* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download e.4.1 state that some presynaptic neurons excite post synaptic
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Vesicular monoamine transporter wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Spike-and-wave wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
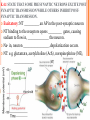
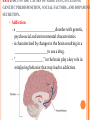
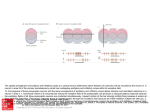
OPTION E E4 NEUROTRANSMITTERS AND SYNAPSES E.4.1 STATE THAT SOME PRESYNAPTIC NEURONS EXCITE POST SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION WHILE OTHERS INHIBIT POST-SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION. Pre-synaptic neurons can either excite or inhibit post-synaptic transmissions. (AP = “______________”) This depends on which __________________(NT) is used and which _______________ they bind to. E.4.1 STATE THAT SOME PRESYNAPTIC NEURONS EXCITE POST SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION WHILE OTHERS INHIBIT POSTSYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION. Excitatory: NT __________ an AP in the post-synaptic neuron NT binding to the receptors opens _________ gates, causing sodium to flow in, ______________ the neuron. Na+ in, neuron _________________, depolarization occurs. NT: e.g. glutamate, acetylcholine (Ach), norepinephrine (NE), _____________ E.4.1 STATE THAT SOME PRESYNAPTIC NEURONS EXCITE POST SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION WHILE OTHERS INHIBIT POSTSYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION. Inhibitory: NT __________ an AP in the post-synaptic neuron NT binding to the receptors opens __________ gates, causing chloride to flow in, _________________ the neuron. Cl- in, neuron _______________, more difficult to depolarize, impulse ____________. NT: e.g. _______, dopamine E.4.1 STATE THAT SOME PRESYNAPTIC NEURONS EXCITE POST SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION WHILE OTHERS INHIBIT POSTSYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION. ____________ = -Aminobutyric acid GABA is a NT that opens _______________________ on the postsynaptic membrane. Cl- rushes in, _____________________ the post-synaptic neuron and _____________ APs. GABA is important in regulating nervous processes – a “_____________” or depressive effect (reducing activity). It prevents neurons from __________, and can be used as a drug to help people with anxiety or stress-related disorders. ________ mimics the effect of GABA, further increasing hyperpolarization and therefore greatly reducing nerve activity. E.4.2 EXPLAIN HOW DECISION-MAKING IN THE CNS CAN RESULT FROM THE INTERACTION BETWEEN THE ACTIVITIES OF EXCITATORY AND INHIBITORY PRESYNAPTIC NEURONS AT SYNAPSES. Important points to remember: - ________ of many neurons feed into the _________ of the post-synaptic neuron - each axon contributes to the _____________________ of the post-synaptic neuron - effects of the each input can be either ___________ or ____________ - effect is ____________ and is added up at the _________________. E.4.2 EXPLAIN HOW DECISION-MAKING IN THE CNS CAN RESULT FROM THE INTERACTION BETWEEN THE ACTIVITIES OF EXCITATORY AND INHIBITORY PRESYNAPTIC NEURONS AT SYNAPSES. If the summative effect of the inputs reaches _____________, an AP is propagated. Spatial Summation: multiple __________ Temporal Summation: multiple _________ from one input http://hsc.uwe.ac.uk/synapses_neuro/summation.htm E.4.3 EXPLAIN HOW PSYCHOACTIVE DRUGS AFFECT THE BRAIN AND PERSONALITY BY EITHER INCREASING OR DECREASING POSTSYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION. Inhibitory drugs Mimic inhibitory NTs -________________ of post-synaptic neuron - _______ APs - e.g. alcohol mimics GABA effects, reducing APs Blocks excitatory NTs - ___________ APs - e.g. opiates (heroin) block pain pathway by competitive inhibition Excitatory drugs Block re-uptake pumps for NTs - NT __________________ -e.g. cocaine’s effect on dopamine Mimic excitatory NTs - __________________, - _______ APs -e.g. nicotine Block inhibitory NTs - prevent _______________ -e.g. caffeine competitively inhibit adenosine http://outreach.mcb.harvard.edu/animations/synapse.swf E.4.4 LIST THREE EXAMPLES OF EXCITATORY AND THREE EXAMPLES OF INHIBITORY PSYCHOACTIVE DRUGS. Excitatory - _______: stimulate alertness and memory, nausea and vomiting - _________________: increases heart rate, respiration, alertness - _________________: causes anxiety and psychosis. http://www.jellinek.nl/brain/index.html E.4.4 LIST THREE EXAMPLES OF EXCITATORY AND THREE EXAMPLES OF INHIBITORY PSYCHOACTIVE DRUGS. Inhibitory - ___________________: muscle relaxant, reduces anxiety. - ________: slows and prevents movement, impairs reasoning skills. - ________: reduces heart rate, breathing rate, and blood pressure. http://www.jellinek.nl/brain/index.html E.4.5 EXPLAIN THE EFFECTS OF THC AND COCAINE IN TERMS OF THEIR ACTION AT SYNAPSES IN THE BRAIN. Excitatory drugs = Cocaine Normal: -Dopamine acts as an ___________________ -Dopamine is ______________ at the pre-synaptic neuron pumps With Cocaine: -____________________ on reuptake pump -Dopamine not re-uptaken; remains in __________________ -_________ dopamine is released -_____________ post-synaptic transmission Effect on mood/behavior -Enhanced feelings of ___________(dopamine is a “pleasure” NT) -___________ energy and alertness -Highly ___________ -Associated with ____________ (body reduces its own dopamine) http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/flash/i/i_03/i_03_m/i_03_m_par/i_03_m_par_cocaine.html#drogues E.4.5 EXPLAIN THE EFFECTS OF THC AND COCAINE IN TERMS OF THEIR ACTION AT SYNAPSES IN THE BRAIN. Inhibitory drugs = THC (cannibis) Normal: -Two pathways to consider 1) pathway released _________, increasing feelings of ________ 2) _______ has an ___________ effect on release of dopamine With THC: -Inhibits _________________ by binding to __________________ -GABA cannot _______________ -__________ dopamine is released -___________ post-synaptic transmission Effect on mood/behavior -Enhanced feelings of __________ (dopamine is a “pleasure” NT) -______________ (drunk feeling), hunger, memory impairment http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/flash/i/i_03/i_03_m/i_03_m_par/i_03_m_par_cannabis.html#drogues E4.6 DISCUSS THE CAUSES OF ADDICTION, INCLUDING GENETIC PREDISPOSITION, SOCIAL FACTORS, AND DOPAMINE SECRETION. Addiction - a __________________________disorder with genetic, psychosocial and environmental characteristics. - is characterized by changes in the brain resulting in a ______________________to use a drug. - “___________________” in the brain play a key role in reinforcing behavior that may lead to addiction. E4.6 DISCUSS THE CAUSES OF ADDICTION, INCLUDING GENETIC PREDISPOSITION, SOCIAL FACTORS, AND DOPAMINE SECRETION. Reward Pathway - makes one feel good when he/she engages in behaviors that are ______________________(e.g. eating, drinking) • ____________ is the NT most prevalent in the reward pathway. - generate a feeling of ___________ - high levels of dopamine cause a feeling of ___________ - user may seek to repeat by using the drug again (____________) - ____________ of the drug leads to anxiety, depression and craving E4.6 DISCUSS THE CAUSES OF ADDICTION, INCLUDING GENETIC PREDISPOSITION, SOCIAL FACTORS, AND DOPAMINE SECRETION. Some people are ______________ more pre-disposed to becoming addicted than others. May be the result of genetically determined deficiency of __________________________ The children of addicts are ______________ to become addicts themselves. E4.6 DISCUSS THE CAUSES OF ADDICTION, INCLUDING GENETIC PREDISPOSITION, SOCIAL FACTORS, AND DOPAMINE SECRETION. Psychosocial factors are a heavy influence in addiction: