* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nerve cells - Dr Magrann
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
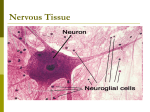
Nerve Cell Flashcards 1. What does the word “innervates” mean? 2. 3 parts of the Nervous System 3. What are the two parts of the CNS? 4. What does the Autonomic Nervous System control and what are its 2 divisions? 5. What kinds of neurons enter the CNS? 6. What kind of neurons leave the CNS? 7. What three things do all neurons do? a. What three characteristics do all neurons share? Refers to a nerve supplying a muscle or organ. For example, “The phrenic nerve innervates the diaphragm muscle”. 1. Central Nervous System (CNS): brain and spinal cord. 2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): nerves of the body 3. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): has parts of the CNS and PNS. Brain and Spinal cord Controls autonomic (automatic) functions (blood pressure, digestion, etc). a. Sympathetic division b. Parasympathetic division Sensory (afferent) signals picked up by sensor receptors. They are carried by nerve fibers of PNS to the CNS Motor (efferent) signals are carried away from the CNS. They innervate muscles and glands 1. Receive a signal. Can be any type of stimulus (change in environment, signal from another neuron, etc). 2. Transmit a signal to another location. E.g. finger touching something signal to spinal cord or brain. 3. Stimulate another cell a. Another neuron transmit signal b. Muscle contraction c. Gland secretion 1. Longevity – can live and function for a lifetime 2. Do not divide – fetal neurons lose their ability to undergo mitosis (the y lose their centrioles); neural stem cells are an exception 3. High metabolic rate – require abundant oxygen and glucose 1 Nerve Cell Flashcards 8. Picture of Sensory vs Motor Neurons axon 9. Photo of NEURON anatomy 10. What receives the signal and carries the nerve conduction toward the cell body? 11. Where are the nucleus, ribosomes, and most organelles located? 12. What has the function of transmitting signals from the cell body to the area with neurotransmitters? 13. What part of a neuron stimulates another cell? DENDRITES The CELL BODY AXON SYNAPTIC KNOBS 2 Nerve Cell Flashcards 14. Describe the correct path an impulse takes across a synapse. Axon of presynaptic neuron SYNAPTIC CLEFT dendrite of post synaptic neuron 15. What are synaptic knobs filled with? The synaptic knob has vesicles filled with a neurotransmitter that carries the signal. 16. What are the supporting cells of the nervous system? 17. Where do most tumors originate from? GLIA 18. What are 4 types of glia cells? Oligodendrocyte Schwann Cell Astrocyte Microglia OLIGODENDROCYTES Most tumors of the brain originate from glial cells. 19. Which cells provide the myelin sheath for neurons in the CNS? 20. Which cells provide the myelin sheath for SCHWANN CELLS neurons in the PNS? 21. What is the function of MYELIN to speed up the rate of nerve impulse conduction. SHEATHS 22. What are the BARE regions of axonal NODES OF RANVIER membranes found only in myelinated axons called? 3 Nerve Cell Flashcards 23. What conducts impulses faster – myelinated Myelinated or unmyelinated axon? 24. Where are unmyelinated axons found? Anywhere except Schwann cells and Oligodendrocytes. They are in the PNS and CNS. 25. Are unmyelinated axons thinner or thicker Unmyelinated axons are thinner. than myelinated? 26. What is myelin made of? Mostly lipid 27. What is an autoimmune disease where the MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS oligodendrocytes (the myelin sheaths) are destroyed, interfering with the neuron functions in the CNS and brain? 28. What is the most common neurological MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS disease of young adults? 29. What are the 3 functions of an a. Physically supports the neurons ASTROCYTE? b. Transmits materials from capillaries to neurons c. Forms blood-brain barrier (BBB), which keeps out harmful substances and many medicines 30. What is the only function of the blood-brain The only function of the blood-brain barrier is to help barrier BBB? protect the central nervous system. 31. Define MICROGLIA and their function They are macrophages They pick up bacteria and debris 32. What is the portion of the CNS that is GREY MATTER unmyelinated (cell bodies of neurons, glia, and dendrites)? 33. What is the portion of the CNS with myelin WHITE MATTER (axons) 34. What is a collection of axons in the PNS? NERVE; No cell bodies, dendrites, or synapses; just axons. 35. What is a collection of axons in the CNS TRACT 36. What is a collection of cell bodies in the Ganglion PNS? 37. What are the neurons that leave the CNS to MOTOR NEURONS effect a muscle or gland? 38. What neurons go from body to CNS, SENSORY NEURON carrying sensory information? 39. What is a small neuron found only in the INTERNEURON CNS? 40. What are the three structural classifications 1. Unipolar of neurons? 2. Bipolar 3. Multipolar 4