* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
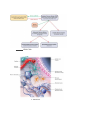
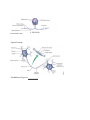
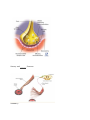
Chapter 6.1 Afferent nerves: sensory transmitters that send impulses from receptors in the skin,_______, and _______to the central nervous system Autonomic nervous system: branch of the nervous system that controls _________ body functions Cell body: part of an axon that contains a ________ Central nervous system(CNS): the ______ and _______ cord Dendrites: branches of a neuron that collect _________ and transport them to the cell body _________ nerves: motor transmitters that carry impulses from the central nervous system out to the muscles and glands Myelin sheath: the fatty bands of _________ surrounding axon fibers Neurilemma: the thin, membranous sheath enveloping a ______ ______ Neuroglia: non-neural tissue that forms the _________ or supporting elements of the CNS; also known as _______ cells Nodes of Ranvier: the uninsulated _______ in the myelin sheath of a nerve fiber where the axon is exposed Peripheral nervous system(PNS): all parts of the nervous system _________ to the brain and spinal cord Somatic nervous system: branch of the nervous system that stimulates the ________ muscles Synapse: the intersection between a neuron and another neuron, a muscle, a gland, or a sensory receptor Organization Of the Nervous System: ________ Glial Cells: PNS Glial Cells: Typical Neuron: The Different Types of ___________: Summary: ● The two major sections of the nervous system are the CNS(_________ and spinal cord) and the PNS(cranial nerves, spinal nerves,__________________) ● ● ● The autonomic nervous system(___________) and somatic nervous system(involuntary)both deal with efferent(motor) nerves A ____________consists of a cell body, dendrites, axon fibers, the myelin sheath, the neurilemma,the nodes of Ranvier and the synapse The three different neuron structures are__________,___________, and ____________ neurons Chapter 6.2 Transmission of Nerve Impulses Autonomic reflexes: involuntary stimuli transmitted to _______ and ________ muscle Conductivity: the ability of a neuron to transmit a _____ ______ Depolarized: a condition in which the inside of a cell membrane is more ____________ charged than the outside Nerve impulse: __________ charge that travels along a nerve fiber when stimulated Polarized: condition that occurs when the inside of a cell membrane is more ___________ charged than the outside Reflexes: simple, rapid,_________, programmed responses to stimuli Refractory period: the time between the completion of the action potential and ____________ ______________: the reestablishment of a polarized state in a cell after depolarization Saltatory conduction: the rapid skipping of an action potential from node to node on ________ neurons Somatic reflexes: involuntary stimuli transmitted to skeletal muscles from neural ________ Connection Between __________: Sensory and _______ Neurons: Summary: Chapter 6.3 Cerebellum: section of the brain that coordinates ________ _______, including balance Cerebrum: the ________ part of the brain, consisting of the left and right hemispheres Diencephalon: area of the brain that includes the epithalamus, thalamus, metathalamus, and hypothalamus; also known as the ___________ Epithalamus: uppermost portion of the diencephalon, which includes the pineal gland and regulates ____________ hormones Fissures: the uniformly positioned, deep ________ in the brain Frontal lobes: sections of the brain located behind the _________ Hypothalamus: a portion of the diencephalon, which regulates functions such as metabolism, ______________, and blood pressure Lobes: the name for the four regions of the brain - _________, ___________,___________, and _____________ Medulla oblongata: the _________ portion of the brainstem, which regulates heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing, and controls several reflexes Meninges: protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord Midbrain: relay station for sensory and motor impulses; located on the _________ end of the brain stem Occipital lobes: sections of the brain located behind the parietal lobes; integrate sensory information from the skin, internal organs,__________, and joints Parietal lobes: sections of the brain located behind the frontal lobes; integrate sensory information from the _______, internal organs, muscles, and joints Pons: the section of the brain that plays a role in regulating _____________ Primary motor cortex: outer region of the brain in the frontal lobes that sends neural impulses to the __________ muscles Primary somatic sensory cortex: outer region of the brain in the ___________lobes that interprets sensory impulses received from the skin, internal organs, muscles, and joints Spinal cord: column of nervous tissue that extends from the brainstem to the beginning of the __________region of the spine Temporal lobes: the most __________ portions of the brain; responsible for speech, hearing, vision, memory, and emotion Thalamus: the largest portion of the diencephalon, which communicates sensory and motor information between the body and the ___________________ ____________ View of The Brain: Lobes of The Brain: Regions Of Sensory _________ and Output: _____________ View Of the Brain Stem: Functions Of The Brain: Summary: ● ● ● The four regions of the brain are the cerebrum,____________, brain stem, and cerebellum Within the cerebrum are the different lobes of the brain: frontal, parietal,__________, and temporal The brain stem includes the______________, the pons, and the medulla oblongata Chapter 6.4 Cranial nerves: __ pairs of nerves that originate in the brain and relay impulses to and from the PNS Craniosacral division: the _____________ nervous system, in which nerves originate in the brain stem or sacral region of the spinal cord Dorsal ramus: the division of __________ spinal nerves that transmit motor impulses to the posterior _________ muscles and relay sensory impulses from skin of the back Edoneurium:a delicate, _____________ tissue that surrounds each nerve fiber Paravertebral ganglia: mass of nerve cell bodies close to the ______________ Perineurium: a ____________ sheath that surrounds a bundle of nerve fibers Plexuses: complex interconnections of _________ Postganglionic neuron the __________ neuron in a series that transmits impulses from the CNS Preganglionic neuron: the ___________ neuron in a series that transmits impulses from the CNS Spinal Nerve: neural _______________ that branch from the left and right sides of the spinal cord Thoracolumbar division: the sympathetic system of nerves that lies near the ________ and _____________regions of the spine Ventral ramus:the ____________ division of spinal nerves that communicate with the muscles and skin of the anterior and lateral trunk Structure Of Nerve: Functions Of The Cranial Nerves: The Cranial nerves: Spinal Nerve: Spinal Nerve Plexuses: Major Nerves: Chapter 6.5 Injuries and Disorders of the Nervous System Alzheimer’s disease: condition involving a progressive loss of brain function with major consequences for_________, thinking, and behavior Cerebral palsy: a group of nervous system disorders resulting from brain damage before or during birth, or in_______________ Dementia: a(n) __________ brain disease involving loss of function in two or more areas of cognition Epilepsy: a group of brain disorders characterized by repeated ____________ over time Meningitis: an infection-induced inflammation of the _________ surrounding the brain and spinal cord Multiple sclerosis: a chronic, slowly progressive disease of the CNS that destroys the _________________ of nerve cell axons Paraplegia: condition characterized by loss of function in the _____________ and legs Parkinson’s disease: chronic nervous system disease characterized by slowly spreading tremor, muscular weakness, and __________ Quadriplegia: disorder characterized by loss of function below the __________ Traumatic brain injury: mild or severe trauma to the head