* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download • The neuron is similar to other cells: •Cell body: lipid bilayer
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Cerebral cortex wikipedia , lookup
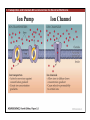
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
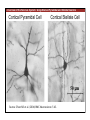
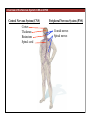
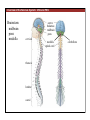
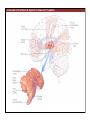
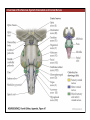
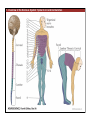
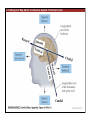
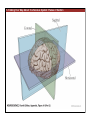
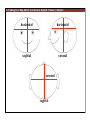
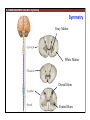
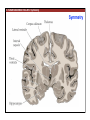
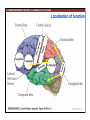
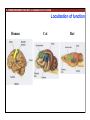
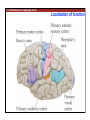
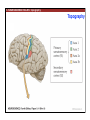
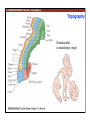
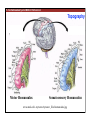
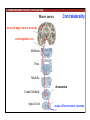
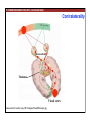
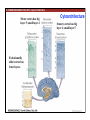
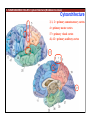
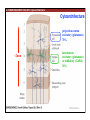
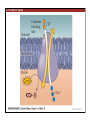
1. Overview of the Nervous System: The Neuron • The neuron is similar to other cells: •Cell body: lipid bilayer membrane •Organelles: nucleus, mitochondria, etc. • The neuron differs from other cells: •Unique morphology: dendrites, axons •Electrically excitable: action potential 2. Overview of the Nervous System: The Neuron Dendrites: Receive signals from other neurons (input) Axons: Send signals to other neurons (output) Potential (mV) action potential 50 0 -50 -65 resting potential 0 1 2 Time (ms) 3. Overview of the Nervous System: Neurons Morphological Variation 4. Overview of the Nervous System: Golgi-Stained Pyramidal and Stellate Neurons Cortical Pyramidal Cell Cortical Stellate Cell 50 !m Source: Churchill et al. (2004) BMC Neuroscience 5:43. 5. Overview of the Nervous System: Glial Cells >3x more glial cells than neurons astrocyte maintain ionic environment oligodendrocyte myelinate neurons microglia scavenge cellular debris 6. Overview of the Nervous System: CNS and PNS Central Nervous System (CNS) Cortex Thalamus Brainstem Spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Cranial nerves Spinal nerves 7. Overview of the Nervous System:: CNS and PNS Brainstem: midbrain pons medulla cortex thalamus midbrain pons cervical thoracic lumbar sacral medulla spinal cord cerebellum 8. Overview of the Nervous System: Cortex and Thalamus 9. Overview of the Nervous System: Brainstem and Cranial Nerves 10. Overview of the Nervous System: Cranial Nerves 11. Overview of the Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Dermatomes 12. Finding Your Way About The Nervous System: Positional Terms Rostr al Dorsa l Ventr al Caud sal Dor al tr Ven Caudal al 13. Finding Your Way About The Nervous System: Positional Terms Superior Rostral Ascending Dorsal Anterior Ventral Descending Caudal Inferior Posterior 14. Finding Your Way About The Nervous System: Positional Terms ipsilateral contralateral same side opposite side proximal distal close to point of reference far from point of reference efferent afferent projecting away from reference projecting towards reference midline medial lateral decussate line separating left and right near midline far from midline cross midline 15. Finding Your Way About The Nervous System: Planes of Section 16. Finding Your Way About The Nervous System: Planes of Section horizontal horizontal sagittal coronal coronal sagittal 17. NEUROSCIENCE RULES Neuroscience Rules! • Symmetry • Localization of Function • Topography • Contralaterality • Cytoarchitecture • Circuitry 18. NEUROSCIENCE RULES: Symmetry Symmetry Gray Matter White Matter Dorsal Horn Ventral Horn 19. NEUROSCIENCE RULES: Symmetry Symmetry 20. NEUROSCIENCE RULES: Localization of Function Language g rin a e H Language Vis ion Cognition Tou ch Mo vem ent Localization of function 21. NEUROSCIENCE RULES: Localization of Function Localization of function Human Cat Rat 22. Left Hemisphere Language areas Localization of function 23. NEUROSCIENCE RULES: Topography Topography 24. NEUROSCIENCE RULES: Topography Topography Homunculus (somatotopic map) 25. Somatosensory and Motor Homunculi Topography Motor Homunculus Somatosensory Homunculus www.umsl.edu/~tsytsarev/tsytsarev_files/homunculus.jpg 26. NEUROSCIENCE RULES: Topography Topography Retinotopic map in primary visual cortex http://www.pc.rhul.ac.uk/courses/Lectures/PS1061/L2/frisby.jpg 27. NEUROSCIENCE RULES: Contralaterality Somatosensory Cortex decussation primary afferent Contralaterality 28. NEUROSCIENCE RULES: Contralaterality Motor cortex Contralaterality axons of upper motor neurons corticospinal tract Midbrain Pons Medulla decussation Caudal Medulla Spinal Cord axons of lower motor neurons 29. NEUROSCIENCE RULES: Contralaterality Contralaterality decussation Thalamus Visual cortex www.owlnet.rice.edu/~psyc351/Images/VisualPathways.jpg 30. NEUROSCIENCE RULES: Cytoarchitecture Motor cortex has big layer 5; small layer 4 Evolutionarily older cortex has fewer layers. Cytoarchitecture Sensory cortex has big layer 4; small layer 5 31. NEUROSCIENCE RULES: Cytoarchitecture (Brodmann’s Areas) Cytoarchitecture 3, 1, 2 = primary somatosensory cortex 4 = primary motor cortex 17 = primary visual cortex 41, 42 = primary auditory cortex 32. NEUROSCIENCE RULES: Cytoarchitecture Cytoarchitecture projection neuron excitatory (glutamate) 70% ~2mm interneuron excitatory (glutamate) or inhibitory (GABA) 30% 33. NEUROSCIENCE RULES: Circuitry (cortex) Circuitry 34. NEUROSCIENCE RULES: Circuitry (spinal cord) Circuitry 35. NEUROSCIENCE RULES Neuroscience Rules! • Symmetry • Localization of Function • Topography • Contralaterality • Cytoarchitecture • Circuitry 36. CSF Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Neurons are surrounded by an aqueous saline solution called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The CSF contains sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), chloride (Cl-), calcium (Ca++), and other ions in solution. The neuronal membrane itself (lipid bilayer) is impermable to the movement of ions. However, ions can cross the membrane by two means... 37. Transporters and Channels Move Ions Across the Neuronal Membrane Ion Pump Ion Channel 38. The Na+/K+ pump 39. Restiing Potential The Resting Potential The resting potential is negative because: 1. The K+ concentration is greater inside than outside the neuron, due to the action of the sodium / potassium transporter “pump.” 2. At rest, the neuron is primarily permeable to K+, because the membrane contains K+ “leak” ion channels. 40. Diffusion and electrostatic (Coulomb) force Two Physical Phenomena Establish the Resting Potential Diffusion: K+ diffuses out down its concentration gradient. Electrostatic force: As K+ diffuses out, the inside becomes negative compared to the outside. Eventually, K+ is attracted strongly enough to the negative inside that the diffusion stops. (Opposite charges attract).