* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous system - Morgan Park High School
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
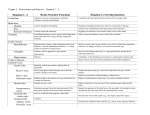
1 Nervous system Central nervous system o The spinal cord o Brain Forebrain Is the largest and most complex of the three major sections of the brain. It encompasses the thalamus, the hypothalamus, the hippocampus, the amygdala, the basal ganglia, corpus callosum, and the cortex. Thalamus; sends information to other parts of the brain; sensory information gets processed through this part. Hypothalamus; below the thalamus and affects eating, drinking, sexual activity Hippocampus; is involved in learning, memory, navigating, and emotional functions Amygdala; controls emotional behavior, attack responses, and fear Basal ganglia; to the left and right of the thalamus, controls movement and posture, speaks to the cerebellum and to other higher brain centers o Caudate nucleus; a basal ganglion in the lateral ventricle of the brain that assist with motor functions. Corpus callosum; conveys information between the two hemispheres, damage resorts in split brain living Cortex (cerebral cortex) ; exterior covering of the cortex, outer fleshy part of the brain, (convolutions- folds in the tissue of the cerebral hemispheres and the overlying cortex.) 2 o Glial cells – glue cells that guide neural connections, provide nutrients, and insulate myelin, and mop up ions and neurotransmitters; neural nannies. o Cingulated gyrus; receives input from the thalamus, somatosensory areas (skin sensation), neocortex (language), and helps regulate an integral part of the limbic system, which is involved with emotion formation and processing, learning, and memory. o Lateral fissure – divides temporal from parietal lobe o Central fissure – divides frontal lobe and parietal lobe Limbic system; the cortex, the thalamus, hypothalamus, located deep within the temporal lobe and influencing emotions, memory, social behavior, and brain disorders such as epilepsy. Pituitary glands; secretes growth hormones, controls metabolism, and maturation Midbrain Houses the motor cortex and the sensory cortex Part of the brain governs temperature, reflex, smoothness of movement Regulates physiological processes, respiration, blood pressure, heart rate and wake-sleep cycles. It is a relay station for motor and sensory messages between parts of the brain and spinal cord Hindbrain Consist of the cerebellum, medulla, the reticular formation, and the pons Cerebellum ( little brain); influences balance, coordination, and movement Medulla; controls heart rate and breathing and is located just above the spinal cord Reticular formation; controls state of arousal, waking, sleeping, as well as responsive bodily functions 3 Pons; located just superior to the medulla and inferior to the midbrain, function as a relay station for the motor and sensory pathways, as well as it regulates breathing. o The cortex and the lobes of the brain Frontal lobe In front of the central fissure; contains the motor cortex and broca’s area Controls memory, movement, speech and language production Initiates motor activity, regulates skilled motor functions and controls the movement of the tongue leading to speech It interprets sensory information from the skin (touch), optic nerves (vision), cochlea (hearing), olfactory tract (smell), and tongue (taste) Controls elaboration of thought and emotions and stores memory Parietal lobe Behind the frontal lobe Sense of touch and body position Basic general sensation Angular gyrus; region of the inferior parietal lobe and close to the temporal lobe which is involved in the processing of auditory and visual input and in the comprehension of language Wernicke’s area; region of the parietal and temporal lobe incolved in the understanding and formulating coherent, propositional speech. Temporal lobe 4 Below lateral fissure and parietal lobe Controls speech, hearing, and some visual information processing Occipital lobe Back of brain, next to and behind parietal and temporal lobe Visual sense Association cortex Areas between parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes Believed to be responsible for complex behaviors that involve thinking and sensory processes Peripheral nervous system o The linkage system of sensory and motor neurons that connect the CNS to the rest of the body o Two components – somatic and autonomic system Somatic The division that controls the body’s skeletal muscle structure Autonomic The division that controls the glands and muscles of the internal organs Two components – sympathetic and parasympathetic Parasympathetic - keeps the body clam and running smoothly. o Pupil is constricted o Slow normal heart beat o Digestion stimulated 5 o Breathing normal o Gallbladder stimulated – bile production o Bladder is normal – urination normal o Sex organs stimulated Sympathetic – keeps the body aroused; fight or flight o Pupil dilates – get bigger; take in more light o Accelerated heart beat o Digestion inhibited o Breathing rapidly o Simulates release of glucose from liver o Adrenaline released; epinephrine and norepinephrine – kidney o Bladder relaxes o Inhibits sexual stimulation Nerves system The cable system that connect the central nervous system with muscles, glands, and sense organs Types of neurons o Motor – Efferon nerves o Sensory – Affereon nerves o Interneurons – communicates between the two, the motor and sensory. What if injuries; you be the doctor 6