* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vocab: Unit 3 Handout made by: Jessica Jones and Hanna Cho
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
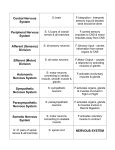
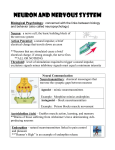
Vocab: Unit 3 Handout made by: Jessica Jones and Hanna Cho Module 9 Biological Psychology: links between biological and psychological processes Neuron: basic building block of the nervous system Dendrites: receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body Axon: passes messages through its branches to other neurons Myelin Sheath: fatty layer encasing the axons of some neurons, enables greater transmission speed Action Potential: brief electrical charge that travels down an axon Refractory Period: period of inactivity after a neuron has fired Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse All-or-none response: neuron’s reaction of either firing (with full strength) or not firing at all Synapse: junction between the axon (sending the neuron) and the dendrite (receiving) the gap is called the synaptic gap Neurotransmitters: messengers that cross the synaptic gap between neurons Reuptake: neurotransmitters reabsorption by the sending neuron Endorphins: natural opiate-like neurotransmitters, linked to pain control and pleasure Agonist: by binding to a receptor site, it stimulates a response Antagonist: blocks a response Module 10 Nervous System: body’s speedy communication network, includes the CNS and the PNS Central Nervous System: (CNS) The brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System: (PNS) sensory and motor neurons that connect the CNS to the body Nerves: “cables” connecting the CNS with muscles, glands, and sense organs Sensory (afferent) neurons: carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to brain and spinal cord Motor (efferent) neurons: carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands Interneurons: neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate with sensory inputs and motor outputs Somatic Nervous System: controls the body’s skeletal muscles Autonomic Nervous System: (ANS) part of PNS, controls glands and muscles of internal organs Sympathetic nervous system: arouses body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations Parasympathetic nervous system: calms the body, conserving its energy Reflex: simple, automatic response to a sensory stimulus Endocrine System: set of glands that slowly secrete hormones into the bloodstream Hormones: chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream and affect other tissues Adrenal glands: sit above the kidneys and helps arouse the body in times of stress Pituitary gland: regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands Module 11 Lesion: tissue destruction, brain lesions are naturally or experimentally caused Electroencephalogram: (EEG) amplified recording of the waves, measured by electrodes placed on the scalp. CT computed tomography scan: X-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by the computer to composite representation of a slice of the brain’s structure. PET positron emission tomography scan: visual display of the brain activity, detects where radioactive forms of glucose goes while the brain is given a task. MRI magnetic resonance imaging: magnetic fields and radio waves that produce computer images of the brain. FMRI functional MRI: a technique that’s used for revealing blood flow, shows brain function and structure. Brainstem: the oldest and central core of the brain, the brainstem is responsible for automatic survival functions Medulla: the base of the brainstem; controls the heartbeat and breathing Thalamus: directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the coretext and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla. Reticular formation: a nerve network that travels through the brainstem and thalamus and plays an important role in arousal. Cerebellum: processes sensory input, coordinates movement output and balance, and enables non verbal learning memory. Limbic System: neural system located below the cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions and drives Amygdala: two-lime bean sized neural clusters in limbic system; linked to emotion Hypothalamus: helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, linked to emotion and reward Module 12 Cerebral Cortex: the body’s ultimate control and information processing center Frontal lobes: lies just behind the forehead; involved in speaking and muscle movements and in plans and making judgement. Parietal lobes: lies on the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and boyd position Occipital lobes: lies at the back of the head; includes areas that receive information from visual fields Glial Cells: (glia) cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons, they may also play a role in learning and thinking Temporal lobes: lies roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information from the opposite ear. Motor cortex: an area at the rear of the frontal lobes, controls voluntary movements Somatosensory cortex: registers and processes body touch and movement sensations (in the front of the parietal lobes) Association area: areas of the cerebral cortex involving the higher mental functions, such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking Plasticity: the brain’s ability to change, by reorganizing after damage of building new pathways Neurogenesis: the formation of new neurons Module 13 Corpus Callosum: the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them Split brain: condition resulting from surgery, isolates the brain’s two hemispheres Consciousness: our awareness of ourselves and the environment Cognitive Neuroscience: linked with cognition, thinking, memory, and language Dual Processing: the principle that information is often simultaneously processed on separate conscious and unconscious tracks Module 14 Behavior genetics: the study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences Environment: every external influence, from prenatal nutrition to the people and things around us Chromosomes: threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain genes DNA: (deoxyribonucleic acid) complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up chromosomes Genes: biochemical units of heredity that make up chromosomes Genome: complete instructions for making an organism, genetic material in the organism’s chromosomes Identical twins: (monozygotic twins) develop from a single fertilized egg that splits in two Fraternal twins: (dizygotic twins) develop from separate fertilized eggs, share a fetal environment Molecular genetics: studies the molecular structure and function of genes Heritability: variation among individuals that can attribute to genes, will vary depending on the range of populations and environments studied Interaction:interplay occurs when the effect of one factor depends on another factor (environment and heredity) Epigenetics: study of environmental influences on gene expression, occurs without DNA change Module 15 Evolutionary psychology: study of evolution of behavior and the mind, using the principles of natural selection Natural selection: range of inherited trait variations, that contribute to reproduction and survival will be most likely passed on to succeeding generations Mutation: error in gene replication that leads to a change