* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 080916_Class_01
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Resilient control systems wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Control theory wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
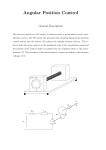
This course is mainly motor control. There are only two labs. Oct 2nd, and Oct 23rd. Test on Oct 30th Final November 20th Motor Control - Usually one of several standard nominal system voltages. eg. 120/240 3-Wire. 208/120, 460/277 "Y" 240, 480, 600 V - Maximum current is set by the wire size. - Fuse or breaker limits the current. - Other Courses go more into detail on this. Starting: - Only copper resistance limits current in a stationary motor. - Power must be added in a controlled way to protect the system. - Other courses go more into detail on this. Speed Control: - It is not always needed. - Many times motors run at a specific speed at all times. - If control is needed, it is different between AC voltage and DC voltages. - General speaking, DC systems vary the voltage, and AC systems vary the frequency. - This is not feedback. - Covered in this course. Motor: - The motor reacts to electrical energy (Voltage & Current) by producing mechanica; energy (torque on turning shaft) - There are relationships between electrical values and mechanical values. - Covered in this course. Speed measurement/feedback: - If load varies, and speed must be fixed, feedback is used to smooth operations. - No details in this course. Serial Communications - RS232 - USB - Mostly a theory course. - Practical hook up in other courses.