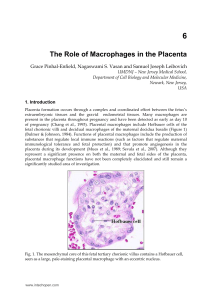
WJG-23-2870 - F6 Publishing Home
... exposure duration to antibiotics, acidic conditions and the immune response[37]. Moreover, as H. pylori is optimally evolved to reduce its exposure to acidic gastric conditions, it can localize in mucus close to the epithelial surface where acidity is tolerable for longer survival. This strategy ado ...
... exposure duration to antibiotics, acidic conditions and the immune response[37]. Moreover, as H. pylori is optimally evolved to reduce its exposure to acidic gastric conditions, it can localize in mucus close to the epithelial surface where acidity is tolerable for longer survival. This strategy ado ...
nature`s everyday - Standard Process
... Supports a balanced immune system response. Promotes healthy macrophage and T cell activity. Is safe for supporting the complete range of respiratory health goals. ...
... Supports a balanced immune system response. Promotes healthy macrophage and T cell activity. Is safe for supporting the complete range of respiratory health goals. ...
Allelic Amino Acid Substitutions Affect the
... have been described, often only in heterozygous combinations because of their low allelic frequency (3). The two most common PLAP phenotypes, S (slow) and F (fast), differ only in an Arg#{176} to p2o9 substitution (4), but additional amino acid replacements have been identified for the I (intermedia ...
... have been described, often only in heterozygous combinations because of their low allelic frequency (3). The two most common PLAP phenotypes, S (slow) and F (fast), differ only in an Arg#{176} to p2o9 substitution (4), but additional amino acid replacements have been identified for the I (intermedia ...
NOD2, an intracellular innate immune sensor involved in
... protein) family of intracellular sensors of pathogen/microbe-associated molecular patterns.1,2 It is encoded by the CARD15 gene (on chromosome 16 in humans) and recognizes muramyl dipeptide (MDP), a component of the peptidoglycan present in the bacterial cell wall. Since its discovery in 2000, numer ...
... protein) family of intracellular sensors of pathogen/microbe-associated molecular patterns.1,2 It is encoded by the CARD15 gene (on chromosome 16 in humans) and recognizes muramyl dipeptide (MDP), a component of the peptidoglycan present in the bacterial cell wall. Since its discovery in 2000, numer ...
ExamView - SUPERVOCAB PRETESTLISTS1THRU17.tst
... The body’s transportation system. The collection of all the genes in a population. ...
... The body’s transportation system. The collection of all the genes in a population. ...
Design of Noninflammatory Synthetic siRNA Mediating Potent Gene
... immune recognition of the duplex siRNA. To confirm that this approach to siRNA design would successfully inhibit inflammatory responses to siRNA in vivo, we assessed the immunostimulatory activity of the 2VOMe-modified h-gal and apoB-1 siRNA in mice. Intravenous administration of lipid-encapsulated ...
... immune recognition of the duplex siRNA. To confirm that this approach to siRNA design would successfully inhibit inflammatory responses to siRNA in vivo, we assessed the immunostimulatory activity of the 2VOMe-modified h-gal and apoB-1 siRNA in mice. Intravenous administration of lipid-encapsulated ...
The Metabolic Functions of Carnitine in Torulopsis
... The carnitine-responsive yeast strain Torulopsis bacina ATCC 260 14 and the wild-type strain T. bot:ina ATCC 22987 were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection, Rockville, Md., USA. Cells were maintained, inocula were prepared and bioautography was done as described by Lewin & Bieber (197 ...
... The carnitine-responsive yeast strain Torulopsis bacina ATCC 260 14 and the wild-type strain T. bot:ina ATCC 22987 were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection, Rockville, Md., USA. Cells were maintained, inocula were prepared and bioautography was done as described by Lewin & Bieber (197 ...
Factors Affecting Wound Healing
... IL 60612, USA; *corresponding author, [email protected] J Dent Res 89(3):219-229, 2010 ...
... IL 60612, USA; *corresponding author, [email protected] J Dent Res 89(3):219-229, 2010 ...
Alopecia Areata - New England Journal of Medicine
... is its creation of a milieu of relative immune privilege that normally renders unlikely an autoimmune attack on intrafollicularly expressed autoantigens.29-31 This relative immune privilege is established mainly by suppression of the surface molecules required for presenting autoantigens to CD8+ T l ...
... is its creation of a milieu of relative immune privilege that normally renders unlikely an autoimmune attack on intrafollicularly expressed autoantigens.29-31 This relative immune privilege is established mainly by suppression of the surface molecules required for presenting autoantigens to CD8+ T l ...
alopecia_areata 2012
... is its creation of a milieu of relative immune privilege that normally renders unlikely an autoimmune attack on intrafollicularly expressed autoantigens.29-31 This relative immune privilege is established mainly by suppression of the surface molecules required for presenting autoantigens to CD8+ T l ...
... is its creation of a milieu of relative immune privilege that normally renders unlikely an autoimmune attack on intrafollicularly expressed autoantigens.29-31 This relative immune privilege is established mainly by suppression of the surface molecules required for presenting autoantigens to CD8+ T l ...
Characterization of an Immuno-dominant Variable Surface
... encoding this antigen (M17) has been isolated from a Xgtll expression library of the virulent stain E. histolytica HM1:IMSS. Monospecific antibodies, purified by binding to phage lysate of AcM17, and mAb FA7 reacted exclusively with the 125-kD antigen by Western blot analysis. Surface binding and ca ...
... encoding this antigen (M17) has been isolated from a Xgtll expression library of the virulent stain E. histolytica HM1:IMSS. Monospecific antibodies, purified by binding to phage lysate of AcM17, and mAb FA7 reacted exclusively with the 125-kD antigen by Western blot analysis. Surface binding and ca ...
Tubules composed of non-structural protein
... Unfortunately the vaccine strategies used for the control of smallpox and polio will not work against influenza unless major advances in vaccine technology are achieved. Based on all these factors, more emphasis will have to be placed on the prevention of infectious diseases through new vaccine str ...
... Unfortunately the vaccine strategies used for the control of smallpox and polio will not work against influenza unless major advances in vaccine technology are achieved. Based on all these factors, more emphasis will have to be placed on the prevention of infectious diseases through new vaccine str ...
Human papillomavirus infections in early childhood
... approximately 8000 base pairs in size and consists of eight or nine open reading frames (ORFs) encoding the major proteins. These ORFs are organized into two functional regions, and were originally named early (E) and late (L) genes based on their expression and functions during the ...
... approximately 8000 base pairs in size and consists of eight or nine open reading frames (ORFs) encoding the major proteins. These ORFs are organized into two functional regions, and were originally named early (E) and late (L) genes based on their expression and functions during the ...
Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6e (Campbell)
... A) have hydrophobic heads that face the center of the membrane and are shielded from water. B) have hydrophilic tails that face outward and are exposed to water. C) often have "kinks" in their tails caused by the presence of a double bond between carbons. D) remain fluid because they are tightly pac ...
... A) have hydrophobic heads that face the center of the membrane and are shielded from water. B) have hydrophilic tails that face outward and are exposed to water. C) often have "kinks" in their tails caused by the presence of a double bond between carbons. D) remain fluid because they are tightly pac ...
Calreticulin, a multi-process calcium
... (A) Linear representation of calreticulin domains is shown. The protein contains an N-terminal amino acid signal sequence (black box), N-domain (blue box), P-domain (red box), C-domain (orange box) and a C-terminal KDEL ER retrieval signal. Repeats A (amino acid sequence PXXIXDPDAXKPEDWDE) and B (am ...
... (A) Linear representation of calreticulin domains is shown. The protein contains an N-terminal amino acid signal sequence (black box), N-domain (blue box), P-domain (red box), C-domain (orange box) and a C-terminal KDEL ER retrieval signal. Repeats A (amino acid sequence PXXIXDPDAXKPEDWDE) and B (am ...
experimental oncology and molecular medicine department
... • Tumor Genomics. The research activity covers all aspects of lung cancer with the final aim of making an impact on a disease that is a major health-care burden in terms of morbidity and mortality. The Unit uses an integrated approach that combines cellular and molecular biology, biochemistry, and ...
... • Tumor Genomics. The research activity covers all aspects of lung cancer with the final aim of making an impact on a disease that is a major health-care burden in terms of morbidity and mortality. The Unit uses an integrated approach that combines cellular and molecular biology, biochemistry, and ...
Endometritis in old mares - Pferdeheilkunde Equine Medicine
... are particularly at risk, as advanced age has been associated with susceptibility to persistent endometritis. Horses of advanced age undergo an alteration of the immune system including a low-grade, systemic pro-inflammatory response, however a direct correlation with this systemic alteration and su ...
... are particularly at risk, as advanced age has been associated with susceptibility to persistent endometritis. Horses of advanced age undergo an alteration of the immune system including a low-grade, systemic pro-inflammatory response, however a direct correlation with this systemic alteration and su ...
Hepatitis B vaccination: a completed schedule...enough to control
... as protective for evaluation of primary vaccination (the so-called “way up”), but it was questioned whether this threshold should be used for evaluation of long-term protection, as a decrease of the antibody level below this cut-off does not mean an absence of protection (the so-called “way down”). ...
... as protective for evaluation of primary vaccination (the so-called “way up”), but it was questioned whether this threshold should be used for evaluation of long-term protection, as a decrease of the antibody level below this cut-off does not mean an absence of protection (the so-called “way down”). ...
Metabolic regulation via intracellular pH - AJP
... examples of intracellular pH (pHi) changes accompanying defined metabolic transitions been reported (Table 1). Indeed, principally because interest in pHi long preceded the technical developments necessary to measure this very subtle parameter, many early and influential workers were led to conclude ...
... examples of intracellular pH (pHi) changes accompanying defined metabolic transitions been reported (Table 1). Indeed, principally because interest in pHi long preceded the technical developments necessary to measure this very subtle parameter, many early and influential workers were led to conclude ...
Evaluation of Immune Responses to Novel Adeno-Associated Viruses
... and a single polyadenylation site near the 3´ end. Dependoviruses were given their name due to the fact that their life cycle is “dependent” on the presence of a helper virus for efficient viral replication, although AAV replication has been observed in the absence of helper viruses under specific c ...
... and a single polyadenylation site near the 3´ end. Dependoviruses were given their name due to the fact that their life cycle is “dependent” on the presence of a helper virus for efficient viral replication, although AAV replication has been observed in the absence of helper viruses under specific c ...
Polyclonal B cell response
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.In the course of normal immune response, parts of pathogens (e.g. bacteria) are recognized by the immune system as foreign (non-self), and eliminated or effectively neutralized to reduce their potential damage. Such a recognizable substance is called an antigen. The immune system may respond in multiple ways to an antigen; a key feature of this response is the production of antibodies by B cells (or B lymphocytes) involving an arm of the immune system known as humoral immunity. The antibodies are soluble and do not require direct cell-to-cell contact between the pathogen and the B-cell to function.Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term ""polyclonal"", which derives from the words poly, meaning many, and clones (""Klon""=Greek for sprout or twig); a clone is a group of cells arising from a common ""mother"" cell. The antibodies thus produced in a polyclonal response are known as polyclonal antibodies. The heterogeneous polyclonal antibodies are distinct from monoclonal antibody molecules, which are identical and react against a single epitope only, i.e., are more specific.Although the polyclonal response confers advantages on the immune system, in particular, greater probability of reacting against pathogens, it also increases chances of developing certain autoimmune diseases resulting from the reaction of the immune system against native molecules produced within the host.