* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Memory and Cognition
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Effects of stress on memory wikipedia , lookup
Fuzzy-trace theory wikipedia , lookup
Transsaccadic memory wikipedia , lookup
Autobiographical memory wikipedia , lookup
Procedural memory wikipedia , lookup
Visual memory wikipedia , lookup
Remember versus know judgements wikipedia , lookup
Source amnesia wikipedia , lookup
Implicit memory wikipedia , lookup
Eyewitness memory wikipedia , lookup
Memory error wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive memory wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal memory wikipedia , lookup
Socioeconomic status and memory wikipedia , lookup
Effects of alcohol on memory wikipedia , lookup
Multiple trace theory wikipedia , lookup
Art of memory wikipedia , lookup
De novo protein synthesis theory of memory formation wikipedia , lookup
Sparse distributed memory wikipedia , lookup
Memory and aging wikipedia , lookup
Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model wikipedia , lookup
Misattribution of memory wikipedia , lookup
Traumatic memories wikipedia , lookup
Exceptional memory wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Eyewitness memory (child testimony) wikipedia , lookup
Music-related memory wikipedia , lookup
Childhood memory wikipedia , lookup
Encoding (memory) wikipedia , lookup
False memory wikipedia , lookup
Motivated forgetting wikipedia , lookup
Emotion and memory wikipedia , lookup
Collective memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Subvocalization wikipedia , lookup
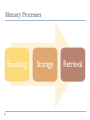
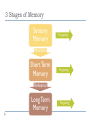
Memory and Cognition When studying material for tests/quizzes, what techniques or strategies do you use to remember the information? Memory The process by which information is encoded, stored, and retrieved Hippocampus = Memory Episodic - events Explicit – specific information Memory Implicit – skills, procedures Semantic – general knowledge Flashbulb Memories Clear memories of emotionally significant events (episodic) Memory Processes Encoding Storage Retrieval Encoding Translation of info into a form that can be stored in memory OTTFFSSENT Encoding Visual coding – create a mental picture/image Acoustic coding – repetition out loud to sequence Semantic coding – attempt to make/assign meaning Which penny is a REAL penny? A Storage The maintenance of encoded information over time Maintenance rehearsal: repetition of new info to avoid forgetting Elaborative rehearsal: creating a link between new and old info Memory is organized into groups/classes like a filing cabinet Retrieval Recalling info from memory storage Write the letters you attempted to memorize a few slides ago… How did you remember these letters? Success of retrieval relies on proper encoding and storage. Retrieval Context-dependent memories info is more easily retrieved in the same context in which it was encoded and stored 3 Stages of Memory Sensory Memory Forgetting Attention Short Term Memory Forgetting Rehearsal Long Term Memory Forgetting Sensory Memory Iconic – mental images of visual stimuli Echoic – traces of sounds are held and can be retrieved for a few seconds Short Term Memory AKA “working memory” 7 +/- 2 pieces of info at a time Chunking - organization of items into meaningful or manageable units How could you have chunked OTTFFSSENT? Interference - when new info takes the place of other info in short term memory Long Term Memory Info stored by rehearsal Unlimited, but we do not remember everything that we have ever experienced/learned We reconstruct and shape memories to reflect the way in which we perceive the world. Loftus Car Crash and Eye Witnesses Types of Retrieval Recognition: identifying info you have already encountered Recall: retrieval of learned info Multiple choice tests Short answer/essays Relearning: learning material a 2nd time Test corrections Types of Forgetting Decay: fading of memories overtime Amnesia: loss of memory, usually tied to a brain injury or biological problem How to Improve Your Memory Maintenance rehearsal Elaborative rehearsal Make connections to past info Use mnemonic devices – any type of memory aid Flashcards, repetition Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally Form unusual associations Peg method Marshmallow Challenge!!!! Build the Tallest Freestanding Structure: The winning team is the one that has the tallest structure measured from the table top surface to the top of the marshmallow. That means the structure cannot be suspended from a higher structure, like a chair, ceiling or chandelier. The Entire Marshmallow Must be on Top: The entire marshmallow needs to be on the top of the structure. Cutting or eating part of the marshmallow disqualifies the team. Use as Much or as Little of the Kit: The team can use as many or as few of the 20 spaghetti sticks, as much or as little of the string or tape. The team cannot use the paper bag as part of their structure. Break up the Spaghetti, String or Tape: Teams are free to break the spaghetti, cut up the tape and string to create new structures. The Challenge Lasts 18 minutes: Teams cannot hold on to the structure when the time runs out. Those touching or supporting the structure at the end of the exercise will be disqualified. Cognition AKA “thinking” Manipulating info stored in memory to create new info Metacognition - thinking about thinking Awareness of your own thought processes We think to solve problems… Problem Solving The problem dictates the solving method used. Algorithm – specific step-by-step procedure that always solves a particular problem. EX: math formulas, a cooking recipe Time-consuming but always right Heuristic – “rules of thumb,” shortcuts in problem solving that work most, but not all, of the time EX: common sense Fast but sometimes wrong Insight Sudden understanding Incubation Arriving at a conclusion after setting a problem aside “Sleep on it…” Functional Fixedness The tendency to think of an object as being useful for only the function that the object is usually used for Creativity The capacity to use info and abilities in a new or original way Convergent thinking - thinking limited to available facts Divergent thinking - thinking that attempts to generate multiple solutions to a problem