* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neuroanatomy - Kelley Kline
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
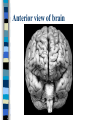
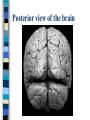
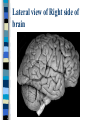
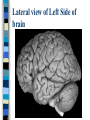
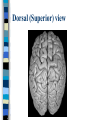
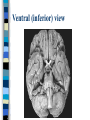
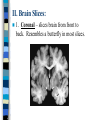
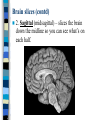
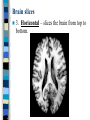
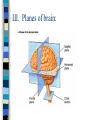
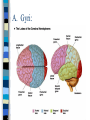
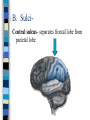
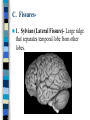
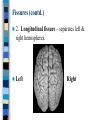
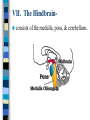
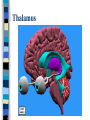
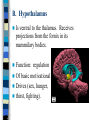
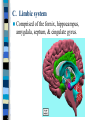
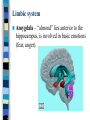
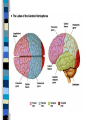
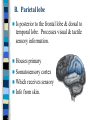
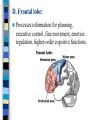
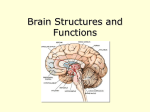
Neuroanatomy The Human Brain I. Directional Terms Dorsal- “toward the back.” Ventral- “towards the stomach or bottom.” Anterior – “towards the front.” Posterior- “towards the rear or back.” Terms contd. Rostral – “towards front nostrils.” Caudal- “towards the tail.” Superior- “top of head” Inferior- “bottom of head” Lateral – “to the side” Medial – “to the middle” Ipsilateral – “same side” Contralateral – “opposite side” Anterior view of brain Posterior view of the brain Lateral view of Right side of brain Lateral view of Left Side of brain Dorsal (Superior) view Ventral (inferior) view II. Brain Slices: 1. Coronal – slices brain from front to back. Resembles a butterfly in most slices. Brain slices (contd) 2. Sagittal (midsagittal) – slices the brain down the midline so you can see what’s on each half. Brain slices 3. Horizontal – slices the brain from top to bottom. III. Planes of brain: IV. Cortical Landmarks 1. Gyrus (gyri) – bulges on the brain’s surface. 2. Sulcus (sulci) – a small ridge in the cortex. 3. Fissure (s) – a large ridge in the cortex. A. Gyri: B. SulciCentral sulcus- separates frontal lobe from parietal lobe. C. Fissures 1. Sylvian (Lateral Fissure)- Large ridge that separates temporal lobe from other lobes. Fissures (contd.) 2. Longitudinal fissure – separates left & right hemispheres. Left Right V. CNS & PNS terms Nuclei – cell bodies in the CNS. Ganglion – cell bodies in the PNS Tracts – Axon bundles in the CNS Nerves – Axon bundles in the PNS Terms contd. White matter –composed of axon bundles. Is white because of the myelin sheaths (white fatty tissue) that cover the axons. Gray matter – composed of clusters of cell bodies, have dark gray appearance from cell body structures. VI. Three Divisions of the Brain 1. Hindbrain – oldest part of brain, governs basic functions (breathing, regulates heart beat). 2. Midbrain – involved in some perceptual & motor functions. 3. Forebrain – governs all higher-order level functions (problem solving, planning, emotion regulation, language). VII. The Hindbrain consists of the medulla, pons, & cerebellum. A. Medulla (oblongata): a structure just above spinal cord. Controls & regulates vital reflexes for survival (respiration, HR, vomiting, salivation, coughing, & sneezing). Damage to the Medulla is almost always fatal. B. Pons: An enlarged protrusion anterior to the medulla. Both pons & medulla form reticular formation & raphe system. Plays a role in arousal & dreaming. C. Cerebellum: (means little brain) Large hindbrain structure that is posterior to the brainstem. Governs motor functions, motor memory. VIII. The Midbrain Most obvious feature is the tectum (“roof”). Two pairs of bumps on tectum: Superior colliculi (vision) Inferior colliculi (audition) Substantia nigra—part of basal ganglia, involved in movement (Parkinson’s disease). IX. The Forebrain Consists of subcortical and cortical structures. 1. Subcortical structures include the thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system, & basal ganglia. A. Thalamus A large two-lobed structure that sits on top of the brainstem. Is brain’s sensory relay station. Several nuclei receive sensory input & send that input to parts of the cortex. Nuclei: Lateral geniculate nuceli (visual), medial geniculate nuceli (auditory) & ventral posterior nuclei (somatosensory) Thalamus B. Hypothalamus Is ventral to the thalamus. Receives projections from the fornix in its mammilary bodies. Function: regulation Of basic motivational Drives (sex, hunger, thirst, fighting). C. Limbic system Comprised of the fornix, hippocampus, amygdala, septum, & cingulate gyrus. Limbic system Fornix (“arch”) is the major pathway of the limbic system; projects in an arc from the hippocampus into mammilary bodies of the hypothalamus. Hippocampus “seahorse” is the structure that lies in between the cortex & thalamus, rests in the temporal lobe; plays a large role in LTM storage. Limbic system Amygdala – “almond” lies anterior to the hippocampus, is involved in basic emotions (fear, anger). 2. Cortical structures Lobes of the brain A. Occipital lobe Most posterior portion of brain. Processes visual sensory information. Houses primary visual cortex (striate cortex). Damage to PVC can cause “cortical blindness.” B. Parietal lobe Is posterior to the frontal lobe & dorsal to temporal lobe. Processes visual & tactile sensory information. Houses primary Somatosensory cortex Which receives sensory Info from skin. C. Temporal lobe Processes auditory and visual information. Houses primary auditory cortex—the primary projection site for auditory stimuli. Language, face recognition, & processing of sounds Occurs here. D. Frontal lobe: Processes information for planning, executive control, fine movement, emotion regulation, higher-order cognitive functions.