* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the brain
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
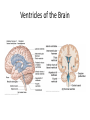
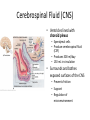
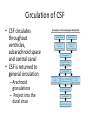
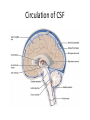
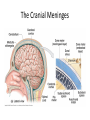
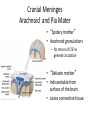
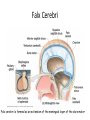
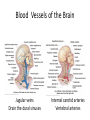
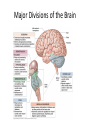
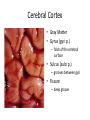
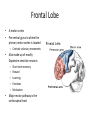
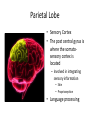
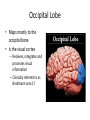
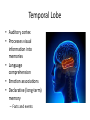
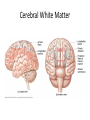
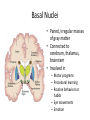
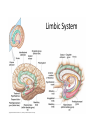
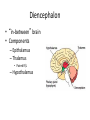
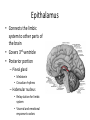
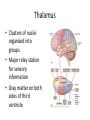
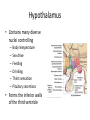
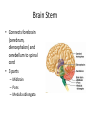
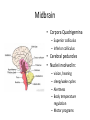
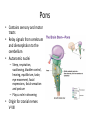
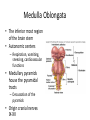
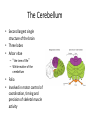
HumanAnatomy Unit4 NERVOUSSYSTEM: THEBRAIN InAnatomyToday VentriclesoftheBrain • Lateralventricles – 2ventriclesshapedlike“ramhorns” – Separatedbytheseptumpellucidum • Thirdventricle – Surroundsthalamusdiencephalonandbrainstem • Fourthventricle – Anteriortocerebellum – Contains3aperturesleadingtothe“subarachnoid space” v Cerebralaqueduct – Canalbetweenthirdandfourthventricle VentriclesoftheBrain CerebrospinalFluid(CNS) • Ventricleslinedwith choroidplexus – Ependymalcells – Producecerebrospinalfluid (CSF) – Produces500ml/day – 150mLincirculation • Surroundsandbathes exposedsurfacesoftheCNS – Preventsfriction – Support – Regulationof microenvironment CirculationofCSF • CSFcirculates throughout ventricles, subarachnoidspace andcentralcanal • CSFisreturnedto generalcirculation – Arachnoid granulations – Projectintothe duralsinus CirculationofCSF TheCranialMeninges CranialMeninges DuraMater • “Toughmother” – Denseirregular connectivetissue – Outermostmeninge • outer=periosteallayer • inner=meningeallayer – “falxcerebri” – 2layersformaspace betweenwhicharethe duralsinuses CranialMeninges ArachnoidandPiaMater • “Spiderymother” • Arachnoidgranulations – forreturnofCSFto generalcirculation • “Delicatemother” • Indissectablefrom surfaceofthebrain • Looseconnectivetissue FalxCerebri Falx cerebri is formed as an extension of the meningeal layer of the dura mater BloodVesselsoftheBrain Jugularveins Draintheduralsinuses Internalcarotidarteries Vertebralarteries MajorDivisionsoftheBrain Cerebrum • Cerebralhemispheres – Leftandrighthalves – Separatedbylongitudinal fissure – Connectedbytracts • Dividedintofunctional lobes • Contain“higherbrain centers” – Nucleiresponsibleformotor coordinationandcontrolof memory,emotionandother functions CerebralCortex • GrayMatter • Gyrus(gyrip.) – foldsofthecerebral surface • Sulcus(sulcip.) – groovesbetweengyri • Fissure – deepgroove TheCerebralLobes • 5majordivisionsin eachhemisphere • 4namedafterbones underwhichtheylie – – – – Frontal Parietal Occipital Temporal • 1oninterior – Insula FrontalLobe • • Amotorcortex Pre-centralgyrusiswherethe primarymotorcortexislocated – Controlsvoluntarymovements • Alsomadeupofmostly Dopaminesensitiveneurons – – – – – • Shorttermmemory Reward Learning Emotions Motivation Majormotorpathwayisthe corticospinaltract ParietalLobe • SensoryCortex • Thepostcentralgyrusis wherethesomatosensorycortexis located – Involvedinintegrating sensoryinformation • Skin • Proprioception • Languageprocessing OccipitalLobe • Mapsmostlytothe occipitalbone • Isthevisualcortex – Receives,integratesand processesvisual information – Clinicallyreferredtoas Brodmannarea17 TemporalLobe • Auditorycortex • Processesvisual informationinto memories • Language comprehension • Emotionassociations • Declarative(long-term) memory – Factsandevents Insula • Smalllobesdeepin lateralsulcusbeneath temporallobes • Involvedin consciousness – Emotion,homeostasis, selfawareness,cognitive functioning • Gustatorycortex New study suggests that the insula is involved in smoking addiction… CerebralMedulla • Myelinatedaxons=whitematter • Arrangedintotractsconnectingdifferentpartsof theCNS • Associationtracts – Connectregionsofcortexwithinsamehemisphere • Commissuraltracts – Bridgesbetweencerebralhemispheres – Ex)corpuscallosum • Projectiontracts – Betweencerebralcortex,caudalbrain,andspinalcord CerebralWhiteMatter BasalNuclei • Paired,irregularmasses ofgraymatter • Connectedto cerebrum,thalamus, brainstem • Involvedin – Motorprograms – Procedurallearning – Routinebehaviorsor habits – Eyemovements – Emotion LimbicSystem • Largegroupofnucleithroughoutdifferent partsofthebrain • Responsibleforcontrolof – Emotion – Sexdrive – Aggression – Memoryconsolidation...amongotherfunctions • Hippocampus – Responsibleformemoryconsolidation LimbicSystem Diencephalon • “in-between” brain • Components – Epithalamus – Thalamus • PairedR/L – Hypothalamus Epithalamus • Connectsthelimbic systemtootherpartsof thebrain • Covers3rd ventricle • Posteriorportion – Pinealgland • Melatonin • Circadianrhythms – Habenularnucleus • Relaystationforlimbic system • Visceralandemotional responsetoodors Thalamus • Clustersofnuclei organizedinto groups • Majorrelaystation forsensory information • Graymatteronboth sidesofthird ventricle Hypothalamus • Containsmanydiverse nucleicontrolling – – – – – – Bodytemperature Sexdrive Feeding Drinking Thirstsensation Pituitarysecretions • Formstheinferiorwalls ofthethirdventricle BrainStem • Connectsforebrain (cerebrum, diencephalon)and cerebellumtospinal cord • 3parts – Midbrain – Pons – Medullaoblongata Midbrain • CorporaQuadrigemina – Superiorcolliculus – Inferiorcolliculus • Cerebralpeduncles • Nucleiinvolvedin: vision,hearing sleep/wakecycles Alertness Bodytemperature regulation – Motorprograms – – – – Pons • Containssensoryandmotor tracts • Relaysignalsfromcerebrum anddiencephalontothe cerebellum • Autonomicnuclei – Sleep,respiration, swallowing,bladdercontrol, hearing,equilibrium,taste, eyemovement,facial expressions,facialsensation andposture – Playsaroleindreaming • Originforcranialnerves V-VIII MedullaOblongata • Theinferiormostregion ofthebrainstem • Autonomiccenters – Respiration,vomiting, sneezing,cardiovascular functions • Medullarypyramids housethepyramidal tracts – Decussationofthe pyramids • Origincranialnerves IX-XII TheCerebellum • Secondlargestsingle structureofthebrain • Threelobes • Arborvitae – “thetreeoflife” – Whitematterofthe cerebellum • Folia • Involvedinmotorcontrolof coordination,timingand precisionofskeletalmuscle activity HistologyoftheCerebellum • Whitematter(medulla) – Myelinatednervefibers • Graymatter(cortex) – Granularlayer • Granulecells – Smallestneuronsandmost numerousneuronsinthe brain – Purkinjelayer • Purkinjecells – Processesformthe dendritrictreeofthe molecularlayer – >200synapses – Molecularlayer • Dendritictree