* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The First Year - Archbishop Hoban High School
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Impact of health on intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
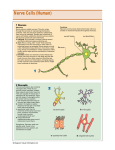
The First Year 8-2 8-3 8-4 The Developing Brain In their first year, babies grow and develop new skills. How the brain takes shape in a baby’s first year of life has profound effects on the baby’s life. Newborns learn about the world primarily through their senses----sight, hearing, smell, taste, and touch. Parts of the Brain • Cerebrum – Controls functions such as speech, memory, and problem solving. • Thalamus – Controls expression of emotion. • Pituitary Gland – Hormones regulate growth, metabolism, and sexual development. Parts of the Brain • Brain Stem – Controls involuntary activities such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. • Cerebellum – Controls muscular coordination and balance. • Spinal Cord – Transmits information from the body to the brain and from the brain to the body. How the Brain Works • The brain is made up of billions of nerve cells – neurons • Born with all neurons • How neurons work (pg. 262) 1. Dendrites receive information from other neurons. How Neurons Work 2. The dendrites pass that information to the cell body, where the information is processed. 3. The cell body sends an instruction to the body through axons which transmit the instruction to dendrites. 4. Chemicals called neurotransmitters are released by the axon and cross the gap to the dendrite of another nerve cell. That gap is called the synapse. How the Brain Becomes Organized • Unique – Organization is unique because it grows out of the child’s experiences. • Connections b/w dendrites and axons grow stronger, a group of neurons becomes linked together. Speeding the Brain’s Work • Axons – Waxy coating • Plays a role in learning • Myelin makes it easier for axons to transmit signals – Speeds their work. Speeding the Brain’s Work • All axons • Some axons become coated with myelin as the child grows. – Cont. age 20 – Different times • Axons – Control skills such as motor abilities, vision, and hearing • Coating earliest Speeding the Brain’s Work • The rate at which axons receive this waxy coating may explain why children have difficulty learning certain tasks. – Presence of myelin • Learning much easier • http://www.pbs.org/wnet/brain/episode1/video.htm l Rules to Build a Brain • Keep it simple and natural. • Match experiences to the child’s mental capacities. • Remember that practice makes perfect. • Make sure the child is active. • Provide variety, but avoid overloading the child. • Avoid pushing the child. Handling and Feeding Infants Pg.269 Feeding Schedules • Newborn – Eating and sleeping unpredictable • Up 6-8 times—24 hours • 2nd or 3rd month – Regular pattern develops • 3-4 times • Eventually – Sleep through the night • 12 lbs. Feeding • 1st year – Breast milk – Formula • Cow’s milk not recommended until 1 yr. • Difficult for baby to digest – Minerals in kidney’s cannot process Feeding • Warm bottle – Stove top – No microwave Hot spots • Cleaning bottle – Sterilization • Bacteria New Foods • Age 6 mo. Introduce new foods – Don’t push new foods – Breast milk & formula provide all nutrition Solid Foods • Cereal – 1st • • • • Vegetable Fruit Meats Milks – Avoid until age 1 Other Infant Care Skills • Bathing a baby – Sponge bath • Navel heals • Sensitive skin • Cradle cap – Skin condition in which the scalp develops patches of yellowish, crusty scales. • Baby oil, lanolin: at night • Wash cloth or soft hairbrush, shampoo: morning Diaper Rash • Diaper rash – Patches of rough, irritated skin the diaper area. – Painful raw spots • Treatment – Change diaper frequently – Use a product with zinc oxide and cod liver oil, protects against diaper rash, helps heal quickly. Sleep • Newborn – 12-20 hours • By 1st year 2-3 sleep periods – Including naps Spending Quality Time • Looking Games – Funny Face, Shadow Figures, Mirror, Peekaboo, Hide-and-seek • Listening Games – Musical games, What’s That?, Mimic • Baby Exercises – Bicycle, Tug-of-war, Airplane