* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System Period 7 - Mercer Island School District
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
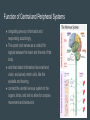
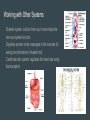
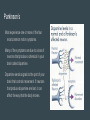
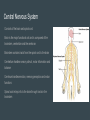
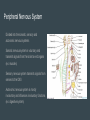
Nervous System Taylor, Kyra, Ryan, and Brennan Function of Central and Peripheral Systems ● integrating sensory information and responding accordingly ● The spinal cord serves as a conduit for signals between the brain and the rest of the body ● cells that detect information like smell and vision, exclusively motor cells, like the eyeballs and hearing ● connect the central nervous system to the organs, limbs, and skin to allow for complex movements and behaviors Cell type Neurons: transmit nerve pulses (signals) Glial cells, multiple types Satellite cells: physical support for neurons in peripheral system Oligodendroglia: provides myelin (insulation) for neurons Microglia: digest parts of dead neurons Astrocytes: regulate the external chemical environment Maintaining Homeostasis The nervous system maintains homeostasis by sending electrochemical signals throughout the body, coordinating and executing both the voluntary and involuntary processes that maintain homeostasis Working with Other Systems Skeletal system: calcium from your bones helps the nervous system function Digestive system: ends messages to the muscles for eating and elimination of waste food Cardiovascular system: regulates the heart rate using baroreceptors Alzheimer’s Brain disease that causes a slow decline in memory, thinking, and reasoning skills. Caused by genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors that affect the brain over time. Attacks the brain’s nerve cells, or neurons, resulting in memory loss, thinking and language skills, and behavioral changes. Parkinson’s Most experience one or more of the four most common motor symptoms. Many of the symptoms are due to a loss of neurons that produce a chemical in your brain called dopamine. Dopamine sends signals to the part of your brain that controls movement. If neurons that produce dopamine are lost, it can affect the way that the body moves. Central Nervous System Consists of the brain and spinal cord Brain is the major functional unit and is composed of the brainstem, cerebellum and the cerebrum Brainstem contains tracts from the spinal cord to the brain Cerebellum handles sensory stimuli, motor information and balance Cerebrum handles emotion, memory perception and motor functions Spinal cord relays info to the brain through tracts in the brainstem Peripheral Nervous System Divided into the somatic, sensory and autonomic nervous systems Somatic nervous system is voluntary and transmits signals from the brain to end organs (ex: muscles) Sensory nervous system transmits signals from senses to the CNS Autonomic nervous system is mostly involuntary and influences involuntary functions (ex: digestive system) Nerve Pulses A nerve impulse is an electrical signal that travels along an axon. When the nerve is activated, there is a sudden change in the voltage across the wall of the axon, caused by the movement of ions in and out of the neuron The speed of nerve impulses varies enormously in different types of neuron. The fastest travel at about 250 mph Neurons that need to transmit electrical signals quickly are sheathed by a fatty substance called myelin Nerve impulses are a way of coding information. Receptor Types Channel- Linked receptors: are cell membrane bound receptors. They act through synaptic signaling on electrically excitable cells Enzyme-linked receptors: is a transmembrane receptor, where the binding of an extracellular ligand causes enzymatic activity on the intracellular side. Intracellular receptors: are receptors located inside the cell rather than on its cell membrane. Classic hormones that use intracellular receptors include thyroid and steroid hormones. N