* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Nervous System
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Brain–computer interface wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
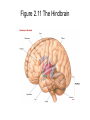
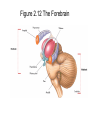
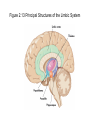
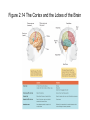
The Nervous System The Neuron • The neuron is the basic unit of the nervous system • Central Neurons in CNS • Peripheral Neurons in PNS The Peripheral and Central Nervous Systems The peripheral nervous system carries information to and from the nervous system The somatic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that carries information to skeletal muscles The Peripheral and Central Nervous Systems • The sympathetic nervous system is the part of the autonomic nervous system that becomes most active during emergency situations The Peripheral and Central Nervous Systems • The parasympathetic nervous system is the part of the autonomic nervous system that controls the ongoing maintenance processes of the body Figure 2.8 The Basic Divisions of the Nervous System Five Principles of Brain Organization 1. The hindbrain, midbrain, and forebrain each involve several brain regions that carry out different types of information processing 2. There are identifiable neural pathways projecting from one area to the next Five Principles of Brain Organization 3. Each part of the brain projects to the next in an orderly fashion creating organized regions that can be mapped 4. The brain is hierarchically organized 5. The brain systems are organized so that one side of the brain controls the other side of the body Figure 2.11 The Hindbrain The Midbrain • The midbrain receives afferent signals from other parts of the brain and relays the information to a more complex part of the brain The Forebrain • The forebrain is the most complicated and advanced of the three divisions of the brain • The thalamus sends information to other parts of the brain • The hypothalamus affects many complex behaviours Figure 2.12 The Forebrain The Forebrain • The limbic system is an interconnected group of structures that influences emotions and memory • The hippocampus is involved in new learning • The amygdala is involved in emotional control Figure 2.13 Principal Structures of the Limbic System The Forebrain • The basal ganglia controls movement and posture • The corpus callosum provides crosshemisphere connections The Cortex • The cortex is divided into a series of lobes The Cortex • The frontal lobe is concerned with directing thought processes • The parietal lobe integrates visual input • The occipital lobe processes visual input • The temporal lobe is important for language comprehension Figure 2.14 The Cortex and the Lobes of the Brain Monitoring Neural Activity • Single-unit recording measures activity in individual neurons • Electroencephalography (EEG) measures electrical activity in the nervous system Monitoring Neural Activity • CT scans are computer-enhanced X- rays • PET tracks radioactive markers that have been injected into the bloodstream Monitoring Neural Activity • MRI uses magnetic fields • fMRI measures brain activity as it takes place