* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
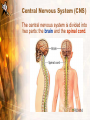
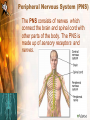
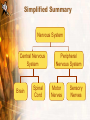
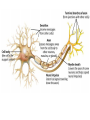
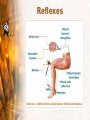
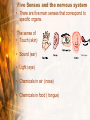
Body Balance Year 9 Science The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) The central nervous system is divided into two parts: the brain and the spinal cord. Central Nervous System (CNS) The CNS acts as the control centre, receiving messages from all parts of the body. It examines the information and then sends out messages to the body telling it what to do. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) The PNS consists of nerves which connect the brain and spinal cord with other parts of the body. The PNS is made up of sensory receptors and nerves. Simplified Summary Nervous System Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System Motor Nerves Sensory Nerves • Cerebellum controls and coordinates movements of the muscles, like walking or swinging the arms. • This means that the movement is smooth and controlled and you don’t fall over when you turn around. • Cerebrum has special areas, which receive messages about sight, touch, hearing and taste. Other areas control movement, speech, learning, intelligence and personality. • The brain stem is in charge of keeping the automatic systems of your body working. Nerves • Movement is directed and controlled by the action of the nervous system. • Nerves act as messengers inside the body, carrying information from one part of the body to another • Nerves are made up of bundles of nerve fibres or nerve cells. Source: HSL3 (2006) pp 191 • Messages are passed through the nervous system by nerve cells called NEURONS. Neuron • Neurons transmit and receive messages in the form of electric impulses called “nerve impulses”. • Nerve impulses travel at very high speeds and normally only travel in one direction. • There are two types of neurons: Motor neurons & sensory neurons Motor Neurons • Send information/messages AWAY from the CNS to effector organs such as muscles. • Muscles and glands are called Effectors because they put the messages into effect. AWAY from CNS Sensory Neurons • Sends information/messages from sensory receptors (such as skin, eyes, nose, tongue, ears) TOWARDS the CNS. • Sensory neurons have specialised endings that are sensitive to a particular stimuli such as heat, pressure or light called Receptors. • Messages are sent as an electrical impulse along the neuron. • This carries the messages from the axon of one neuron to the dendrite of the next neuron. Reflexes Reflexes • A reflex action is an involuntary, or automatic, action that your body does in response to something - without you even having to think about it. • Reflexes protect your body from things that can harm it. For example: if you put your hand on a hot stove, a reflex causes you to immediately remove your hand before the message, "Hey, this is hot!" even gets to your brain. Reflex Action • Sometimes your body reacts very fast without waiting for instructions from the brain. Such as blinking, sweating, coughing, knee jerking. What happens? • An impulse is sent to the spinal cord and acted on immediately. This impulse uses a pathway know as a reflex arc which does not involve the brain directly. • A message is sent to the brain shortly afterwards. • Actions that need to be carried out automatically and without thinking are very fast because they involve only a few neurons. There are five main senses that correspond to specific organs. What are they? Five Senses and the nervous system • There are five main senses that correspond to specific organs. The sense of • Touch (skin) • Sound (ear) • Light (eye) • Chemicals in air (nose) • Chemicals in food ( tongue) The tongue Receptors • Information is collected from cells called receptors. • There are many different types of receptors that respond to different types of stimuli. Mechanoreceptors Sensitive to touch e. . i s e ur Text smooth h, ro u g Receptors Photoreceptors Sensitive to light n) Nig u ht (S t h g i l y Da Thermoreceptors Chemoreceptor Sensitive to chemicals Sensitive to temperature Food Tast e Su m me Win r (H ea t) old C ( r te )