* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Module 10 Guided Notes The Nervous and Endocrine Systems
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
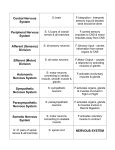
Module 10 Guided Notes The Nervous and Endocrine Systems THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. What role does the Central Nervous System play? The decision maker 2. What role does the peripheral nervous system play? Gathers information and transmits decisions made by CNS to other parts of body 3. What role do nerves play? Electrical cables made up of millions of axons connecting the CNS with body’s sensory receptors, muscles, and glands 4. What are the 3 types of Neurons through which information travels? 1. Sensory Neurons = carry messages from body’s tissues inward to the brain and spinal cord for processing. Sensory Neurons located dorsally (or on back of spinal cord) 2. Motor Neurons = Carry instructions from the CNS out to the body’s muscles and glands Motor Neurons located anterior of spinal cord (the front) 3. Interneurons = Facilitate the processing of information within the brains internal communication system – Make reflexes happen 5. What are the 2 Parts of the Peripheral Nervous System? Somatic and Autonomic o Somatic = Enables control of voluntary skeletal muscles (walking, jumping, MOVING) o Autonomic = Controls glands and internal organs (usually operates on Autopilot) Broken into 2 systems (Sympathetic and Parasympathetic) 6. Explain the different functions of the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous Systems Sympathetic = creates arousal and expends energy o Accelerate heart rate, raise blood sugar, raise blood pressure, generate sweat – In response to stress Parasympathetic = Produces opposite effects – Calms and conserves energy o Slows heart rate, lowers blood pressure and blood sugar *** These two systems work together regularly to keep our body operating at a steady internal rate. *** Opponent Process – Working in direct opposition to each other to help maintain Homeostasis The Central Nervous System: 7. How many Neurons exist in our brain? 40 Billion – each connected with 10,000 other neurons = 400 Trillion Synapses 8. Why do Neurons form Neural Networks Like people moving to the same city…it makes doing their job easier (forming complex circuits) If neurons are communicating a similar message they will bundle with other like Neurons to improve the efficiency of the message delivery 9. What role does the Spinal Cord play in Neural Communication? Information super highway o Sensory message travel up the spinal cord to the brain along ascending neural fibers o Descending fibers send motor neurons back down to the body 10. Why is the brain not involved in Reflexive movement? Interneurons in the spinal cord receive sensory message, interpret it, then send a motor message back out all before the message has made it to the brain o EX: Moving hand away from flame before actually feeling pain 11. What would happen if your spinal cord were severed? The brain loses the ability to communicate with the body. Loss of all sensation and voluntary movement with sensory and motor connections. o Reflexes might still exist o Autonomic system may still work ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 12. How does the endocrine system communicate throughout the body? Through the release of hormones in the blood stream interacting with body tissue and the brain o Hormones influence the brains interest in Sex, food, and aggression 13. What is the biggest difference between the way the Nervous System and Endocrine System communicate. Nervous – Very fast…zipping messages from eyes to brain to hand in fractions of seconds Endocrine – Takes seconds for messages to trudge through the blood stream *** Hormonal Messages tend to last longer (outlast the effects of) 14. What role do the Adrenal Glands play. They secrete hormones (epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine) that help arouse body during stress. – Create “Fight-or-Flight” response o Located on top of Kidneys 15. Why is the pituitary gland considered the most influential gland in the body? It is located in the core of the brain (controlled by hypothalamus) Releases growth hormone for development and oxytocin birthing, milk flow, orgasm, promotes group bonding/cohesion Master gland, influencing the release of hormones by other glands Hypothalamus receives message from CNS then communicates w/ Pituitary which then communicates with other glands to release necessary hormones into the body.