* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download This course is mainly motor control. There are only two labs. Oct 2nd
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Resilient control systems wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Control theory wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
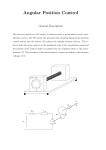
This course is mainly motor control. There are only two labs. Oct 2nd, and Oct 23rd. Test on Oct 30th Final November 20th Motor Control ‐ Usually one of several standard nominal system voltages. eg. 120/240 3‐Wire. 208/120, 460/277 "Y" 240, 480, 600 V ‐ Maximum current is set by the wire size. ‐ Fuse or breaker limits the current. ‐ Other Courses go more into detail on this. Starting: ‐ Only copper resistance limits current in a stationary motor. ‐ Power must be added in a controlled way to protect the system. ‐ Other courses go more into detail on this. Speed Control: ‐ It is not always needed. ‐ Many times motors run at a specific speed at all times. ‐ If control is needed, it is different between AC voltage and DC voltages. ‐ General speaking, DC systems vary the voltage, and AC systems vary the frequency. ‐ This is not feedback. ‐ Covered in this course. Motor: ‐ The motor reacts to electrical energy (Voltage & Current) by producing mechanica; energy (torque on turning shaft) ‐ There are relationships between electrical values and mechanical values. ‐ Covered in this course. Speed measurement/feedback: ‐ If load varies, and speed must be fixed, feedback is used to smooth operations. ‐ No details in this course. Serial Communications ‐ RS232 ‐ USB ‐ Mostly a theory course. ‐ Practical hook up in other courses.