* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous and Endocrine Systems
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
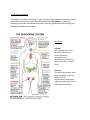
The Nervous and Endocrine Systems The nervous system is the body’s speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells. It’s broken down into two sections: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system is responsible for gathering information and for transmitting CNS decisions to other body parts. Nerves, electrical cables formed of bundles of axons, link the CNS with the body’s sensory receptors, muscles, and glands. The optic nerve, for example, bundles a million axons into a single cable carrying the messages each eye sends to the brain. Information travels through three types of neurons 1. Sensory neurons which carry messages from the body’s tissues and sensory receptors to the spinal cord and brain 2. Motor neurons which carry instructions from the central nervous system out to the body’s muscles and glands. 3. Interneurons are neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs The Central Nervous System (CNS) Simply put, the Central Nervous System consists of the brain and the spinal cord. The brain enables all our humanity—our thinking feeling, and acting. It’s connected to our peripheral nervous system by the spinal cord--our two-way information highway The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) The PNS has two components: 1. The somatic nervous system which enables voluntary control of our skeletal muscles 2. The autonomic nervous system which controls our glands and the muscles of the internal organs a. Sympathetic nervous system: part of ANS that arouses and mobilizes the body b. Parasympathetic nervous system: part of ANS that calms and conserves energy The Endocrine System The endocrine system is the body’s “slow” chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Hormones are chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands and travel through the bloodstream affect other tissues. Key Glands Adrenal: pair of glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) that help arouse the body in times of stress. Pituitary: The endocrine system’s most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, the pituitary regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands