* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Guided notes 2 Histology - Liberty Union High School District
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
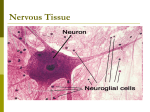
Histology of the Nervous Tissue ppt 2 Label the structures of a nerve: Within this nerve there are many nerve cells Nervous tissue is made up of 2 kinds of cells: _________________ and ____________________________________________ The supporting cells of the CNS are: 1. 2. 3. 4. The supporting cells of the PNS are: 1. 2. These supporting cells serve many functions: ____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ Structure of a Nerve Cell: All have a cell Body sometimes called a _______ This is the control center and contains the nucleus Cytoplasm contains:_________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ Cytoskeleton contains:_________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ Dendrites are:___________________________________ They are the primary site for _________________________________________ The more dendrites the more_________________________________________ DENDRITES provide_____________________________________________________ Axons (nerve fiber) are __________________________________________________ Axons are responsible for ________________________________________________ They branch into ____________________________ They are covered by _________________________________________________ Axons end in axon terminals called:________________________________________ The ends contains synaptic vesicles full of ______________________________ What do Schwann cells and myelin have to do with it???? Myelin is a______________________________________________________________ Axons are ____________________________________and this is deposited by layers of ___________________________ Schwann cells layer around the axon and squeeze the cytoplasm out of themselves leave layers of__________________ ___________________surrounding the axion. This layer is called the ______________________________________. This is discontinuous…so there are spaces with no sheath. These areas are called________________________________ What is the purpose of myelin?: _______________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________. Synaptic terminal:_also called the ___________________________ does not touch the next neuron. It has a tiny gap Called a _______________________. Neurotransmitters are ____________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ There are many kinds of neurotransmitters…more later What do the Axons do besides transmit signals? Axonal transport is responsible for moving molecules destined for degradation from the axon back to the cell body, where they are broken down by lysosomes. Movement toward the cell body is called retrograde transport and movement toward the synapse is called anterograde transport. Microtubules guide materials along the axon. Motor Proteins carry materials as they crawl along the microtubules. There are 2 basic kinds of these motor proteins: 1. Kinesin:____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Dynein:_____________________________________________________________________________________ More about the Neuroglial cells (glial cells) remember these are supporting cells. 1.__________________________________________ 2,____________________________________________ 3.___________________________________________________________________________________ 4._______________________________________________________________________________________________ Types of glial cells: CNS 1. Oligodendrocytes: 2. Ependymal cells: 3. Microglia: 4. Astrocytes: Types of Glial cells PNS: 1. Schwann Cells: 2. Satellite cells: Glial cells and Brain Tumors: Tumors are:______________________________________________________ Mature neurons do NOT ____________________________ and seldom form tumors. Brain Tumors arise from: 1. 2. 3. Gliomas ___________________________________________ Very problematic because_____________________________________________________________ Treatment consists of ________________________________________________. More facts about Myelin: In CNS is formed by____________________________________ In PNS is formed by___________________________________________ Consists of :__________________________________________________________ Myelination begins :_________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Diseases of the Myelin Sheath: Multiple Sclerosis: Tay Sachs Disease: