* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 13: Insect nerve system (NS)
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
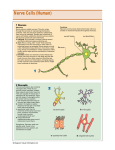
Lecture 13: Insect nerve system (NS) Brain Thoracic ganglia Subesophageal ganglion Abdominal ganglia Ventral nerve cord Signal transducer, transmitter, processor (integrator) Overview • Structures (Anatomy) – Cells – Anatomy • Functions – Signal transduction – Signal transmission Cells in the nerve system 1.Nerve cells (=Neurons): Conducting cells that transduce, transmit or process nerve impulses. 2.Glial cells: Non-conducting supporting cells that surround neurons and help to protect neurons and maintain stable ionic environment Neuron has projections Neurons similar to other cells, but: 1. have specialized extensions called dendrites and axons. Dendrites bring information to the soma and axons take information away from the soma. 2. Neurons communicate with each other through specialized structures called synapses and chemicals (e.g. neurotransmitters). Neuron-neuron junction: synapse Synaptic cleft terminal arborization axon axon soma stimulus Nerve impulse dendrite dendrite Presynaptic neuron soma Postsynaptic neuron Remember: electric synapse Types of neuron: unipolar one projection extending from the soma Stimulus Terminal arborization axon Nerve impulse dendrite soma Types of neuron: bipolar Terminal arborization axon Stimulus Nerve impulse dendrite soma • Two projections extending from the cell body • Typical of sensory neuron Types of neuron: multipolar axon soma dendrite Many projections extending from the soma But only one axon Types of neuron: two ways of classification By the number of extensions • unipolar neurons have one projection extending from the soma. • Bipolar neurons have two projection extending from the soma • Multipolar neurons have many projections extending from the soma. However, each has only one axon By the direction of information that they send (function) • Afferent (sensory) neurons --bipolar or multipolar cells have dendrites that are associated with sense organs. They carry information TOWARD the central nervous system (CNS). • Efferent (motor) neurons -- unipolar cells that conduct signals AWAY from CNs and stimulate responses in muscles and glands. • Interneuron (association neuron) -unipolar cells that form connections between afferent and efferent neurons and conduct signals WITHIN CNS. Sensory neuron Where are motor neurons and interneurons? Aggregate in Ganglion Inside ganglion • Cell bodies cluster on outside ring Lamella perineurium • Center region: axons and dendrites of interneurons and motor neurons AND axon arborizations of sensory neurons Soma of neuron • Center region = NEUROPIL glial cell body processes of glial cells axons Inside ganglion: glial cells • • • • • • Surround ganglion Neural lamella: mechanical support for NS, secreted by perineurium Perineurium=brain-blood barrier: a layer of glial cells that maintain stable ionic environment Nerve sheath= lamella + perineurium Surround individual nerve (axon) Protect, insulate and repair neuron Pass nutrients to nerve and control ionic environment More glial cells than neurons Hemolymph Lamella perineurium Soma of neuron glial cell body processes of glial cells axons Glial cells: go with sensory neurons Insect Nerve system: anatomy • Central nerve system (CNS) - most ganglia included: brain+ventral nerve cord • Stomatogastric nerve system (SNS) - Frontal ganalion + hypocerebral ganglion + ventricular ganglion; innervate muscles of the mouth cavity, foregut, midgut; and regulate food uptake and food transport • Peripheral Nerve system (PNS)- all sensory neurons; not bundled in ganglia; located in integument PNS: all sensory neurons • In epidermis • Sensory neurons • Outside ganglion SNS: FG, HG and VG Manduca sexta • FG: Frontal ganglion • HG: Hypocerebral ganglion Fly • VG: Ventricular ganglion or cluster of neurons Brain Hypocerebral ganglion Recurrent nerve Frontal ganglion Frontal nerve Gastric nerve Subesophageal ganglion • FG: connect with tritocerebrum and HG, send axons to pharynx and esophagus. control of food passage through the gut and crop emptying • HG: sends axons to CC and VG • VG: associate with foregut and midgut CNS: brain + ventral nerve cord Brain Thoracic ganglia Subesophageal ganglion Abdominal ganglia Ventral nerve cord • Brain: a compound ganglion, major association center • Ventral nerve cord: SG + TG + AG: local association center • SG: a compound ganglion (mandible maxillae, and labium) Ventral nerve cord: trend towards ganglia (fusing) condensing More ventral ganglia in primitive species than in advanced ones More in larvae than in adult Brain: proto-, deuto- and tritocerebrum Brain: another perspective Hypocerebral ganglion Protocerebrum Mushroom body Pars intercerebralis Optic lobe Central complex Accessary lobe Deuto- and tritocerebrum Tritocerebrum Antennal lobe =deutocerebrum • Antennal lobe: the centers that receive the antennal nerves • Tritocerebrum: the origin of the labral nerves that run to the upper lip Mushroom body: center for higher-order sensory integration and learning McGuire et al. 2001, Science Dubnau et al. 2002, Nature • Receive information mainly from olfactory (antennal lobe). Hymenoptera also from optic lobe • Olfactory learning and memory, place memory, associative memory, and roles in motor control Roles of central complex • control of locomotor activity, particularly flight and walking • center for direction perception and spatial navigation • coordinates L and R brain?
































![Neuron [or Nerve Cell]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000229750_1-5b124d2a0cf6014a7e82bd7195acd798-150x150.png)