* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The building blocks of matter (elements and molecules) form the
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
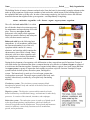
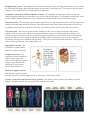
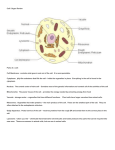
Name _______________________________________________________ Period _____ Body Organization The building blocks of matter (elements and molecules) form the basis for increasingly complex substances that make up living organisms. Single atoms combine to form molecules which in turn are the building blocks for the organelles that make up living cells. In order of increasing complexity, the list below shows the different structural elements that together make up an organism – an independently living thing: atoms – molecules - organelles - cells - tissues - organs - organ systems - organism The cell is the basic unit of life. It is within the cell that the chemical reactions necessary for maintenance and reproduction of life take place. There are two types of cells, prokaryotic cells (single-celled organisms that do not contain a nucleus) and eukaryotic cells (cells that contain a nucleus). Eukaryotic cells have the following basic components: A cell membrane which forms the outermost boundary layer of the cell, cytoplasm which consists of a watery substance, and a nucleus which contains the chromosomes where DNA is found. Many eukaryotic cells have other organelles such as an endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, and ribosomes. During the development of an organism, cells differentiate so they can perform specific functions. Groups of cells with similar specializations that form a common function are referred to as a tissue. Organs are groups of several tissues that function together. Examples of organs include kidneys, spleen, liver, heart, lungs and brain. An organ system is a group of organs that work together to perform a specific function. Examples of organ systems include skeletal system, muscular system, and digestive system. The human body is made up of several organ systems that work together as one unit. The major organ systems of the body work together, either directly or indirectly, to keep the body functioning normally. Circulatory system - The circulatory system transports blood throughout an animal's body and consists of the heart, blood, arteries, veins, and capillaries. Digestive system - The digestive system enables animals to break down food that they eat and obtain energy and nutrients for other body processes. It consists of the stomach, intestines, and esophagus. Endocrine system - The endocrine system is made up of glands (such as the thyroid and pituitary) and hormones, which are chemicals released from glands into the bloodstream. These glands and hormones control or influence various body functions such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction. Integumentary system - The integumentary system is an animal’s outer covering, such as skin, scales, feathers, fur, and other body parts, that protect the animal and prevent it from drying out. This system is the first barrier to disease and is responsible for controlling body temperature. Lymphatic system (also called the Immune System) - The lymphatic system helps to filter out diseasecausing organisms and helps to drain fluid waste from in and around tissues. The lymphatic system helps in the defense against infection and disease. The lymph nodes and white blood cells are part of this system. Muscular system - The muscular system enables animals to move and control movement. The muscular system consists of skeletal muscles which help move the skeleton and control movement, smooth muscles which are involuntary and control the stomach and intestine, and cardiac muscles which include the heart muscles. Nervous system - The nervous system enables animals to send, receive, and process nerve and sensory impulses. The nervous system can be broken down into three categories which include the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord), the peripheral nervous system (the nerves that branch off of the brain and spinal cord and carry nerve signals to muscles and glands), and the autonomic nervous system (controls involuntary actions such as heartbeat and digestion). This system controls all bodily functions. The key parts of this system are the brain, nerves and spinal cord. Reproductive system - The reproductive system enables animals to produce offspring. Respiratory system - The respiratory system includes an animal's nose, lungs, and trachea. The respiratory system brings oxygen into the body and releases waste carbon dioxide back into the air. Skeletal or support system The skeletal or support system provides internal or external support (such as a skeleton, exoskeleton or shell). Urinary system (also called the Excretory System) - The urinary system consists of the kidneys and the bladder. It enables animals to expel waste fluids in the form of urine.