* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 9-2_DescPathwaysBS_BusF
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
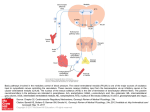
Bús Flóra EMK0EA Organization rules of the brain stem: descending neuronal pathways Brain stem has structurally 3 parts: Mesencephalon, Pons, Medulla oblongata. First of all, important somatic and autonomic centers are located in there, and the processing centers of the cranial nerves are also. Moreover, it’s a functionally significant system because the reticular formation controlling vital respitatory and circulatory mechanism and arousal, is also part of the brain stem. Furthermore, major motor and sensory projections pass through the brain stem. I categorized the descending neuronal pathways into 3 groups: 1. Descending neural pathways originating from the brain stem 1. tractus tectospinalis: originates from the colliculus superior of the mesencephalon. Controls the movement of the head. 2. tractus vestibulospinalis: it arises from the lateral vestibular nucleus (pons), it mediates cerebellar and vestibular information toward the spinal cord. Exerts facilitatory influance on spinal reflexes and controls muscle tone. 3. tractus rubrospinalis: originates from the red nucleus of the brain stem (mesencephalon) and terminates on ventral horn interneurons. It conveys information from the cortex and cerebellum mainly to motor neurons innervating flexor and extensor muscles. 4. tractus reticulospinalis: carries information from the reticular formation to the dorsal and ventral horns. Controls voluntary movements, muscle tone, central sensory transmission. Regulates respitatory and circulatory activities. 5. fasciulus longitudinalis medialis: originates from the caudal part part of the brain stem. Carries information from secondary vestibular neurons to cervical segments. Controls the movement of the head, commands for eye movement. 2. Descending neuronal pathways through the brain stem: tractus corticospinalis: it has motor function: face muscles and voluntary movements a. Tractus corticospinalis cruciatus: originates from the cerebral cortex, runs through the internal capsule, crossed in the medulla oblongata and terminates on interneurons of the ventral horn that are associated with motoneurons. The main regulatory tract of lower motoneurons. b. tractus corticospinalis directus: crossing at level of target segment. Carries motor commands to neurons. Originates from the cerebral cortex and terminates in the intermediate zone of the grey matter. 3. Descending Neuronal pathways terminating in the brain stem: 1. tractus corticorubralis: originates from the cerebral cortex terminates in the red nucleus of the mesencephalon 2. tractus corticopontinus: orignates from the cerebral cortex, descend in the internal capsule and terminate in the nuclei pontis of the pons. 3. fasciulus tegmentalis centralis: originates from the thalamus or from the red nucleus and terminates in the olivia inferior of the medulla oblongata. 4. tractus corticobulbaris,tractus corticomesencephalicus: The corticobulbar tract is one of the pyramidal tracts, it’s carrying the motor function of the non-oculomotor cranial nerves. 5. fasiculus longitudinalis dorsalis: originates from the hypothalamus and terminates in the reticular formation.