* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Central Nervous System
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Spinal cord wikipedia , lookup
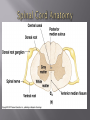
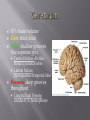
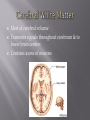
Consists of : 1. Brain 2. Spinal Cord a. b. c. Protected by glial cells & meninges High metabolic rate that requires nutrients and oxygen Must be isolated from compounds in blood that could interfere with functioning 3 layers of specialized membranes surrounding brain & spinal cord A) Dura Mater: 2 fibrous layers; outermost; very tough, holds brain in place B) Arachnoid: middle; small amt lymphatic fluid (reduces friction) & CSF Contains fluid, blood vessels & some adipose tissue Provides stability & shock absorption to CNS tissue Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF): absorbs shock & transports gases, nutrients, chemical messengers, & wastes C) Pia Mater: innermost; extensive circulatory supply due to high rate of metabolism Meningitis: inflammation of meninges due to bacterial or viral infection Sends sensory info to brain & motor info from brain to rest of body Spinal Reflexes: automatic responses controlled solely w/in spinal cord (i.e. withdraw from pain) Central Canal: narrow central opening filled w/ CSF Gray Matter: inside; contains neuron cell bodies & neuroglia…forms an H or butterfly shape White Matter: outside; contains axons of neurons Dorsal Roots: carry sensory info to spinal cord Ventral Roots: carry motor info to muscles and glands 31 segments designated by letter and number: C1 C8 Cervical Vertebrae T1 T12 Thoracic Vertebrae L1 L5 Lumbar Vertebrae S1 S5 Saccral Vertebrae CO1 Coccygeal near tailbone Each segment has a dorsal root ganglia a. Dorsal Root- axons of sensory neuron b. Ventral Root- Axons of CNS motor neuron All spinal nerves are mixed because they contain sensory and motor neurons “Rostral” = anterior (towards nose) “Caudal” = posterior (towards tail) 4 Major Parts: 1) Cerebrum: divided into 2 hemispheres w/ 5 lobes Corpus Callosum: thick bundles of nerves connecting 2 hemis. 2) Cerebellum: inferior to cerebrum Sensory perception, motor output, motor control (heart, blood pressure, breathing, etc.) 3) Brain Stem: btwn cerebrum & foramen magnum Attention, arousal, consciousness Composed of midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata 4) Diencephalon: inner core; btwn cerebral hemisph. sensory processing, emotion, hormone production 1. Cerebrum- 2. Diencephalon (Hypothalamus to pituitary gland)3. Midbrain 4. Pons 5. Medulla Oblongata 6. Cerebellum 83% brain volume Gyri: thick folds Sulci: shallow grooves that separate gyri Central Sulcus: divides frontal/parietal lobes Lateral Sulcus: distinguishes temporal lobe Fissures: deep grooves throughout Longitudinal Fissure: divides R/L hemispheres 1) Frontal: voluntary (skeletal) muscle control, motivation, memory 2) Parietal: sensory reception, taste, some vision 3) Temporal: hearing, smell, learning, memory, emotional behavior 4) Occipital: main visual center 5) Insula: deep inside; understanding speech, taste, sensory integration Most of cerebral volume Transmits signals throughout cerebrum & to lower brain centers Contains axons of neurons Neural Integration Contains neuron cell bodies & neuroglia 1) Cerebral Cortex: thin layer covering hemispheres Stellate Cells: receive sensory input & process local info Pyramidal Cells: transmit signals to other parts CNS Receive & send signals to midbrain & motor cortex Important for emotion & memory 2) Basal Nuclei: deep masses w/in white matter 3) Limbic System: includes amygdala & hippocampus












![[SENSORY LANGUAGE WRITING TOOL]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014348242_1-6458abd974b03da267bcaa1c7b2177cc-150x150.png)






