HardasNails-Marianco
... it in one of my weight gainer shakes, i get tired after! what could this mean and how do you test for insulin insensitivity or whatever the condition is called? glucose resistance? To test for insulin resistance, a person does the 3-hour glucose tolerance test. This test has a person fast for 12 hou ...
... it in one of my weight gainer shakes, i get tired after! what could this mean and how do you test for insulin insensitivity or whatever the condition is called? glucose resistance? To test for insulin resistance, a person does the 3-hour glucose tolerance test. This test has a person fast for 12 hou ...
Amphetamine Paradoxically Augments Exocytotic Dopamine Release and Phasic Dopamine Signals
... release events associated with learning and goal-directed behavior. One prominent exception to this notion would appear to be amphetamine (AMPH) and related analogs, which are proposed instead to disrupt normal patterns of dopamine neurotransmission by depleting vesicular stores and promoting nonexo ...
... release events associated with learning and goal-directed behavior. One prominent exception to this notion would appear to be amphetamine (AMPH) and related analogs, which are proposed instead to disrupt normal patterns of dopamine neurotransmission by depleting vesicular stores and promoting nonexo ...
A Literature Review on the Status and Effects of Salvia Divinorum on
... divinorum produces powerful hallucinogenic effects when the leaves are chewed, orally consumed in a liquid state, or dried and smoked. It’s active ingredient is Salvinorin-A (Roth et al., 2002; Siebert, 1994), a highly selective kappa (κ)-opioid receptor agonist (Roth et al., 2002), that researchers ...
... divinorum produces powerful hallucinogenic effects when the leaves are chewed, orally consumed in a liquid state, or dried and smoked. It’s active ingredient is Salvinorin-A (Roth et al., 2002; Siebert, 1994), a highly selective kappa (κ)-opioid receptor agonist (Roth et al., 2002), that researchers ...
Lecture 11: Thyroid and Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands: Learning
... Lie just above the point of entry of the inferior thyroid arteries into the thyroid gland Usually at the level of the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage Inferior parathyroid glands Lie just below the arterial entry point Usually near inferior poles of thyroid, but position is more va ...
... Lie just above the point of entry of the inferior thyroid arteries into the thyroid gland Usually at the level of the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage Inferior parathyroid glands Lie just below the arterial entry point Usually near inferior poles of thyroid, but position is more va ...
Duloxetine Inhibits Effects of MDMA (``Ecstasy``) In Vitro and in
... effects of 3,4–methylenedioxy-methamphetamine (MDMA, ecstasy) in vitro and in 16 healthy subjects. The clinical study used a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, four-session, crossover design. In vitro, duloxetine blocked the release of both 5-HT and NE by MDMA or by its metabolite 3,4-met ...
... effects of 3,4–methylenedioxy-methamphetamine (MDMA, ecstasy) in vitro and in 16 healthy subjects. The clinical study used a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, four-session, crossover design. In vitro, duloxetine blocked the release of both 5-HT and NE by MDMA or by its metabolite 3,4-met ...
AP Psych Chap 3A handouts
... PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, © 2010 ...
... PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, © 2010 ...
Neuropharmacology of N,N-dimethyltryptamine
... N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) is an indole alkaloid widely found in plants and animals. It is best known for producing brief and intense psychedelic effects when ingested. Increasing evidence suggests that endogenous DMT plays important roles for a number of processes in the periphery and central ner ...
... N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) is an indole alkaloid widely found in plants and animals. It is best known for producing brief and intense psychedelic effects when ingested. Increasing evidence suggests that endogenous DMT plays important roles for a number of processes in the periphery and central ner ...
Clinical pharmacology of dobutamine and dopamine in preterm
... Dobutamine is a b1 selective stimulant. b Receptor agonists are used to stimulate the rate and the force of cardiac contraction. The chronotropic effect is useful for the treatment of arrhythmias whereas the inotropic effect is useful to augment the myocardial contractility. Dobutamine is about four ...
... Dobutamine is a b1 selective stimulant. b Receptor agonists are used to stimulate the rate and the force of cardiac contraction. The chronotropic effect is useful for the treatment of arrhythmias whereas the inotropic effect is useful to augment the myocardial contractility. Dobutamine is about four ...
Lesson Overview - Diman Regional
... the inner part is the adrenal medulla. The adrenal cortex produces more than two dozen steroid hormones called corticosteroids. ...
... the inner part is the adrenal medulla. The adrenal cortex produces more than two dozen steroid hormones called corticosteroids. ...
neuroregulatory effects of nicotine
... Nicotine acts on a select group of receptors centrally, and receptor interactions appear to be quite specific, resembling those of few other compounds. The exceptions are alkaloidal analogs such as cytisine and anabasine and the chemical stereo-isomers, 3-methyl-pyrridyl-pyrolidine and (+)nicotine ( ...
... Nicotine acts on a select group of receptors centrally, and receptor interactions appear to be quite specific, resembling those of few other compounds. The exceptions are alkaloidal analogs such as cytisine and anabasine and the chemical stereo-isomers, 3-methyl-pyrridyl-pyrolidine and (+)nicotine ( ...
Endocrine and Nervous System
... Alert you to important documentation issues and possible shortcomings, as they apply to procedures of the endocrine and nervous systems Discuss application of most-frequently used CPT® modifiers Introduce ICD-9-CM and HCPCS Level II codes and coding Supply hands-on examples and review material to im ...
... Alert you to important documentation issues and possible shortcomings, as they apply to procedures of the endocrine and nervous systems Discuss application of most-frequently used CPT® modifiers Introduce ICD-9-CM and HCPCS Level II codes and coding Supply hands-on examples and review material to im ...
Stress and the neuroendocrine system: implications for animal well
... stressful internal and external stimuli. The endocrine system allows not only the individual organism but also the species to survive. Anciently threatened animals and humans respond to stress with multiple physical changes, including endocrine changes that prepare them to react or retreat. This pro ...
... stressful internal and external stimuli. The endocrine system allows not only the individual organism but also the species to survive. Anciently threatened animals and humans respond to stress with multiple physical changes, including endocrine changes that prepare them to react or retreat. This pro ...
Phenylpropanolamine There are four optical isomers of
... indirect actions on the adrenergic receptor system, which is part of the sympathetic nervous system or SNS. Central nervous system or CNS involvement is present, but the predominant clinical effects are caused by involvement with the sympathetic segment of the peripheral nervous system due to the fa ...
... indirect actions on the adrenergic receptor system, which is part of the sympathetic nervous system or SNS. Central nervous system or CNS involvement is present, but the predominant clinical effects are caused by involvement with the sympathetic segment of the peripheral nervous system due to the fa ...
How to Reduce Trenbolone Enanthate Side Effects
... Tren Enanthate increases the amount of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF-1). IGF-1 is a proteinbased peptide that is naturally produced in the body. It promotes cell growth and regeneration. A side effect of Tren Enanthate is that it increases the number of IGF-1 receptors in the body and increases th ...
... Tren Enanthate increases the amount of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF-1). IGF-1 is a proteinbased peptide that is naturally produced in the body. It promotes cell growth and regeneration. A side effect of Tren Enanthate is that it increases the number of IGF-1 receptors in the body and increases th ...
Arrhythmia/Electrophysiology
... gene-targeted mice in vivo, and thus, clonidine-like drugs represent novel structures for future HCN channel inhibitors. (Circulation. 2007;115:&NA;-.) Key Words: receptors, adrenergic, alpha 䡲 heart rate 䡲 ion channels 䡲 pharmacology ...
... gene-targeted mice in vivo, and thus, clonidine-like drugs represent novel structures for future HCN channel inhibitors. (Circulation. 2007;115:&NA;-.) Key Words: receptors, adrenergic, alpha 䡲 heart rate 䡲 ion channels 䡲 pharmacology ...
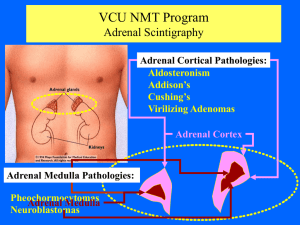
CSTCC NMT Program Adrenal Scintigraphy
... •mIBG should only be used for Adrenal Medulla pathologies. •Before administering mIBG the patient should be treated with Lugol’s solution which blocks thyroid uptake of free I131. ...
... •mIBG should only be used for Adrenal Medulla pathologies. •Before administering mIBG the patient should be treated with Lugol’s solution which blocks thyroid uptake of free I131. ...
acetylcholine
... adenyl cyclase and their activation leads to increased cAMP levels, which leads to and increase in intracellular calcium and so to an increased cardiac force of ...
... adenyl cyclase and their activation leads to increased cAMP levels, which leads to and increase in intracellular calcium and so to an increased cardiac force of ...
The Pharmacology of Psychedelic Drugs
... while the dihexyl compound is completely inactive. The psychotropic activity is proportional to the rate of metabolism in the liver, and the ability to be 6-hydroxylated (the higher homologues are 6-hydroxylated slowly or not at all). Szara and Axelrod (1959) reported that DMT is metabolized to 6hyd ...
... while the dihexyl compound is completely inactive. The psychotropic activity is proportional to the rate of metabolism in the liver, and the ability to be 6-hydroxylated (the higher homologues are 6-hydroxylated slowly or not at all). Szara and Axelrod (1959) reported that DMT is metabolized to 6hyd ...
Adrenal Glands - Meridian Kinesiology
... When the body is under Stress the Adrenal Glands secrete Glucocorticoids. The Negative Feedback Mechanism between the Pituitary Gland and the Adrenal Glands that occurs within the Hippocampus helps to regulate the body's production of Glucocorticoids. These Substances Improve the Health of the Adren ...
... When the body is under Stress the Adrenal Glands secrete Glucocorticoids. The Negative Feedback Mechanism between the Pituitary Gland and the Adrenal Glands that occurs within the Hippocampus helps to regulate the body's production of Glucocorticoids. These Substances Improve the Health of the Adren ...
C16.1 PPT - Destiny High School
... The Adrenal Glands The adrenal medulla secretes the hormones epinephrine (also called adrenaline) and norepinephrine. Epinephrine increases heartbeat and respiration, raises blood pressure, and suppresses the digestive process during periods of high emotion. ...
... The Adrenal Glands The adrenal medulla secretes the hormones epinephrine (also called adrenaline) and norepinephrine. Epinephrine increases heartbeat and respiration, raises blood pressure, and suppresses the digestive process during periods of high emotion. ...
PDF - the Houpt Lab
... Long-term, transcriptional stress response mediated by glucocorticoids (GC): CRH from hypothalamus –> long portal vessels –> anterior pituitary –> pituitary cells called corticotropes –> adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) ACTH in blood –> cortex of adrenal gland –> ACTH receptors increase cAMP –> i ...
... Long-term, transcriptional stress response mediated by glucocorticoids (GC): CRH from hypothalamus –> long portal vessels –> anterior pituitary –> pituitary cells called corticotropes –> adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) ACTH in blood –> cortex of adrenal gland –> ACTH receptors increase cAMP –> i ...
Autonomic Dysfunction - Internal Medicine of Northern Virginia
... Copyright © 1990 Butterworth Publishers ...
... Copyright © 1990 Butterworth Publishers ...
Endocrine System
... • Anterior Pituitary Gland – Secretes peptide hormones that act on target organs including the adrenal gland, liver, bone, thyroid gland, and gonads. • Parathyroid - Releases parathyroid hormone, which regulates the level of calcium in the blood with the help of calcitonin, which is produced in the ...
... • Anterior Pituitary Gland – Secretes peptide hormones that act on target organs including the adrenal gland, liver, bone, thyroid gland, and gonads. • Parathyroid - Releases parathyroid hormone, which regulates the level of calcium in the blood with the help of calcitonin, which is produced in the ...
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine, also called noradrenaline, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the human brain and body as a hormone and neurotransmitter. Noradrenaline is the common name in the United Kingdom (BAN), while norepinephrine is the International Nonproprietary Name and typically used in the United States. Areas of the body that produce or are affected by norepinephrine are referred to everywhere as noradrenergic.Norepinephrine is synthesized and released by the central nervous system and also by a division of the autonomic nervous system called the sympathetic nervous system. In the brain, norepinephrine comes from several nuclei that are small in size but project to most other parts of the brain and exert powerful effects on their targets. The most important source of norepinephrine in the brain is the locus coeruleus, located in the pons. In the sympathetic nervous system norepinephrine is used as a neurotransmitter by sympathetic ganglia located near the spinal cord or in the abdomen, and is also released directly into the bloodstream by the adrenal glands. Regardless of how and where it is released, norepinephrine acts on target cells by binding to and activating noradrenergic receptors located on the cell surface.In the most basic terms, the function of norepinephrine is to mobilize the brain and body for action. Norepinephrine release is lowest during sleep, rises during wakefulness, and reaches much higher levels during situations of stress or danger, in what has been called the fight-or-flight response. In the brain norepinephrine increases arousal and alertness, promotes vigilance, enhances formation and retrieval of memory, and focuses attention; it also increases restlessness and anxiety. In the rest of the body, norepinephrine increases heart rate and blood pressure, triggers the release of glucose from energy stores, increases blood flow to skeletal muscle, reduces blood flow to the gastrointestinal system, and promotes voiding of the bladder and large intestines.A variety of medically important drugs work by altering the actions of norepinephrine systems. Norepinephrine itself is widely used as an injectable drug for the treatment of critically low blood pressure. Beta blockers, which counter some of the effects of norepinephrine, are frequently used to treat glaucoma, migraine, and a range of cardiovascular problems. Alpha blockers, which counter a different set of norepinephrine effects, are used to treat several cardiovascular and psychiatric conditions. Alpha-2 agonists often have a sedating effect, and are commonly used as anesthesia-enhancers in surgery, as well as in treatment of drug or alcohol dependence. Many important psychiatric drugs exert strong effects on norepinephrine systems in the brain, resulting in side-effects that may be helpful or harmful.