* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 46 Chapter Review: Fill-in-the
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Impact of health on intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
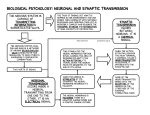
CHAPTER 2: BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR 46 Handout Master 2.10 Chapter Review: Fill-in-the-Blank Key Terms Exercise 1. , produced naturally by the brain and the pituitary gland, reduce pain and positively affect mood. 2. The most common cause of damage to adult brains, arising when blockage of an artery cuts off the blood supply to a particular area of the brain or when a blood vessel bursts, is _ 3. The gray, convoluted covering of the cerebral hemispheres that is responsible for higher mental processes such as language, memory, and thinking is called the _ 4. The sudden reversal of the resting potential, which initiates the firing ofa neuron, is called the 5. During the process, neurotransmitter molecules are taken from the synaptic cleft back into the axon terminal for later use, thus terminating their excitatory or inhibitory effect on the receiving neuron. 6. The is the junction where the axon of a sending neuron communicates with a receiving neuron across the synaptic cleft. 7. A person's includes his/her actual characteristics. 8. is the specialization of one of the cerebral hemispheres to handle a particular function. 9. is a neurotransmitter that plays a role in learning, attention, and movement; a deficiency of it is associated with Parkinson's disease, and anoversensitivity to it is associated with some cases of schizophrenia. 10. The control voluntary body mo;'ements, speech production, and such functions as thinking, motivation, planning for the future, impulse control, and emotional responses. 11. The field of research that investigates the relative effects of heredity and environment on behavior and ability is _ 12. is a pattern of inheritance in which a trait is influenced by both genes and environmental factors. 13. The is the structure that is located above the brain stem and acts as a relay station for information flowing into or out of the higher brain centers. 14. The strip of tissue at the front ofthe parietal lobes where touch, pressure, temperature, and pain register in the cerebral cortex is called the . 15. The is the largest part ofthe brain, where cognitive functions as well as many of the motor functions of the brain are carried out. 16. The nerves in the connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body. 17. The primary visual cortex, where vision registers, and association areas involved in the interpretation of visual information are located in the -:-".--.,.--,-. 18. is the ability of the brain to reorganize and compensate for brain damage. 19. The branchlike extensions of a neuron that receive signals from other neurons are called the 20. The is a set of inheritance rules in which the presence of a single dominant gene causes a trait to be expressed but two genes must be present for the expression of a recessive trait. 21. The is a brain- imaging technique that reveals activity in various parts of the brain, based on the amount of oxygen and glucose consumed. 22. The is a group of structures in the brain, including the amygdala and hippocampus, that are collectively involved in emotion, memory, and motivation. 23. The right and left halves of the cerebrum, covered by the cerebral cortex and connected by the corpus callosum, are called the . 24. The are the sex glands; the ovaries in females and the testes in males. 25. The white, fatty coating wrapped around some axons that acts as insulation and enables impulses to travel much faster is the . 26. is a neurotransmitter that plays an important role in regulating mood, sleep, aggression, and appetite; a serotonin deficiency is associated with anxiety, depression, and suicide. 27. A brain-imaging technique that reveals both brain structure and brain activity is the _ Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.