* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Roles of Different Neurotransmitters
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Serotonin syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Norepinephrine wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
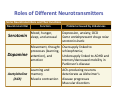
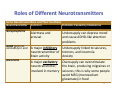
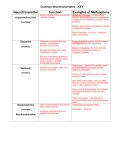
Roles of Different Neurotransmitters Some Neurotransmitters and Their Functions Neurotransmitter Function Mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal Problems Caused by Imbalances Depression, anxiety, OCD Serotonin Some antidepressant drugs raise serotonin levels Movement, thought Oversupply linked to processes (learning, schizophrenia; Dopamine attention), and Undersupply linked to ADHD and emotion tremors/decreased mobility in Parkinson’s disease Learning and ACh‐producing neurons Acetylcholine memory deteriorate as Alzheimer’s (ACh) Muscle contraction disease progresses Muscular disorders Roles of Different Neurotransmitters Some Neurotransmitters and Their Functions Neurotransmitter Function Problems Caused by Imbalances Norepinephrine Alertness and arousal GABA (gamma‐ aminobutyric acid A major inhibitory Undersupply linked to seizures, neurotransmitter of tremors, and insomnia brain activity Anxiety Glutamate A major excitatory Oversupply can overstimulate neurotransmitter; the brain, producing migraines or involved in memory seizures; this is why some people avoid MSG (monosodium glutamate) in food Undersupply can depress mood and cause ADHD‐like attention problems 13 Drug Effects on the Nervous System Add to your notes… • Psychoactive drugs have inhibitory or excitatory effects on the nervous system • Agonists are drugs that mimic the effect of the neurotransmitter • Antagonists are drugs that inhibit the effect of the neurotransmitter • Prozac is an antidepressant drug that works as an agonist of serotonin • Many psychoactive drugs have side effects because the drug of choice may work on different neural pathways. For example, Prozac treats depression, but can alter sleep, eating patterns, and other thought processes 14