages across synapse (the space between neurons) Signal direction Dendrites Cell body Cell body Nucleus Axon Supporting cell Signal pathway Synaptic knobs Nodes of Ranvier Myelin sheath Figure 27.3 Moves in only one direction From dendrite to cell body, axon, then synaptic knob Signal direction Dendrites Cell body Cell body Nucleus Axon Supporting cell Signal pathway Synaptic knobs Nodes of Ranvier Myelin sheath Figure 27.3 The three interconnected functions of the nervous system are carried out by the three types of neurons Sensory input Sensory neuron Integration Sensory receptor Motor neuron Interneuron Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) Figure 27.2 Nervous System explained Nervous System Rap How Neurons Work Draw a large motor neuron on a white piece of paper. Label Cell body Nucleus Dendrites axon Then Myelin sheath Schwann cells Node of Ranvier Synaptic knob draw arrows to show the message direction Identify the motor neuron functions Synaptic knob