* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Central Nervous System CNS
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
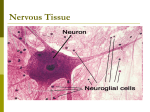
The Central Nervous System CNS Lecture 2 1 Nervous System and Senses • The nervous system consists of two types of cells: 1. Nerve cells are called neurons. 2. Various support cells are associated with the neurons, most typically, Schwann cells. • The parts of a neuron include the dendrite which receives the impulse (from another nerve cell or from a sensory organ), the cell body (numbers of which sideby-side form gray matter) where the nucleus is found, and the axon which carries the impulse away from the cell. 2 • Wrapped around the axon are the Schwann cells, and the spaces/junctions between Schwann cells are called nodes of Ranvier. • Collectively, the Schwann cells make up the myelin sheath (numbers of which side-by-side form white matter). • Having an intact myelin sheath and nodes of Ranvier are critical to proper travel of the nerve impulse. 3 • Diseases which destroy the myelin sheath (demyelinating disorders) can cause paralysis or other problems. • Schwann cells are analogous to the insulation on electrical wires, and just as electrical wires short out if there’s a problem with the insulation, so also, neurons cannot function properly without intact myelin sheaths. 4 • The outer layer of myelin is surrounded by a neurilemma (neurilemmal sheath) made up of the cytoplasm and nuclei of the Schwann cell. • Narrow gaps in the myelin sheath between Schwann cells are called nodes of Ranvier. • The smallest axons lack a myelin sheath and are unmyelinated fibers. • White matter in the CNS is due to myelin sheaths in this area. • Unmyelinated nerve tissue in the CNS appears gray. 5 Types of Neurons Neurons can be grouped in two ways: 1. on the basis of structural differences (bipolar, unipolar, and multipolar neurons) 2. by functional differences (sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons). 6 Types of Neurons 7 Bipolar neurons are found in the eyes, nose, and ears, and have a single axon and a single dendrite extending from opposite sides of the cell body. Unipolar neurons are found in ganglia outside the CNS and have an axon and a dendrite arising from a single short fiber extending from the cell body. Multipolar neurons have many nerve fibers arising from their cell bodies and are commonly found in the brain and spinal cord. 8 Another Classification of Neurons • Sensory neurons (afferent neurons) conduct impulses from peripheral receptors to the CNS and are usually unipolar, although some are bipolar neurons. • Interneurons are multipolar neurons lying within the CNS that form links between other neurons. • Motor neurons (efferent neurons) are multipolar neurons that conduct impulses from the CNS to effectors. 9 Motor Neuron 10 Neuroglial Cells 1. 2. 3. 4. Microglial cells Oligodendrocytes Astrocytes Ependyma 11 Functions of Neuroglial Cells 1. fill spaces 2. support neurons 3. provide structural frameworks 4. produce myelin, and carry on phagocytosis 12 • Microglial cells are small cells that phagocytize bacterial cells and cellular debris. • Oligodendrocytes form myelin in the brain and spinal cord. • Astrocytes are near blood vessels and support structures, aid in metabolism, and respond to brain injury by filling in spaces. • Ependyma cover the inside of ventricles and form choroid plexuses within the ventricles 13 Nervous system Functions The nervous system has three basic functions: 1. receive information from the sensory receptors through the Sensory neurons. 2. transfer and interpret impulses through the Interneurons. 3. send appropriate impulses/ instructions to the muscles and glands through Motor neurons . 14