* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Nervous System
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
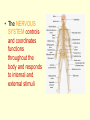
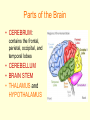
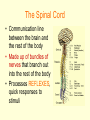
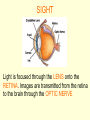
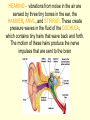
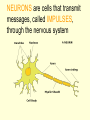
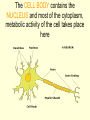
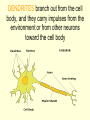
The Nervous System • The NERVOUS SYSTEM controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external stimuli The Nervous System can be broken into two parts: • The CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: composed of the brain and the spinal cord • The PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: composed of all the nerves that aren’t part of the brain or spinal cord Central Nervous System • The skull and vertebral column protect the brain and spinal cord • The brain and spinal cord are protected in three layers of tissue called MENINGES • The space between the meninges and the brain and spinal cord is filled with CEREBROSPINAL FLUID, which acts as a shock absorber and helps protect the central nervous system. Parts of the Brain • CEREBRUM: contains the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes • CEREBELLUM • BRAIN STEM • THALAMUS and HYPOTHALAMUS The Cerebrum • Folds in the Cerebrum increase the surface area of the brain • Responsible for voluntary actions, intelligence, learning, and judgment • Divided into two hemispheres, left and right • Outer Layer – Gray matter composed of nerve cell bodies • Inner Layer – White matter composed of bundles of axons with myelin sheaths The Cerebellum: • Second largest region of the brain • Located in the back of the skull • Responsible for balance and muscle coordination The Brain Stem: • Connects the brain to the spinal cord • Regulates the flow of information from the brain to the rest of the body • Controls basic life functions, such as heartbeat, breathing, swallowing, etc Thalamus and Hypothalamus • Located between the brain stem and the cerebellum • The THALAMUS receives signals from the body and sends them to the cerebrum to be processed • The HYPOTHALAMUS recognizes and analyzes hunger, thirst, fatigue, anger, and body temperature. The Spinal Cord • Communication line between the brain and the rest of the body • Made up of bundles of nerves that branch out into the rest of the body • Processes REFLEXES, quick responses to stimuli Peripheral Nervous System • SENSORY DIVISION transmits impulses from the sense organs to the brain • MOTOR DIVISION transmits impulses from the brain to the muscles or glands Peripheral Nervous System • SOMATIC – regulates voluntary impulses • AUTONOMIC regulates the involuntary body functions SIGHT Light is focused through the LENS onto the RETINA. Images are transmitted from the retina to the brain through the OPTIC NERVE HEARING – vibrations from noise in the air are sensed by three tiny bones in the ear, the HAMMER, ANVIL, and STIRRUP. These create pressure waves in the fluid of the COCHLEA, which contains tiny hairs that wave back and forth. The motion of these hairs produce the nerve impulses that are sent to the brain SMELL • SCENT is the detecting of trace amounts of chemicals • CHEMORECEPTORS in the lining of the nasal passages detect these chemicals and send an impulse to the brain • Smell is closely tied to memory and feeling, and can generate responses in people almost immediately Taste • Taste is closely related to smell, and taste is the detection of chemicals by chemoreceptors on the tongue • Tastes are classified as bitter, sour, salty, and sweet • The human mouth has over 10,000 taste buds, even on the roof! TOUCH • Nerve endings in the skin respond to temperature, touch and pain • The areas that are most sensitive to touch have the highest concentration of nerve endings: the feet, hands, and face How are messages moved in the nervous system? NEURONS are cells that transmit messages, called IMPULSES, through the nervous system The CELL BODY contains the NUCLEUS and most of the cytoplasm, metabolic activity of the cell takes place here DENDRITES branch out from the cell body, and they carry impulses from the environment or from other neurons toward the cell body The AXON carries impulses away from the cell body. The axon is covered in a membrane called the MYELIN SHEATH. There are gaps in the myelin sheath, called NODES. The signal can jump from node to node, increasing the speed of the impulse. • http://animations.3d4medical.com/Nerveimpulse-animation_AN2162.html A RESTING NEURON is one that is not transmitting an impulse. A neuron can transfer a signal to another cell at locations called SYNAPSES. At the synapse, chemicals called NEUROTRANSMITTERS are released, which sends the impulse to receptors in an adjacent cell.