* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ACh - Perkins Science
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
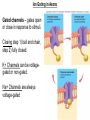
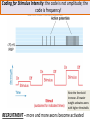
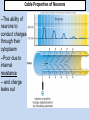
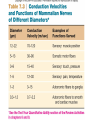
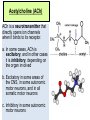
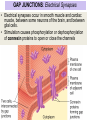
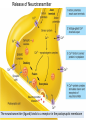
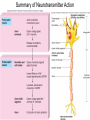
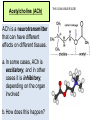
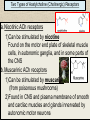
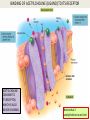
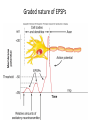
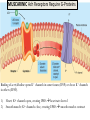
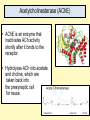
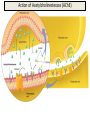
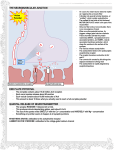
INTRODUCTION TO NEUROBIOLOGY LECTURE 9 CH 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM: NEURONS AND SYNAPSES • Students must review the beginning of Chapter 7 on their own. • See Intro to Neurobiology “A” lecture for assistance; there may be questions on this section on the exams. • This lecture begins with “Electrical Activity in Axons” Section 7.2 (but you are required to know 7.1, which is Anatomy). Fig. 7.11 - Observing Depolarization and Hyperpolarization - Oscilloscope - Measures the potential difference - - 70 mV = resting (neuron), polarized - Depolarization = + charge moves in (excitatory) - Hyperpolarization = neg. charge moves in. (inhibitory) - Repolarization = return to resting. Click HERE Ion Gating in Axons Gated channels – gates open or close in response to stimuli. Closing step 1) ball and chain, step 2) fully closed. K+ Channels can be voltagegated or non-gated. Na+ Channels are always voltage-gated Depolarization of an Axon All-or-None Law Coding for Stimulus Intensity: the code is not amplitude; the code is frequency! Note the threshold increase. A heavier weight activates axons with higher thresholds RECRUITMENT – more and more axons become activated Refractory Period: time when axon is not responsive to a 2nd stimulus The absolute refractory period occurs during the action potential. Na+ channels are inactive (not just closed). Relative refractory period can be overcome by a strong stimulus. (while K+ diffuses outward). Each action potential remains a separate, all-or-none event. Cable Properties of Neurons --The ability of neurons to conduct charges through their cytoplasm --Poor due to internal resistance -- and charge leaks out Conduction of Nerve Impulses When an action potential occurs at a given point on a neuron membrane, voltage- gated Na+ channels open as a wave down the length of the axon. The action potential at one location serves as the depolarization stimulus for the next region of the axon Saltatory Conduction in a Myelinated Neuron Myelin provides insulation, improving the speed of action potential. Nodes of Ranvier allow Na+ and K+ to cross the membrane every 1−2 mm. Na+ ion channels are concentrated at the nodes. Action potentials “leap” from node to node. The Synapse A synapse is the functional connection between a neuron and the cell it is signaling a.In the CNS, this second cell will be another neuron. b.In the PNS, the second cell will be in a muscle or gland; often called myoneural or neuromuscular junctions Otto Loewi (1921) CHEMICAL SYNAPSES • Discovered Vagusstoff, a chemical secreted by the vagus nerve (acetylcholine). • EXPERIMENT: Acetylcholine (ACh) ACh is a neurotransmitter that directly opens ion channels when it binds to its receptor. a. In some cases, ACh is excitatory, and in other cases it is inhibitory, depending on the organ involved b. Excitatory in some areas of the CNS, in some autonomic motor neurons, and in all somatic motor neurons c. Inhibitory in some autonomic motor neurons GAP JUNCTIONS: Electrical Synapses • Electrical synapses occur in smooth muscle and cardiac muscle, between some neurons of the brain, and between glial cells. • Stimulation causes phosphorylation or dephosphorylation of connexin proteins to open or close the channels Chemical Synapses Vesicles are produced in the Golgi and stored at the end of an axon (terminal boutons) The synaptic cleft is very small, 10nm, and the presynaptic and postsynaptic cells are held close together by cell adhesion molecules (CAMs). Release of Neurotransmitter The neurotransmitter (ligand) binds to a receptor in the postsynaptic membrane Summary of Neurotransmitter Action 7.4 Acetylcholine Acetylcholine (ACh) ACh is a neurotransmitter that can have different effects on different tissues. a.In some cases, ACh is excitatory, and in other cases it is inhibitory, depending on the organ involved b.How does this happen? THIS IS AN EARLIER SLIDE! Two Types of Acetylcholine (Cholinergic) Receptors a.Nicotinic ACh receptors 1)Can be stimulated by nicotine Found on the motor end plate of skeletal muscle cells, in autonomic ganglia, and in some parts of the CNS b.Muscarinic ACh receptors 1)Can be stimulated by muscarine (from poisonous mushrooms) 2)Found in CNS and plasma membrane of smooth and cardiac muscles and glands innervated by autonomic motor neurons BINDING OF ACETYLCHOLINE (LIGAND) TO ITS RECEPTOR ACETYLCHOLINE CAN BIND TO ITS RECEPTOR, WHICH IS ALSO AN ION CHANNEL Notice that 2 acetylcholines must bind Graded nature of EPSPs Question? What would happen if a person had a disease that caused a deactivation of nicotinic ACh receptors located in the motor end plates* of skeletal muscle cells? Discuss this with your neighbor. *motor end plates are the part of the muscle cell that is activated by neurons. MUSCARINIC Ach Receptors Require G-Proteins Binding of acetylcholine opens K+ channels in some tissues (IPSP) or closes K+ channels in others (EPSP). 1) 2) Heart: K+ channels open, creating IPSPs heart rate slowed Smooth muscle: K+ channels close, creating EPSPs smooth muscles contract Agonists and Antagonists Agonists: drugs that can stimulate a receptor a)Nicotine for nicotinic ACh receptors b)Muscarine for muscarinic ACh receptors Antagonists: drugs that inhibit a receptor a)Atropine from plants, is an antagonist for muscarinic receptors. b)Curare (from plants) is an antagonist for nicotinic receptors. Clinically, curare is used as a muscle relaxant. Lethal in high doses; poison dart use. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) • AChE is an enzyme that inactivates ACh activity shortly after it binds to the receptor. • Hydrolyzes ACh into acetate and choline, which are taken back into the presynaptic cell for reuse. Action of Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)


















![AP_Chapter_2[1] - HopewellPsychology](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008569681_1-9cf3b4caa50d34e12653d8840c008c05-150x150.png)