* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Nervous System
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
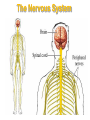
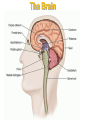
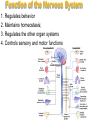
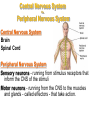
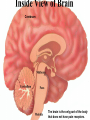
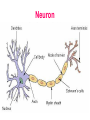
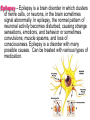
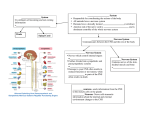
The Nervous System The Brain Function of the Nervous System 1. Regulates behavior 2. Maintains homeostasis; 3. Regulates the other organ systems 4. Controls sensory and motor functions Central Nervous System Vs. Peripheral Nervous System Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System Sensory neurons - running from stimulus receptors that inform the CNS of the stimuli Motor neurons - running from the CNS to the muscles and glands - called effectors - that take action. Major Parts of the Brain Cerebrum – controls conscious activities, intelligence, memory, language, skeletal muscle movements, and senses Cerebellum – controls balance, posture and coordination Brainstem - Medulla oblongata, pons and midbrain – controls involuntary activities such as breathing and heart rate. Cerebrum The brain is the only part of the body that does not have pain receptors. Parts and Function of a Nerve Cell Cell Body (soma) - contains nucleus Dendrites - branch-like extensions that receive impulses and carry them to the cell body Axon - extension of the neuron – carries impulses away from the cell body and towards other neurons AxonTerminals - connects to muscle, gland or another neuron, releases a chemical message (neurotransmitter) Neuron Diseases of the Nervous System Cerebral Palsy – caused by abnormalities in parts of the brain that control muscle movements. The early signs of cerebral palsy usually appear before a child reaches 3 years of age. Most common symptoms are a lack of muscle coordination when performing voluntary movements (ataxia); stiff or tight muscles and exaggerated reflexes (spasticity); walking with one foot or leg dragging; walking on the toes, a crouched gait, or a “scissored” gait; and muscle tone that is either too stiff or too floppy. Cerebral palsy can’t be cured, but treatment will often improve a child's capabilities. Epilepsy – Epilepsy is a brain disorder in which clusters of nerve cells, or neurons, in the brain sometimes signal abnormally. In epilepsy, the normal pattern of neuronal activity becomes disturbed, causing strange sensations, emotions, and behavior or sometimes convulsions, muscle spasms, and loss of consciousness. Epilepsy is a disorder with many possible causes. Can be treated with various types of medication. Parkinson’s Disease – affects nerve cells, or neurons, in a part of the brain that controls muscle movement. Neurons that make a chemical called dopamine die or do not work properly. Dopamine normally sends signals that help coordinate your movements. No one knows what damages these cells. Symptoms of Parkinson's disease may include; Trembling of hands, arms, legs, jaw and face, stiffness of the arms, legs and trunk, slowness of movement, poor balance and coordination. As symptoms get worse, people with the disease may have trouble walking, talking or doing simple tasks. They may also have problems such as depression, sleep problems or trouble chewing, swallowing or speaking.