* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sleep Brain Labelling
Sleep paralysis wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Rapid eye movement sleep wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience of sleep wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Sleep and memory wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Effects of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Start School Later movement wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Circadian rhythm wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural binding wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
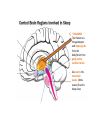
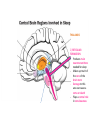
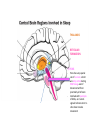
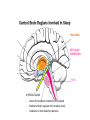
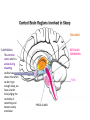
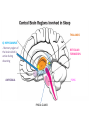
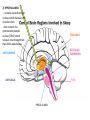
1) THALAMUS - The thalamus is the gatekeeper and stops signals from the body/brain from going to the cerebral cortex - Also starts the slow brain waves (delta waves) found in deep sleep THALAMUS 2) RETICULAR FORMATION - Produces main neurotransmitters needed for sleep - Makes up much of the core of the brain stem - Damage to this area can cause a coma or death - Plays a central role in consciousness THALAMUS RETICULAR FORMATION 3) PONS - - Pons has very special set of neurons which are only active during REM sleep, even if disconnected from practically all of brain Involved with paralysis of limbs, as it sends signals to brain stem to shut down muscle movement THALAMUS RETICULAR FORMATION PONS 4) PINEAL GLAND - where the hormone melatonin is produced - Melatonin helps regulate the circadian clock - melatonin is stimulated by darkness THALAMUS 5) AMYGDALA - The emotion centre which is active during dreaming - studies have shown that when we don’t get enough sleep, we have a harder time judging the neutrality of something and become overly emotional RETICULAR FORMATION PONS PINEAL GLAND THALAMUS 6) HIPPOCAMPUS - Memory region of the brain which is active during dreaming RETICULAR FORMATION AMYGDALA PONS PINEAL GLAND 7) HYPOTHALAMUS - contains suprachiasmatic nucleus which maintains the circadian clock - Also contains the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus (VRLO) which releases neurotransmitters that inhibit wakefulness THALAMUS RETICULAR FORMATION HIPPOCAMPUS AMYGDALA PONS PINEAL GLAND