* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell / Organ Review Parts of a cell: Cell Membrane: controls what
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
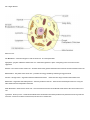
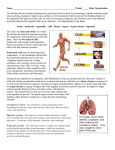
Cell / Organ Review Parts of a cell: Cell Membrane: controls what goes in and out of the cell. It is semi-permiable. Cytoplasm: jelly-like substance that fills the cell – holds the organelles in place. Everything in the cell is found in the cytoplasm. Nucleus: The control center of tohe cell – Contains most of the genetic information and controls all of the activities of the cell Mitochondria: The power house of the cell – provides the energy needed by extracting energy from food Vacuole: storage center – organelles that have different functions. Plant cells have larger vacuoles than animal cells. Ribosomes: Organelles that make proteins – the main produce of the cell. These are the smallest part of the cell. They are often attached to the endoplasmic reticulum Golgi Apparatus: Postal service of the cell – receives proteins from the rough ER and sends them to the correct place in the cell. Lysosome: Clean up crew – chemicals that break down old melcules and waste products into parts that can be recycled into new ones. These are common in animal cells, but are rare in animal cells. Parts of a Plant Cell Cytoplasm Cell Wall: (only found in a plant) – A rigid outer barrier that supports and protects the cell Chloroplast: (only found in a plant) – organelles that make food through photosynthesis. The plants convert sunlight into sugar. Diffusion – Movement of particles across a semipermeable membrane from a high concentration to a low concentration. This continues until equilibrium is reached and the particles move across in both directions at equal speeds. Osmosis – The diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane. LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION CELLS TISSUES ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEMS ORGANISM (SIMPLE) (MOST COMPLEX) SPECIALIZED CELLS: The cells each have their own jobs and work together to perform all functions. SPECIALIZED TISSUES: Plant Tissue Transport (transports water and food) Protective tissue (a covering that forms to protect the plant) Ground Tissue (where photosynthesis takes palce)Observe and distinguish the cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, chloroplast, and cytoplasm of cells. Animal Tissue Nerve – makes up your brain and nervous system. The nerves carry electrical impulses to the brain. Muscle – performs the necessary movements and helps you to do things. 3 types of muscle tissue (cardiac, smooth, and skeletal) Connective – holds bones and muscles together Protective – skin shields body from the elements and helps it to maintain healthy levels of moisture and nutrients. SPECIALIZED ORGANS: Plant Organs Leaves Roots Stems Animal Organs Groups of tissue that carry on a specific job in a living organism. Examples include liver, heart, lungs, stomach, and kidneys. ORGAN SYSTEMS: Several organs work together to form an organ system. Organs within the systems may overlap Integumentary System skin (also includes nails and hair) 1. Protective covering of the body 2. Helps maintain homeostasis 3. Prevents water loss 4. Barrier to microorganisms 5. Fingernails protect tips of fingers 6. Muscular System Muscles found along the walls of 1. organs Hair keeps body warm Voluntary – we can control movement 2. Muscles throughout body Involuntary – we do not control movement 3. Muscle fibers are long, thin cells that allow muscles to contract or relax and enable us to move Nervous System 4. 3 types of muscle 1. Controls muscles and maintains balance 2. Controls all the other organ systems 3. Sense surroundings 4. Sense environment inside body 5. Prepare body to fight or flee in an emergency Digestive System 6. Use language 1. Eliminates waste 2. Maintains water and Mouth, esophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, small and large intestine Excretory System Kidneys, bladder, skin, lungs chemical balance Respiratory System Nose, mouth, air passages, lungs 1. Carries air into and out of lungs 2. Gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) are exchanged Skeletal System Bones 1. Provides structure 2. Supports and protects internal organs Circulatory System Heart, blood vessels, blood 1. Transports nutrients and wastes to and from all body tissues Endocrine System Works with the nervous system to 1. Works with the nervous send chemical signals throughout system to send chemical body signals throughout the body Miscellaneous facts to know: 1. Robert Hooke –first man to see cells. He made a microscope in 1665. 2. Anton von Leeuwenhoek build a microscope and saw tiny animals in pond water. They were later classified as protists. He was the first person to see bacteria. 3. 4. Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann developed the cell theory.