* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review questions: Neuroanatomy
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
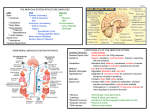
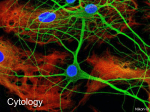
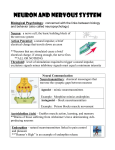
Review questions: Neuroanatomy 1. Classify the structures of the nervous system into divisions. CNS – Brain and Spinal Cord PNS – Nerves: 31 spinal, 12 cranial. Ganglia: Collection of nerve cell bodies in PNS. Cells which perform similar functions. Receptors: Pick up stimulus at end of nerves (dendrites) Functional divisions: Afferent nervous system: Sensory Somatic and visceral sensory nerve fibres Sends into TO CNS from periphery Efferent nervous system: Motor Motor nerve fibres conducts. Motor commands FROM CNS to effectors (muscles and glands) Somatic nervous system (SNS): Conscious awareness. Input from skin, sensory organs, proprioceptors (responsible for awareness of body position and movement. Output to skeletal muscles Autonomic nervous system (ANS): Involuntary response Input from receptors inside body, organs and vessels. Output to smooth muscles, organs, vessels and glands. 2. Describe the structure of a neuron and the function of each structural component. Soma: cell body, large nucleus, large numbers of golgi apparatus. Synthesise and secrete proteins. Signal integration and summation of nerve impulses. Dendrites: Receptors receive info from other neurons and carry to cell body. Lots of typically short branches. Carries info into cell. Axon: Usually only one long. Capable of propagating an electrical signal. Carries info away from cell Message – dendrites – soma – axon – telodendria – dendrites. Synapses: Where one neuron communicates with another. Cells connect to on another via axodendritic, axosomatic, axoanonic synapses. 3. Contrast the structural characteristics and functions of neuroglia and neurons. Neuroglia: nerve glue Provides structural support for neurons. Assist in the removal of waste products from neurons. Assist in transfer of nutrients from blood to neurons. Ependymal cells (CNS): Line cavities of brain and spinal cord. Ciliated Permeable barrier between CSF in cavities and fluid bathing CNS cells. Astrocytes (CNS): Star shaped Provides structural support Provide blood/brain barrier Hold down layers of meninges Blood brain barrier allows for selective crossing of materials and limits chemical variations in the environment of brain so there is no uncontrolled excitement. Microglia (CNS): Phagocytic ` Takes in material to break down and be eliminated by body Able to move to areas where needed Oligodendrocytes (CNS): Provide myelin sheath in CNS Schwann cells (PNS): Provide myelin sheath in PNS Nodes of Ranvier (PNS): Gaps between Schwann cells on axon. 3. Describe cellular organisation in both the CNS and the PNS. Grey matter: Cluster of neuron bodies in the CNS and unmyelinated fibres. White matter: bundles of myelinated axons in CNS. Nucleus: functional groups of cell bodies in CNS. Made of grey matter. Tract: Bundle of neuron processes in the CNS Eg: branches of spinal cord. Nerve: bundle of neuron processes in the PNS. Axons held together with connective tissue. Sensory nerves: carry info into body Motor nerves: carry info out of body. Made up of group of axons, blood vessels and connective tissue. Review questions: CNS Anatomy 1. Compare the structure and function of the 3 layers of meninges. Layers: Dura mater – 2 layers (outer: periosteal layer, inner: meningeal layer) Tough outer layer, attaches to cranial bones. Inner layer continues around cord. Arachnoid Fine elastic middle layer. Web-like extensions go into the subarachnoid space. Large blood vessels located under subarachnoid space. Pia mater Fine, filmy coating that goes into each fold and cavity of brain. Filled with tiny blood vessels. Clings tightly to brain. Held to brain by astrocytes. 5. Describe the locations and functions of the 3 areas of the brain stem. Midbrain: Nerve pathway of cerebral hemispheres. Auditory and Visual reflex centres. Pons: Respiratory Centre Medulla Oblongata: Crossing of motor tracts. Cardiac Centre. Respiratory Centre. Vasomotor (nerves having muscular control of the blood vessel walls) Centre, Centres for cough, gag, swallow, and vomit. 2. Describe how the sensation of being touched is dealt with in the 3 functional areas of the cerebral cortex. 3. Explain what is meant by the term “the emotional brain”. 4. Define proprioception. In which part of the brain is it processed? AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM REVIEW QUESTIONS: 1. Describe the neural organisation of the autonomic nervous system and the differences in the two divisions. 2. What are the three sympathetic ganglionic groups and where would you find them? 3. What's so special about the adrenal medulla? 4. Compare and contrast activation of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. 5. How can the responses of sympathetic and parasympathetic activation be explained in terms of activation of adrenergic and cholinergic receptors? 6. What is autonomic tone? Why does it matter? 7. How can emotional states effect such things as digestive and cardiac function?