* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The NERVOUS System
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
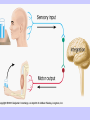
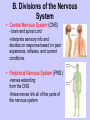
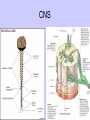
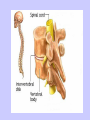
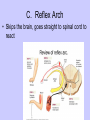
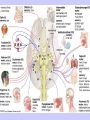
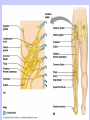
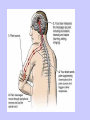
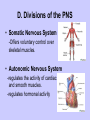
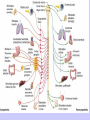
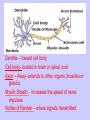
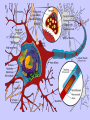
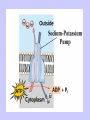
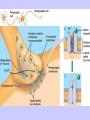
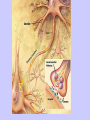
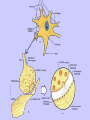
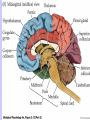
Unit II. Nervous and Endocrine Part 2: The Nervous System The NERVOUS System A. Functions of the Nervous System 1. Monitors stimuli (Sensory input) 2. Processes, makes decisions about how to respond to stimuli. 3. Causes a response by activating muscles, or glands (motor output) B. Divisions of the Nervous System • Central Nervous System (CNS) - brain and spinal cord -interprets sensory info and decides on response based on past experience, reflexes, and current conditions. • Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): -nerves extending from the CNS -these nerves link all of the parts of the nervous system CNS C. Reflex Arch • Skips the brain, goes straight to spinal cord to react D. Divisions of the PNS • Somatic Nervous System -Offers voluntary control over skeletal muscles. • Autonomic Nervous System -regulates the activity of cardiac and smooth muscles. -regulates hormonal activity Autonomic E. Characteristics of Nerves • Nerves (Neurons) • amitotic: they do not divide (cannot be replaced if destroyed) -high metabolic rate-require constant O2 and glucose, die within a few minutes without O2 Dentrite – toward cell body Cell body- located in brain or spinal cord Axon – Away- extends to other organs (muscles or glands). Myelin Sheath - increases the speed of nerve impulses. Nodes of Raniver – where signals transmitted. F. How Neurons Act 1. Neuron AT REST • Resting Potential: the inside of the cell membrane is more negatively charged than the outside. At rest, there is more Na+ outside than inside the cell. (More K+ is inside the cell) 2. Sodium Potassium Pump! • Sodium and Potassium: Na+ and K+ are exchanged across the cell membrane to signal action. • ATP is needed!! • Like the wave 3. The role of Calcium • Calcium is needed to open the Neurotransmitter channels in our axon terminal. • Neurons communicate at synapses - gap G. Diseases • Multiple Sclerosis – Myelin Sheaths are gradually degenerate. • ALS • Congenital Insensitivity to Pain Drugs can affect your nervous system. • Article