* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neurons - Yavapai College
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
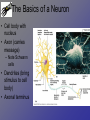
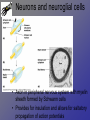
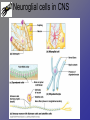
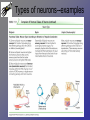
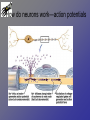
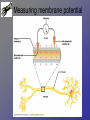
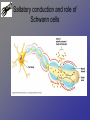
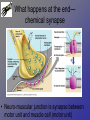
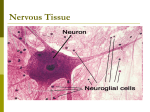
Neurons • Neurons and neuroglia (multiple sclerosis and neuroglia) • Where are neurons in the body? • Types of neurons and their functions • How do neurons work? – Action potentials – Synapses The Basics of a Neuron • Cell body with nucleus • Axon (carries message) – Note Schwann cells • Dendrites (bring stimulus to cell body) • Axonal terminus Neurons and neuroglial cells • Axon in peripheral nervous system with myelin sheeth formed by Schwann cells • Provides for insulation and allows for saltatory propagation of action potentials Neuroglial cells in CNS Neuroglial cells in CNS • Astrocytes – Most abundant and versatile – Control chemical environment around neurons – Also signal among themselves with slow chemical signals • Microglia – Monitor health of neurons and transform into immune macrophages (normal immune cells have no access to CNS) • Ependymal cells – Line cavities of brain/CNS – Barrier between CSF and tissue fluid – Cilia beat to move CSF • Oligodendrocytes – Myelin sheaths in CNS Types of Neurons--structural classes Types of Neurons—where in body Types of neurons--examples How do neurons work—action potentials Measuring membrane potential Diffusion and action potential Saltatory conduction and role of Schwann cells What happens at the end— chemical synapse • Neuro-muscular junction is synapse between motor unit and muscle cell (motor unit)