* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Histology Laboratories Molecules to Systems
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
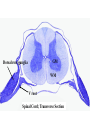
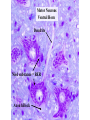
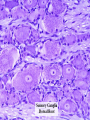
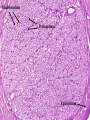
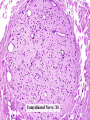
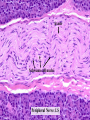
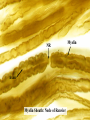
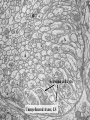
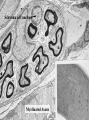
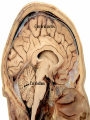
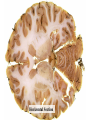
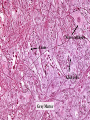
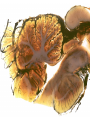
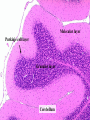
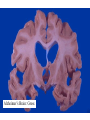
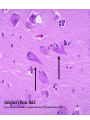
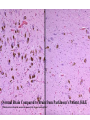
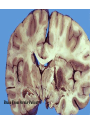
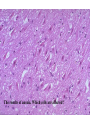
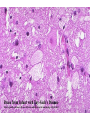
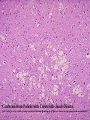
Histology Laboratories Molecules to Systems 2003 Compiled by James D. Jamieson, MD/PhD Thomas L. Lentz, MD No part of this image collection may be distributed outside of the Yale University Intranet. Acknowledgements Sources of Micrographs, Diagrams and Figures Alberts, B. et al. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4th Edition, Garland Science, New York, 2002. Gartner, L. P. and Hiatt, J. L. Color Atlas of Histology, Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, 1994. Kerr, J. B. Atlas of Functional Histology. Mosby, London, 1999. Kessel, R. G. and Kardon, R. H. Tissues and Organs: a text-atlas of scanning electron microscopy. W. H. Freeman, San Francisco, 1979. Lentz, T. L. Cell Fine Structure. W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia, 1971. Lodish, H. et al. Molecular Cell Biology. W. H. Freeman, New York, 2000. Mizoguti, H. Color Slide Atlas of Histology. Nihon Shashin Shinbunsha, Tokyo. Young, B. and Heath, J. W. Wheater’s Functional Histology. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, 2000. Micrographs taken by George Palade, Marilyn Farquhar, James D. Jamieson, Nicolai Simionescu, Maya Simionescu, David Castle, Thomas L. Lentz. Web Resources http://info.med.yale.edu/webpath/webpath.htm Cushing Library Educational Software/Cell Biology/Several Histology Resources Nervous System Laboratory Spinal Cord GM Dorsal root ganglia WM V root Spinal Cord; Transverse Section Motor Neurons Ventral Horn Dendrite Nissl substance = RER Axon hillock Sensory Ganglia Dorsal Root Peripheral Nerves Endoneurium Perineurium Epineurium Myelinated Nerve: XS Epineurium Unmyelinated Nerve: XS Axons Schwann cell nuclei Peripheral Nerve: LS NR Axon Myelin Sheath: Node of Ranvier Myelin A A Schwann cell cyto. Unmyelinated Axon; LS Schwann cell nucleus A A Myelinated Axons Cerebral Cortex Cerebral cortex Cerebellum Horizontal Section GM WM Cerebral Cortex Nerve cell body Axons Glial cells Grey Matter Astrocytes Neuroglia Cerebellum Molecular layer Purkinje cell layer Granular layer Cerebellum Cerebellum: Purkinje Cells ML Dendrites PC GL Some pathology to think about. Alzheimer’s Brain: Gross Alzheimer’s Brain, H&E Do you see anything different in the cytoplasm of the neurons? What might this do to them? Normal Brain Compared to Brain from Parkinson’s Patient, H&E Which section is from the normal brain and why do you conclude this? Brain From Stroke Patient Section from Brain of Stroke victim The results of anoxia. Which cells are affected? Brain from Infant with Tay-Sach’s Disease What organelles in these cells are defective and how does the morphology reflect this? Cerebrum from Patient with Creutzfeldt-Jacob Disease. Note “holes” in cortex resulting from prion amyloid deposits. Human form of “mad cow disease: bovine spongioform encephalopathy”.