* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Brain and Nervous System - Mr. Conzen
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
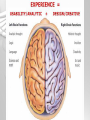
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
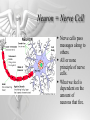
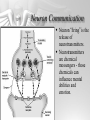
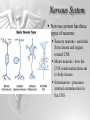
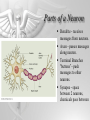
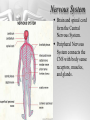
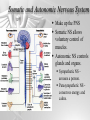
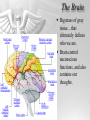
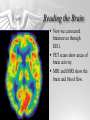
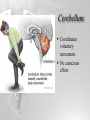
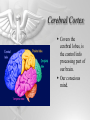
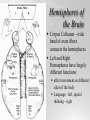
The Brain and Nervous System How do we function? People are made up of billions of cells - in Psychology we focus on the nervous system. Nervous system sends messages throughout the body that encompass thought, perception, emotion, etc. Neuron = Nerve Cell Nerve cells pass messages along to others. All or none principle of nerve cells. What we feel is dependent on the amount of neurons that fire. Neuron Communication Neuron “firing” is the release of neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers - those chemicals can influence mental abilities and emotion. Nervous System Nervous system has three types of neurons: Sensory neurons - send info from tissues and organs toward CNS Motor neurons - how the CNS sends instructions out to body tissues. Interneurons - processes internal commincation in the CNS Parts of a Neuron Dendrite - receives messages from neurons. Axon - passes messages along neuron. Terminal Branches “buttons” - push messages to other neurons. Synapse - space between 2 neurons, chemicals pass between So how do we feel? Nervous System Brain and spinal cord form the Central Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System connects the CNS with body sense receptors, muscles, and glands. Somatic and Autonomic Nervous System Make up the PNS Somatic NS allows voluntary control of muscles. Autonomic NS controls glands and organs. Sympathetic NS arouses a person. Parasympathetic NS conserves energy and calms. The Brain Big mass of gray tissue…that ultimately defines who we are. Brain control unconscious functions, and also contains our thoughts. Reading the Brain Now we can record brainwaves through EEG. PET scans show areas of brain activity. MRI and fMRI show the brain and blood flow. Brainstem Oldest part of the brain - includes the spinal cord. Medulla - controls breathing and heartbeat. Reticular Formation filters nerve messages to parts of the brain, also has to do with arousal. Thalamus - like a sensory switchboard. Cerebellum Coordinates voluntary movement. No conscious effort. LIMBIC SYSTEM Influencing emotions and motives Hippocampus processes memory. Amygdala influence fear and aggression. Hypothalamus influences motives for hunger, thirst, sex - releases hormones by controlling the pituitary gland. Cerebral Cortex Covers the cerebral lobes, is the control/info processing part of our brain. Our conscious mind. Motor Cortex Part of our cerebral cortex that controls movement. Right hemisphere controls left side of body and vice versa. Sensory Cortex is similar, it reports senses around your body. Neural Prosthetics Frontal Lobe Frontal lobe has to do with decision making, thinking, personality. Phineas Gage was a railroad working in 1848 that had a spike go through his brain. He could think and had memories, but his personality was total different. Hemispheres of the Brain Corpus Callosum - wide band of axon fibers connects the hemispheres. Left and Right Hemispheres have largely different functions: affect movement on different sides of the body Language - left, spatial thinking - right Split Brain Purpose of the corpus callosum is to send information to the other hemisphere severed patients have difficulty. Patients brain hemispheres will interpret events differently, and not communicate.