* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Peripheral Nervous System
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
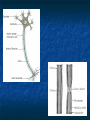
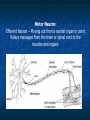
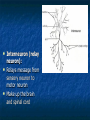
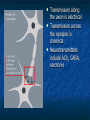
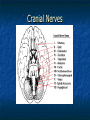
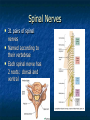
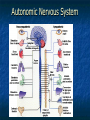
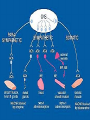
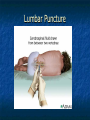
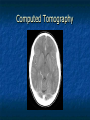
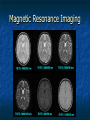
Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Objectives Name and state the function of the cranial nerves State which division of the nervous system is responsible for: Slowing heart rate Vasoconstriction Increased peristalsis Relaxation of the bladder sphincter Increase in adrenalin Thick viscid saliva Peripheral Nervous System Objectives Describe the neuro assessment Plan essentials of nursing care for the unconscious patient Explain the nursing responsibility for specific neurological function tests. Peripheral Nervous System Vocabulary Acetylcholine Cholinesterase Sympathomemetic/ adrenergic Cholinergic Sympathetic Parasympathetic Muscarinic Nicotinic The Nervous System Two divisions Central Peripheral Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Sympathetic Parasympathetic Neurons Three types Sensory (afferent) Motor (efferent) Somatic Visceral Somatic Visceral Interneurons Motor Neuron: Efferent Neuron – Moving out from a central organ or point Relays messages from the brain or spinal cord to the muscles and organs Sensory Neuron: Afferent Neuron – Moving towards a central organ or point Relays messages from receptors to the brain or spinal cord Interneuron (relay neuron): Relays message from sensory neuron to motor neuron Make up the brain and spinal cord Transmission along the axon is electrical Transmission across the synapse is chemical Neurotransmitters include ACh, GABA, serotonin Nerves and Nerve Tracts Nerve Sensory or motor Mixed Group of like neurons Both motor and sensory Nerve tract Groups of neurons within the CNS All neurons either sensory or motor Sensory Pathway Receptors Sensory neurons Sensory tracts Sensory areas Characteristics of sensation The Senses Cutaneous Referred Pain Muscle sense Taste Smell Hunger and Thirst Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves Named according to their vertebrae Each spinal nerve has 2 roots: dorsal and ventral Reflexes Unconscious Involuntary Mediated at the level of the spine Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic Also called thoracolumbar Dominant in stressful situations Parasympathetic Craniosacral Cranial nerve pairs 3,7,9, 10 Dominates in non-stress situations The Autonomic Nervous System Parasympathetic Stimulation P Iris (eye muscle) Pupil dilation Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine Dopamine Found at neuromuscular junctions Primarily in the brain As a medication it works on sympathetic NS Norepinepherine Epinepherine Aging and the nervous system Decreased number of neurons does not cause mental impairment Reflexes and voluntary movement slowed Dry eyes and constipation due to aging ANS Transient HOTN dt decreased sympathetic stimulation Neurologic Testing Nurse’s role Bedside testing Lumbar puncture CT MRI Lumbar Puncture Electroencephalography Radiologic Studies Brain scan Angiography Computed tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Computed Tomography Magnetic Resonance Imaging Brain Scan Radioactive isotope distribution Detect abscess, tumor, contusion, vascular occlusion, hemorrhage, hematoma