* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neurotransmitters
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Vesicular monoamine transporter wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
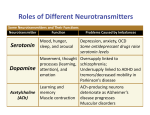
SECTION 29 Neurotransmitters The Neurochemical Basis of Human Behavior • Neurotransmitters are chemicals that relay and modulate messages between neurons. • Much of human behavior is mediated by the action of neurotransmitters in the brain. Researchers are also demonstrating that behavioral pathology is largely due to imbalances in one or more neurotransmitter systems. Physical diseases may also be due to specific neurotransmitter pathway disturbances (eg, Parkinson disease). • Neurotransmitters are chemicals that are stored in and released from the terminal boutons of neurons; they are released into the synaptic cleft. • Once in the synaptic cleft, neurotransmitters can be destroyed by enzymatic degraders, chemical substances that break down a neurotransmitter so that the postsynaptic neuron can repolarize in order to fire again. • Neurotransmitters can also be reabsorbed by the presynaptic terminal boutons in a process called reuptake. • Sometimes there is a decrease in the number of receptors for a neurotransmitter on the postsynaptic neuron due to long-term exposure to the neurotransmitter. This is called downregulation. • Neurotransmitters can be classified into 4 major groups: 1. Amino acids (eg, glutamate, gamma-aminobutyric acid [GABA], aspartic acid, glycine) 2. Peptides (eg, vasopressin, somatostatin) 3. Monoamines (norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin) 4. Acetylcholine (ACh) • There are multiple neurotransmitter systems in the brain (and in the enteric nervous system). • In the peripheral nervous system (PNS), only 2 neurotransmitters are used: ACh and norepinephrine. • Neurotransmitters can be excitatory or inhibitory, depending on which receptor sites they bind to. They work like the brain’s brake and accelerator systems.1-3 MAJOR NEUROTRANSMITTERS ABOUT WHICH INFORMATION IS KNOWN • • • • • • • • • ACh Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) Glutamate (GLU) Dopamine (DA) Serotonin (5-HT) Norepinephrine (NE) Substance P Endorphins Histamine 338 Gutman SA. Quick Reference Neuroscience for Rehabilitation Professionals: The Essential Neurologic Principles Underlying Rehabilitation Practice, Third Edition (pp 338-352). © 2017 SLACK Incorporated.