* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Brain
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Split-brain wikipedia , lookup
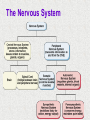
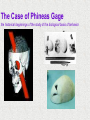
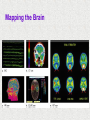
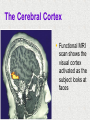
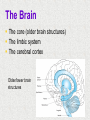
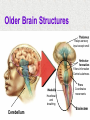
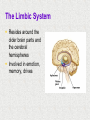
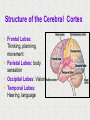
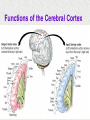
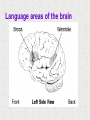
Module 4 The Brain The Nervous System The Brain Centerpiece of the nervous system weighs 1300 - 1400 g made up of about 100 billion neurons works by firing millions of synapses and releasing billions of neurotransmitter molecules. “the most complex living structure on the universe” The Case of Phineas Gage the historical beginnings of the study of the biological basis of behavior Lesions, autopsies, EEG Lesions: the site and extent of the brain tissue damage are important guides to the kind of disruption in behavior that is observed and vice versa. Lesioned brains can be autopsied and studies in detail Electrocephalograms (EEG): Electrodes are attached to the subject’s scalp, and the device records the patterns of brain waves. How do we study the brain? Autopsies Clinical observations Lesions EEG Neuroimaging Neuroimaging PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Radioactive form of sugar is given Sugar goes to the region of the brain that is active MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) uses magnetic fields and radio waves Generates images that distinguish among different types of soft tissue Functional MRI Reveals blood flow, therefore brain activity Compares successive MRI scans while the patient is performing a task Mapping the Brain The Cerebral Cortex Functional MRI scan shows the visual cortex activated as the subject looks at faces The Brain The core (older brain structures) The limbic system The cerebral cortex Older/lower brain structures Older Brain Structures Relays sensory input except smell Filters information Controls alertness Heartbeat and breathing Cerebellum Pons Coordinates movements Brainstem Older brain structures Brainstem – the crossover point Medulla – autonomic vital functions Pons – Coordination of movement Reticular Formation – nerve network Filters and relays information from spinal cord Controls arousal and alertness Thalamus – sensory switchboard for sight, hearing, touch, and taste Cerebellum - the “little brain” at the rear of the brainstem Enables non- verbal behavior & memory Decision making Coordinate voluntary movement and balance The Limbic System Resides around the older brain parts and the cerebral hemispheres Involved in emotion, memory, drives The Limbic System Hippocampus: processes memory Amygdala: influences aggression and fear Perception of these emotions Processing of emotional memories Hypothalamus: monitors the pituitary gland Influences feelings of hunger, thirst, body temperature and sexual arousal Houses the pleasure or reward centers The Cerebral Cortex: our resource for adaptability Largest part of the brain Cerebral cortex Cerebral hemispheres Corpus callosum Body’s ultimate control and information processing system Adaptation of species resulted in changes in the cerebral cortex 15 Structure of the Cerebral Cortex Frontal Lobes: Thinking, planning, movement Parietal Lobes: body sensation Occipital Lobes: Vision Temporal Lobes: Hearing, language Functions of the Cerebral Cortex Functions of the Cerebral Cortex Motor Functions Message send out to the body is controlled by the motor cortex – the area at the rear of the frontal lobes Sensory Functions Incoming messages are controlled by the sensory cortex - area at the front of the parietal lobes The rest (90% of the cortex): Association areas Integrate information Involved in higher mental functions such as language, remembering, thinking. Our divided brain Hemispheres control and receive information from the opposite sides of the body Hemispheric Specialization Left hemisphere: language, logic, and complex motor behavior Right hemisphere: non-linguistic functions including recognition of faces, places, and sounds (music) Localizing cognitive activities Are abilities asymmetrically represented in the two hemispheres? Left Hemisphere (LH) hemisphere critical for language the idea of hemispheric specialization by the end of 1860s hemispheric specialization : : the tendency for a given psychological function to be served by one of the hemispheres evidence: LH lesions disrupt damage language; RH damage disrupt visual-spatial abilities language faculty served by the LH; musical and visual-spatial cognition by the RH Language areas of the brain Split-Brain research removal of corpus callosum, the connective tissue that communicates info between the LH and the RH, from epilectic patients background: lateralization of visual, auditory, and tactile systems one side of the brain controls the opposite of the body and information receiving field set up a task that poses a question to one hemisphere and requires the answer from another Split brain: visual field study HE ART Left visual field Right visual field Interpretation of split-brain work the RH of a split-brain patient has some awareness of the stimulus when a stimulus is presented to the left visual field but cannot perform tasks where language skills are required Hemispheric specialization/lateralization: the RH has a limited ability to perform language skills The brain acts as a unifed whole Ex: Language functions READING Register in visual area Transform words into auditory code Auditory code received and understood Motor area produces the word Brain Plasticity The brain’s capacity for modification Not only genes but also our expriences shape the brain Brain reorganizes itself following damage (especially in children) Many possibilities within the neural networks Brain reorganizes itself through intense learning experiences Blind people– use a finger to read Braille Video--- woman born with half a brain