How Do We Know That We Know? The Accessibility Model
... correct (e.g., the ease of accessing the answer, the extent of corroborative evidence collected). However, even when retrieval fails, these very clues contain important information that can be used in judging whether the target can be recalled or recognized in the future. In general, FOK judgments a ...
... correct (e.g., the ease of accessing the answer, the extent of corroborative evidence collected). However, even when retrieval fails, these very clues contain important information that can be used in judging whether the target can be recalled or recognized in the future. In general, FOK judgments a ...
Changes in Resting-State Functional Connectivity Following Delay
... permanent or durable form. Several studies with laboratory animals have uncovered valuable information about the process of consolidation, but less is known about the process of consolidation in healthy humans. The current study examined the consolidation of emotional memories in different brain cir ...
... permanent or durable form. Several studies with laboratory animals have uncovered valuable information about the process of consolidation, but less is known about the process of consolidation in healthy humans. The current study examined the consolidation of emotional memories in different brain cir ...
Dissection of genetic factors modulating fetal growth in
... inherited at the respective position. The haplotype, for which a positive effect on fetal growth was calculated in the regression analysis, was denoted “Q”, and the haplotype, for which a negative effect was calculated, was denoted “q”. All Q carrying and all q carrying haplotypes, respectively, wer ...
... inherited at the respective position. The haplotype, for which a positive effect on fetal growth was calculated in the regression analysis, was denoted “Q”, and the haplotype, for which a negative effect was calculated, was denoted “q”. All Q carrying and all q carrying haplotypes, respectively, wer ...
Dissection of Genetic Factors Modulating Fetal Growth in
... one chromosome with a length of 1.2 M and an average marker density for the variance component analyses of 0.02927 M. LRT significance thresholds for a ¼ 0.05 and a ¼ 0.0001 were 10.5 and 24. The variance component approach used to model a random QTL effect (Perez-Enciso and Misztal 2004) further co ...
... one chromosome with a length of 1.2 M and an average marker density for the variance component analyses of 0.02927 M. LRT significance thresholds for a ¼ 0.05 and a ¼ 0.0001 were 10.5 and 24. The variance component approach used to model a random QTL effect (Perez-Enciso and Misztal 2004) further co ...
4 - Radboud Repository
... how easily glucocorticoids can bind to them. The MR is mostly expressed in the hippocampus, the amygdala, lateral septum, parts of the prefrontal cortex, and the cerebellum (Arriza et al, 1988). These structures are among others associated with cognitive functions such as spatial orientation, detect ...
... how easily glucocorticoids can bind to them. The MR is mostly expressed in the hippocampus, the amygdala, lateral septum, parts of the prefrontal cortex, and the cerebellum (Arriza et al, 1988). These structures are among others associated with cognitive functions such as spatial orientation, detect ...
Coexposure of Neonatal Mice to a Flame
... manifested as disrupted spontaneous behavior, reduced habituation, and impaired learning/memory abilities. This is seen in the low dose range, where the sole compounds do no give rise to developmental neurotoxic effects. The effects seen are more than just additive. Furthermore, a significant effect ...
... manifested as disrupted spontaneous behavior, reduced habituation, and impaired learning/memory abilities. This is seen in the low dose range, where the sole compounds do no give rise to developmental neurotoxic effects. The effects seen are more than just additive. Furthermore, a significant effect ...
Eyeblink Conditioning During an Interstimulus Interval Switch in
... shortly before a blink-eliciting unconditioned stimulus (US), such as a puff of air directed at the cornea. In the most basic procedure, delay conditioning, the CS and US overlap and coterminate. Initially, naı̈ve subjects produce a reflexive, unconditioned blink response that follows US onset. Afte ...
... shortly before a blink-eliciting unconditioned stimulus (US), such as a puff of air directed at the cornea. In the most basic procedure, delay conditioning, the CS and US overlap and coterminate. Initially, naı̈ve subjects produce a reflexive, unconditioned blink response that follows US onset. Afte ...
The Roles of the Amygdala and the Hippocampus in Fear
... structure of the paper will be divided into three main sections that will investigate pre-existing neuroscientific studies conducted in the field of fear conditioning and its dependency on information about environmental context. The first section will examine the neural substrates of the amygdala a ...
... structure of the paper will be divided into three main sections that will investigate pre-existing neuroscientific studies conducted in the field of fear conditioning and its dependency on information about environmental context. The first section will examine the neural substrates of the amygdala a ...
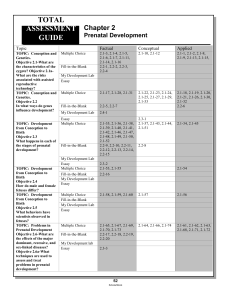
Sample
... 2.1-29. Some studies suggest that genomic imprints a. will always come from the mother's ovum. b. results in Prader-Willi syndrome if from the father. c. always leads to obesity and mental retardation. d. may be particularly important in diseases that appear later in life, such as heart disease. e. ...
... 2.1-29. Some studies suggest that genomic imprints a. will always come from the mother's ovum. b. results in Prader-Willi syndrome if from the father. c. always leads to obesity and mental retardation. d. may be particularly important in diseases that appear later in life, such as heart disease. e. ...
Creating associative memory distortions
... Memory illusions, which have fascinated researchers for decades, refer to situations in which a person either declares that he or she remembers something that did not really occur or remembers a fact that did occur but in a manner that seriously differs from actually experienced events (Roediger, 19 ...
... Memory illusions, which have fascinated researchers for decades, refer to situations in which a person either declares that he or she remembers something that did not really occur or remembers a fact that did occur but in a manner that seriously differs from actually experienced events (Roediger, 19 ...
fulltext
... with a stimulus that elicits a physiological reaction (Unconditioned Stimuli; UCS), becomes a conditioned stimulus (CS) that in itself produces the physiological reaction. The process of conditioning was first reported by Ivan Pavlov in 1907 and is sometimes simply called Pavlovian conditioning (Pav ...
... with a stimulus that elicits a physiological reaction (Unconditioned Stimuli; UCS), becomes a conditioned stimulus (CS) that in itself produces the physiological reaction. The process of conditioning was first reported by Ivan Pavlov in 1907 and is sometimes simply called Pavlovian conditioning (Pav ...
Learning and memory in zebrafish larvae
... the response of an animal to repeated presentations of a stimulus of fixed intensity or strength gradually declines; furthermore, this decline is not due to sensory adaptation, motor fati, or injury (Thompson and Spencer, 1966; Rankin et al., 2009). Despite habituation’s simplicity and apparent ubiq ...
... the response of an animal to repeated presentations of a stimulus of fixed intensity or strength gradually declines; furthermore, this decline is not due to sensory adaptation, motor fati, or injury (Thompson and Spencer, 1966; Rankin et al., 2009). Despite habituation’s simplicity and apparent ubiq ...
Laminar Cortical Dynamics of Cognitive and Motor Working Memory
... sequential working memory storage, categorization, and motor planning and execution during both cognitive and sensory-motor tasks. The model makes predictions about the laminar organization of prefrontal cortical circuits that go beyond present neurophysiological and anatomical knowledge. It formula ...
... sequential working memory storage, categorization, and motor planning and execution during both cognitive and sensory-motor tasks. The model makes predictions about the laminar organization of prefrontal cortical circuits that go beyond present neurophysiological and anatomical knowledge. It formula ...
Psychosocial Stress in Rats: Animal Model of PTSD Based on
... et al. 2003). People with PTSD also demonstrate greater baseline and stress-induced elevations of SNS activity (Buckley and Kaloupek 2001), as measured by elevated baseline heart rate (HR), systolic blood pressure (BP), and diastolic BP, findings which resonate with research reporting an association ...
... et al. 2003). People with PTSD also demonstrate greater baseline and stress-induced elevations of SNS activity (Buckley and Kaloupek 2001), as measured by elevated baseline heart rate (HR), systolic blood pressure (BP), and diastolic BP, findings which resonate with research reporting an association ...
Aerobic Glycolysis in the Frontal Cortex Correlates with Memory
... regardless of A-mediated impairment of mitochondrial respiration. However, it is currently unknown whether aerobic glycolysis and the associated production of lactate is either beneficial or detrimental in an AD context. Here we examined CNS metabolism within an APP/PS1 mouse model of AD to test th ...
... regardless of A-mediated impairment of mitochondrial respiration. However, it is currently unknown whether aerobic glycolysis and the associated production of lactate is either beneficial or detrimental in an AD context. Here we examined CNS metabolism within an APP/PS1 mouse model of AD to test th ...
Isolated Retrograde Amnesia
... The syndrome of isolated retrograde amnesia refers to a neuropathological state of impaired memory for information acquired prior to the onset of brain damage (retrograde memory) contrasted with normal or near-normal learning of new information after the onset of the disease (anterograde memory). Wh ...
... The syndrome of isolated retrograde amnesia refers to a neuropathological state of impaired memory for information acquired prior to the onset of brain damage (retrograde memory) contrasted with normal or near-normal learning of new information after the onset of the disease (anterograde memory). Wh ...
do simultaneously presented visual and auditory
... auditory and visual stimuli convey the same or different types of information? Does auditory or visual stimuli tend to attract more of our attention while, for example, watching TV, or attending a meeting or class? Could it be possible to process both auditory and visual information when those stimu ...
... auditory and visual stimuli convey the same or different types of information? Does auditory or visual stimuli tend to attract more of our attention while, for example, watching TV, or attending a meeting or class? Could it be possible to process both auditory and visual information when those stimu ...
Memory
... – Strategies—the use of mental activities to improve the processing of information—improve in these areas: • Organization: More likely to be used by older children and adults. • Elaboration: Adolescents are more likely to use elaboration spontaneously than children. • Imagery: Encouraging children t ...
... – Strategies—the use of mental activities to improve the processing of information—improve in these areas: • Organization: More likely to be used by older children and adults. • Elaboration: Adolescents are more likely to use elaboration spontaneously than children. • Imagery: Encouraging children t ...
Cannabis and cognition: short- and long
... cannabis has been shown in many studies to acutely impair attention, learning, short-term memory, working memory, executive function, abstract ability and decision making (Hall and Solowij, 1998; Solowij, 1998; Iversen, 2003; Fletcher and Honey, 2006; Ranganathan and D’Souza, 2006; Solowij and Michi ...
... cannabis has been shown in many studies to acutely impair attention, learning, short-term memory, working memory, executive function, abstract ability and decision making (Hall and Solowij, 1998; Solowij, 1998; Iversen, 2003; Fletcher and Honey, 2006; Ranganathan and D’Souza, 2006; Solowij and Michi ...
Episodic memory, amnesia, and the hippocampal–anterior thalamic
... makes it relatively easy to test animals. In contrast, examining the recall of episodic information by animals has proved much more problematic. As a consequence the favoured test of recognition, delayed nonmatching-to-sample (DNMS), has become the litmus test for models of anterograde amnesia. In D ...
... makes it relatively easy to test animals. In contrast, examining the recall of episodic information by animals has proved much more problematic. As a consequence the favoured test of recognition, delayed nonmatching-to-sample (DNMS), has become the litmus test for models of anterograde amnesia. In D ...
Progressive Mitochondrial Compromise in Brains
... uninfected 2-year-old children born to HIV-1–infected mothers receiving NRTI therapy during pregnancy (Poirier et al., 2003). Taken together, these findings suggest that long-term follow-up of infants exposed in utero to NRTIs, and development of relevant experimental models, should be given high pr ...
... uninfected 2-year-old children born to HIV-1–infected mothers receiving NRTI therapy during pregnancy (Poirier et al., 2003). Taken together, these findings suggest that long-term follow-up of infants exposed in utero to NRTIs, and development of relevant experimental models, should be given high pr ...
Neural and cognitive mechanisms underlying human
... given moment we could either lay down a distinctive memory trace to allow for subsequent retrieval, or we could retrieve memories that are related to the familiar components of an unfolding event. This conflict leads to certain crucial questions about the human memory system: Are we able to simultan ...
... given moment we could either lay down a distinctive memory trace to allow for subsequent retrieval, or we could retrieve memories that are related to the familiar components of an unfolding event. This conflict leads to certain crucial questions about the human memory system: Are we able to simultan ...
Chapter 13 Stress and Glucocorticoid Contributions to Normal and
... whereas middle levels facilitate these measures, giving a characteristic “invertedU” shaped doseresponse curve (see [56] for a review). Stressors given immediately prior to assessment of learning and memory may similarly impair [57, 58] or facilitate [59] memory. The effects of repeated stress or ...
... whereas middle levels facilitate these measures, giving a characteristic “invertedU” shaped doseresponse curve (see [56] for a review). Stressors given immediately prior to assessment of learning and memory may similarly impair [57, 58] or facilitate [59] memory. The effects of repeated stress or ...
Auditory working memory: contributions of lateral prefrontal cortex
... Traditionally, working memory and its neural underpinnings have been studied in the visual domain. A rich and diverse amount of research has investigated the lateral prefrontal cortex (lPFC) as a primary area for visual working memory, while another line of research has found the neurotransmitter ac ...
... Traditionally, working memory and its neural underpinnings have been studied in the visual domain. A rich and diverse amount of research has investigated the lateral prefrontal cortex (lPFC) as a primary area for visual working memory, while another line of research has found the neurotransmitter ac ...
The impact of iconic gestures on foreign language word learning
... whether the enhancing effect on verbal memory when performing a speech gesture during word learning is caused by the physical performance of the action itself, by the reactivation of a mental image, or possibly both. We reason that if the enhancement only depends on motor activity or on multimodalit ...
... whether the enhancing effect on verbal memory when performing a speech gesture during word learning is caused by the physical performance of the action itself, by the reactivation of a mental image, or possibly both. We reason that if the enhancement only depends on motor activity or on multimodalit ...
Prenatal memory

Prenatal memory, also called fetal memory, is important for the development of memory in humans. Many factors can impair fetal memory and its functions, primarily maternal actions. There are multiple techniques available not only to demonstrate the existence of fetal memory but to measure it. Fetal memory is vulnerable to certain diseases so much so that exposure can permanently damage the development of the fetus and even terminate the pregnancy by aborting the fetus. Maternal nutrition and the avoidance of drugs, alcohol and other substances during all nine months of pregnancy (especially the critical period when the nervous system is developing) is important to the development of the fetus and its memory systems. As shown here, certain uses of these substances can entail long-term permanent effects on the fetus that can carry into his or her lifespan. Fetal memory is thus critical to survival of the infant and serves many purposes.