* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrophysiological Methods for Mapping Brain Motor and Sensory
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Electromyography wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain–computer interface wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neurocomputational speech processing wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Transcranial direct-current stimulation wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Muscle memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Motor cortex wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
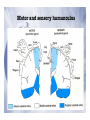
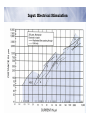
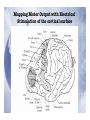
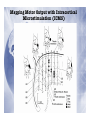
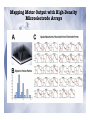
Electrophysiological Methods for Mapping Brain Motor and Sensory Circuits RADI 6017 Oct 27th, 2010 Historical Perspective • Periphery mapped to central brain regions • Motor and Sensory maps: • Localization of function • Way the brain is organized • How does the brain work? Maps of Motor Cortex by Electrical Stimulation Fritsch and Hitzig (1870) : Dog cortex orderly and specific peripheral movements Ferrier (1876, 1886): Rhesus monkey and dogs Motor and sensory humunculus Methods of Brain Stimulation Direct Electrical Stimulation • surface electrodes • Deep needle electrodes • Single-unit microelectrode Transcranial • Electrical stimulation (TES): Merton and Morton, 1980 • Magnetic Stimulation (TMS): Barker et al, 1987 Structural vs. Functional Brain maps Structural maps • Neural hardware/anatomical connectivity • By electrical stimulation of neurons and pathways • Stimulate at one site and record at a remote site • Output variables: • Intracellular potentials • Field potentials • Extracellular unit potentials • Electromyography (EMG) Functional maps: • Spatial representation of a natural parameter • Localization of natural stimuli (sensory) and movements (motor) Strengths of Electrophysiological mapping Advantages • Spatial resolution: at the level of single neuron • Construct more global mapping • Temporal resolution: milliseconds Disadvantages • invasive • Time and labor intensive • Limited to primary motor and sensory (somatosensory, auditory and visual) areas Microelectrodes • Sharpened rods of tungsten, platinum/iridium • Insulated with glass, epoxy • Uninsulated tip of 5-12µA • Low impedance: 0.7 – 1.5 MΩ Sensory vs. Motor Mapping Sensory Maps • Mapping a specific sensory parameter to a brain region • One input variable: Stimulus • One output measure: unit recording from region of interest • One anatomical map and one functional map • Receptive fields: naturally occurring stimulus modality to which the neuron is most responsive Sensory vs. Motor Mapping Motor Maps • Several input and output measures • Harder than sensory mapping • Activation of muscles in isolation is difficult • Motor fields: all movements that engage a neuron • Functional (type of movement) • Structural (target muscles) • Neuroantomic labeling • TMS Topographical organization of pathways from somatosensory cortex, pontine nuclei, and cerebellar hemispheres Leergaard et al., European Journal of Neuroscience, Vol. 24, pp. 2801–2812, 2006 ★ ★ (active and passive) Input Measures: Electrical stimulation Common method in motor mapping Magnitude of response depends on: • Stimulus current • Stimulus duration • Stimulus polarity • Electrode dimensions Extent of effective current spread from a stimulating electrode I = a + kd2 Input: Electrical Stimulation Transcranial Stimulation TES TMS Mapping Motor Output with Electrical Stimulation of the cortical surface# Mapping Motor Output with Intracortical Microstimulation (ICMS)# Mapping Motor Output with High-Density Microelectrode Arrays# Mapping Motor Output: Other Methods Spike triggered averaging of EMG activity from single neurons Stimulus triggered averaging of EMG activity (single pulse ICMS) 500 pulses 14,000 triggers 40x10 pulses