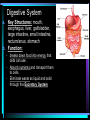
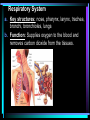
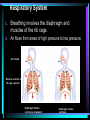
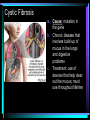
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Body_Systems_Overview
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
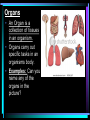
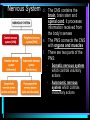
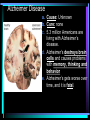
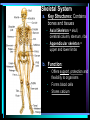
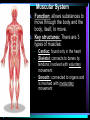
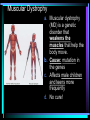
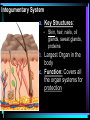
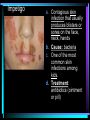
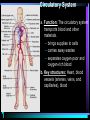
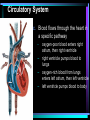
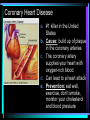
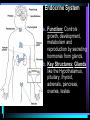
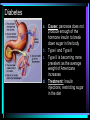
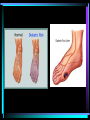
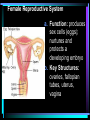
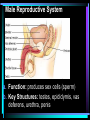
Warm Up 1. What do you want to accomplish in this class before the end of the school year? 2. What have we learned about the human body so far in this class? Agenda • Objectives: SWBAT create a flowchart of the levels of organization within an organism and be able to provide examples based on a particular system of the human body. • Reminders: Progress Reports---Today at lunch and after school is your last chance to improve your progress report grades • Start unit on the Human Body! • Notes on Levels of Organization and Worksheets • Exit Ticket Are these things alive? Plant air wind animals bacteria viruses rocks soil fire water Characteristics of Life Living things are organized at different levels. Levels of Organization: Cell(Smallest) Tissue Organ Organ System Organism(Biggest) Cells • The most basic unit of life. • If we wanted to dig deeper, we would say that cells are built out of Organelles. • Examples: Tissues • Tissues are groups of cells that are linked together. • Tissues link cells, allowing the cells to carry out a specific function. • Examples: Organs • An Organ is a collection of tissues in an organism. • Organs carry out specific tasks in an organisms body. • Examples: Can you name any of the organs in the picture? Organ Systems • Organ systems are groups of organs, linked together, all performing a single job together. • Examples: Organism: So many varieties! Giant Squid Praying Mantis Levels of Organization Chart Brain Pop Video • http://www.brainpop.com/science/diversi tyoflife/humanbody/ • Brain pop Activity Reading Guide • This is to be done individually • You may use highlighters to help you answer the questions and identify vocabulary Exit Ticket • Name each level of organization in the body and provide an example for each one. Warm Up • Name each level of organization in the body and provide an example of each. Agenda and Announcements • Objective: SWBAT complete a chart on systems of the body as well as write a reflection on one of the systems • Today – Start overview of systems of the body – Opportunity for Community Service – Turn in Reading Guide and Brain Pop Activity from yesterday. – Individual Readings MAJOR BODY SYSTEMS • • • • • • • • • Nervous Skeletal Muscular Integumentary (skin) Digestive Respiratory Circulatory Endocrine Reproductive Draw Chart Nervous System a. Function: receives and relays info about body activities - Two Parts - Central Nervous System: Processes information from the senses Peripheral Nervous System: Controls voluntary and involuntary actions by connecting the CNS with the organs and muscles. b. Key Structures: Made up of nerve cells (neurons), brain, spinal cord Nervous System d. The CNS contains the brain, brain stem and spinal cord. It processes information received from the body’s senses e. The PNS connects the CNS with organs and muscles f. There are two parts of the PNS: - - Somatic nervous system which controls voluntary actions Autonomic nervous system which controls involuntary actions Alzheimer Disease a. Cause: Unknown b. Cure: none c. 5.3 million Americans are living with Alzheimer’s disease. d. Alzheimer's destroys brain cells and causes problems with memory, thinking and behavior e. Alzheimer’s gets worse over time, and it is fatal. Skeletal System a. Key Structures: Contains bones and tissues - Axial Skeleton = skull, cerebral column, sternum, ribs - Appendicular skeleton = upper and lower limbs b. Function: - Offers support, protection and flexibility to organisms Forms blood cells Stores calcium Osteoporosis a. Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break. b. Causes: not enough calcium and vitamin D, low weight, heredity c. Women are 4 times more likely to get it d. Treatment: vitamins, weight-bearing exercise Muscular System a. Function: allows substances to move through the body and the body, itself, to move. b. Key structures: There are 3 types of muscles: - - Cardiac: found only in the heart Skeletal: connects to bones by tendons; involved with voluntary movement Smooth: connected to organs and is involved with involuntary movement Muscular System c. There are two types of filaments in muscles made up of certain proteins: Myosin and Actin d. When a muscle contracts, the thin filament (actin) slides over the thick filament (myosin) Muscular Dystrophy a. Muscular dystrophy (MD) is a genetic disorder that weakens the muscles that help the body move. b. Cause: mutation in the genes c. Affects male children and teens more frequently d. No cure! Integumentary System a. Key Structures: - Skin, hair, nails, oil glands, sweat glands, proteins b. Largest Organ in the body c. Function: Covers all the organ systems for protection Impetigo a. Contagious skin infection that usually produces blisters or sores on the face, neck, hands b. Cause: bacteria c. One of the most common skin infections among kids. d. Treatment: antibiotics (ointment or pill) Digestive System a. Key Structures: mouth, esophagus, liver, gallbladder, large intestine, small intestine, rectum/anus, stomach b. Function: - breaks down food into energy that cells can use. - Absorb nutrients and transport them to cells. - Eliminate waste as liquid and solid through the Excretory System Diarrhea and other diseases a. frequent loose or liquid bowel movements b. Causes: viruses, parasites, bacteria in food or drinking water c. Common death in developing countries; 2nd leading cause of infant deaths worldwide d. Can lead to dehydration, which can lead to death e. Cholera, a rapidly fatal disease, involves both diarrhea and dehydration Reflection Directions: Respond to the following questions in complete sentences in your notebooks. • Which system of the body was the most interesting to you? • What was something new you learned about the system? Reading Guides • By the end of this week, you should pick a system of the body for a mini project that you will complete • In order to help you choose, you will complete at least 4 of these short Reading Guides by Monday. • You choose which ones you want to do. • I will have more options available tomorrow. Warm Up 1. What does the nervous system do for the body? 2. What is a disease that affects the skeletal system? 3. What is another disease/health issue that you think may affect the nervous, skeletal, muscular or integumentary systems? Agenda • Objective: SWBAT complete a chart on systems of the body as well as write a reflection on one of the systems • Today – Complete overview of systems of the body – Opportunity for Community Service – Go over Mini Project – Individual Readings Respiratory System a. Key structures: nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, lungs b. Function: Supplies oxygen to the blood and removes carbon dioxide from the tissues. Respiratory System c. Breathing involves the diaphragm and muscles of the rib cage. d. Air flows from areas of high pressure to low pressure. Air inhaled. Air exhaled. Muscles and rib cage relax. Muscles contract and rib cage expands. Diaphragm flattens and moves downward. Diaphragm relaxes and rises. Cystic Fibrosis a. Cause: mutation in the gene b. Chronic disease that involves build-up of mucus in the lungs and digestive problems c. Treatment: use of devices that help clear out the mucus; must use throughout lifetime Circulatory System a. Function: The circulatory system transports blood and other materials. – brings supplies to cells – carries away wastes – separates oxygen-poor and oxygen-rich blood b. Key structures: Heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, and capillaries), blood Circulatory System c. Blood flows through the heart in a specific pathway - oxygen-poor blood enters right atrium, then right ventricle – right ventricle pumps blood to lungs – oxygen-rich blood from lungs enters left atrium, then left ventricle – left ventricle pumps blood to body Coronary Heart Disease a. #1 killer in the United States b. Cause: build up of plaque in the coronary arteries c. The coronary artery supplies your heart with oxygen-rich blood d. Can lead to a heart attack e. Prevention: eat well, exercise, don’t smoke, monitor your cholesterol and blood pressure Endocrine System a. Function: Controls growth, development, metabolism and reproduction by secreting hormones from glands. b. Key Structures: Glands like the Hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, adrenals, pancreas, ovaries, testes Diabetes a. Cause: pancreas does not produce enough of the hormone insulin to break down sugar in the body b. Type I and Type II c. Type II is becoming more prevalent as the average weight of Americans increases d. Treatment: Insulin injections, restricting sugar in the diet Female Reproductive System a. Function: produces sex cells (eggs); nurtures and protects a developing embryo b. Key Structures: ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina Male Reproductive System a. Function: produces sex cells (sperm) b. Key Structures: testes, epididymis, vas deferens, urethra, penis STDs Imagine this on your privates… a. b. c. d. No cure: AIDS, genital herpes Curable: gonorrhea, chlamydia Cause: unprotected sex Treatment: depends on the specific type of STD – Genital warts: freezing – Antibiotics Reading Guides • By the end of this week, you should pick a system of the body for a mini project that you will complete • In order to help you choose, you will complete at least 4 of these short Reading Guides by Monday. • You choose which ones you want to do. • There are more options available today! Warm Up 1. Which two systems of the body make sure that we have blood with oxygen flowing through our body? 2. Which system of the body will you pick for your mini project? (skeletal, muscular, circulatory, digestive, respiratory, reproductive, nervous, endocrine) 3. What do you want to learn about the system you picked? Agenda and Announcements • Today – SWBAT: complete a jigsaw activity in which each student becomes an expert on one system of the body and then shares the information with their base group members. – We will video tape 20-40 minutes of the lesson today • Tomorrow – Continue Jigsaw Activity and video tape another 20-40 minutes Directions • You will be assigned to two groups that you will work with today and tomorrow. • One is your Expert group – You will work together to collect information from readings on a particular system • The other is your Base group – You will share the information you gathered about each system of the body • No matter which group you are with, you need to write the information in your own words! Expectations • Everyone will read their texts and work on putting the terms into their own words • I will not see students copying off of one another Groups Overview • Hand out Project Information Warm Up 1. What is something interesting that you learned about a system of the body yesterday? 2. Which system of the body will you pick for your mini project? (skeletal, muscular, circulatory, digestive, respiratory, reproductive, nervous, endocrine) 3. What do you want to learn about the system you picked? Agenda • Today – SWBAT: complete a jigsaw activity in which each student becomes an expert on one system of the body and then shares the information with their base group members. • Monday – In class time to work on your projects (Bring materials so you’ll have something to do!!) • Projects due Wednesday at the beginning of class. Jigsaw Activity Information • Expectations Chart • Group Assignments Jigsaw Activity • Today you will be answering questions about a system of the body in your expert groups and will share that information with your base groups. You will be working with the same groups today, unless I tell you otherwise. • Remember: – Discuss the questions with your group mates to determine an answer. – Respond in your won words in complete sentences. – Read your answers to the members of your base group and answer their questions. Monday Warm-Up 1. What does the endocrine system do? 2. Which systems of the body protect and support important organs as well as the body from germs? 3. What is an example of a disease or problem that you can use for your system of the body. Monday Agenda and Announcements • Today Finish the Jigsaw Activity • In class work time on your mini project • Reminders – Mini Project due at the beginning of class on WEDNESDAY