* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download midbrain Brain stem
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Superior colliculus wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
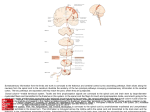
Chapter Opener 12 © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.1 Embryonic development of the human brain. Neural tube (contains neural canal) Anterior (rostral) Primary brain vesicles Secondary brain vesicles Adult brain structures Cerebrum: cerebral hemispheres (cortex, white matter, basal nuclei) Lateral ventricles Telencephalon Prosencephalon (forebrain) Diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus), retina Third ventricle Diencephalon Mesencephalon (midbrain) Mesencephalon Brain stem: midbrain Cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon Brain stem: pons Rhombencephalon (hindbrain) Cerebellum Myelencephalon Posterior (caudal) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Adult neural canal regions Fourth ventricle Brain stem: medulla oblongata Spinal cord Central canal Figure 12.1a Embryonic development of the human brain. Neural tube (contains neural canal) Anterior (rostral) Posterior (caudal) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.1b Embryonic development of the human brain. Primary brain vesicles Prosencephalon (forebrain) Mesencephalon (midbrain) Rhombencephalon (hindbrain) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.1c Embryonic development of the human brain. Secondary brain vesicles Telencephalon Diencephalon Mesencephalon Metencephalon Myelencephalon © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.1d Embryonic development of the human brain. Adult brain structures Cerebrum: cerebral hemispheres (cortex, white matter, basal nuclei) Diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus), retina Brain stem: midbrain Brain stem: pons Cerebellum Brain stem: medulla oblongata Spinal cord © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.1e Embryonic development of the human brain. Adult neural canal regions Lateral ventricles Third ventricle Cerebral aqueduct Fourth ventricle Central canal © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.2 Brain development. Anterior (rostral) Metencephalon Mesencephalon Diencephalon Telencephalon Myelencephalon Posterior (caudal) Midbrain Cervical Flexures Spinal cord Week 5: Two major flexures form, causing the telencephalon and diencephalon to angle toward the brain stem. Cerebral hemisphere Outline of diencephalon Midbrain Cerebellum Pons Medulla oblongata Spinal cord Week 13: Cerebral hemispheres develop and grow posterolaterally to enclose the diencephalon and the rostral brain stem. Cerebral hemisphere Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem • Midbrain • Pons • Medulla oblongata © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Birth: Shows adult pattern of structures and convolutions. Figure 12.2a Brain development. Anterior (rostral) Metencephalon Mesencephalon Diencephalon Telencephalon Myelencephalon Posterior (caudal) Midbrain Cervical Flexures Spinal cord Week 5: Two major flexures form, causing the telencephalon and diencephalon to angle toward the brain stem. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.2b Brain development. Cerebral hemisphere Outline of diencephalon Midbrain Cerebellum Pons Medulla oblongata Spinal cord Week 13: Cerebral hemispheres develop and grow posterolaterally to enclose the diencephalon and the rostral brain stem. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.2c Brain development. Cerebral hemisphere Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem • Midbrain • Pons • Medulla oblongata Birth: Shows adult pattern of structures and convolutions. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.3 Ventricles of the brain. Lateral ventricle Anterior horn Interventricular foramen Septum pellucidum Inferior horn Posterior horn Third ventricle Inferior horn Median aperture Cerebral aqueduct Lateral aperture Fourth ventricle Lateral aperture Central canal Anterior view © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Left lateral view Figure 12.3a Ventricles of the brain. Lateral ventricle Anterior horn Interventricular foramen Septum pellucidum Inferior horn Third ventricle Lateral aperture Cerebral aqueduct Fourth ventricle Central canal Anterior view © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.3b Ventricles of the brain. Lateral ventricle Anterior horn Interventricular foramen Posterior horn Third ventricle Inferior horn Median aperture Cerebral aqueduct Fourth ventricle Lateral aperture Central canal Left lateral view © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.4 Lobes, sulci, and fissures of the cerebral hemispheres. Anterior Longitudinal fissure Frontal lobe Left cerebral hemisphere Cerebral veins and arteries covered by arachnoid mater Parietal lobe Right cerebral hemisphere Left cerebral hemisphere Occipital lobe Transverse cerebral fissure Brain stem Cerebellum Posterior Left lateral view Superior view Precentral gyrus Frontal lobe Central sulcus Postcentral gyrus Frontal lobe Central sulcus Parietal lobe Parieto-occipital sulcus (on medial surface of hemisphere) Lateral sulcus Occipital lobe Temporal lobe Fissure (a deep sulcus) Transverse Cerebral fissure Cerebellum Pons Medulla oblongata Spinal cord Gyrus Cortex (gray matter) Sulcus White matter Lobes and sulci of the cerebrum © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Gyri of insula Temporal lobe (pulled down) Location of the insula lobe Figure 12.4a Lobes, sulci, and fissures of the cerebral hemispheres. Anterior Longitudinal fissure Frontal lobe Cerebral veins and arteries covered by arachnoid mater Parietal lobe Left cerebral hemisphere Right cerebral hemisphere Occipital lobe Posterior Superior view © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.4b Lobes, sulci, and fissures of the cerebral hemispheres. Left cerebral hemisphere Brain stem Transverse cerebral fissure Cerebellum Left lateral view © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.4c Lobes, sulci, and fissures of the cerebral hemispheres. Precentral gyrus Frontal lobe Central sulcus Postcentral gyrus Parietal lobe Parieto-occipital sulcus (on medial surface of hemisphere) Lateral sulcus Fissure (a deep sulcus) Occipital lobe Temporal lobe Transverse cerebral fissure Cerebellum Pons Medulla oblongata Spinal cord Gyrus Cortex (gray matter) Sulcus White matter Lobes and sulci of the cerebrum © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.4d Lobes, sulci, and fissures of the cerebral hemispheres. Frontal lobe Central sulcus Gyri of insula Temporal lobe (pulled down) Location of the insula lobe © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.5 Functional neuroimaging (fMRI) of the cerebral cortex. Longitudinal fissure © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Left frontal lobe Left temporal lobe Central sulcus Areas active in speech and hearing (fMRI) Figure 12.6 Functional and structural areas of the cerebral cortex. Motor areas Central sulcus Primary motor cortex Premotor cortex Frontal eye field Broca's area (outlined by dashes) Sensory areas and related association areas Primary somatosensory cortex Somatic Somatosensory sensation association cortex Gustatory cortex (in insula) Prefrontal cortex Working memory for spatial tasks Executive area for task management Working memory for object-recall tasks Solving complex, multitask problems Wernicke's area (outlined by dashes) Primary visual cortex Visual association area Auditory association area Primary auditory cortex Lateral view, left cerebral hemisphere Premotor cortex Cingulate gyrus Primary motor cortex Corpus callosum Vision Hearing Central sulcus Primary somatosensory cortex Frontal eye field Parietal lobe Somatosensory association cortex Parieto-occipital sulcus Prefrontal cortex Occipital lobe Processes emotions related to personal and social interactions Visual association area Orbitofrontal cortex Olfactory bulb Olfactory tract Fornix Temporal Primary lobe olfactory cortex Parasagittal view, right cerebral hemisphere © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Taste Primary motor cortex Motor association cortex Primary sensory cortex Uncus Calcarine sulcus Parahippocampal gyrus Sensory association cortex Primary visual cortex Multimodal association cortex Figure 12.6a Functional and structural areas of the cerebral cortex. Motor areas Central sulcus Primary motor cortex Premotor cortex Frontal eye field Broca's area (outlined by dashes) Sensory areas and related association areas Primary somatosensory cortex Somatic Somatosensory sensation association cortex Gustatory cortex (in insula) Prefrontal cortex Working memory for spatial tasks Executive area for task management Working memory for object-recall tasks Solving complex, multitask problems Wernicke's area (outlined by dashes) Primary visual cortex Visual association area Auditory association area Primary auditory cortex Lateral view, left cerebral hemisphere Primary motor cortex © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Taste Motor association cortex Primary sensory cortex Sensory association cortex Vision Hearing Multimodal association cortex Figure 12.6b Functional and structural areas of the cerebral cortex. Premotor cortex Cingulate Primary gyrus motor cortex Corpus callosum Central sulcus Primary somatosensory cortex Frontal eye field Parietal lobe Somatosensory association cortex Parieto-occipital sulcus Prefrontal cortex Occipital lobe Processes emotions related to personal and social interactions Visual association area Orbitofrontal cortex Olfactory bulb Olfactory tract Fornix Temporal lobe Primary olfactory cortex Parasagittal view, right cerebral hemisphere Primary motor cortex © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Motor association cortex Primary sensory cortex Uncus Calcarine sulcus Parahippocampal gyrus Sensory association cortex Primary visual cortex Multimodal association cortex Figure 12.7 Body maps in the primary motor cortex and somatosensory cortex of the cerebrum. Posterior Motor Sensory Anterior Hip Trunk Neck Motor map in precentral gyrus Sensory map in postcentral gyrus Foot Knee Toes Genitals Jaw Tongue Swallowing © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Primary motor cortex (precentral gyrus) Primary somatosensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) Intraabdominal Figure 12.8 White fiber tracts of the cerebral hemispheres. Longitudinal fissure Superior Lateral ventricle Basal nuclei • Caudate • Putamen • Globus pallidus Thalamus Third ventricle Association fibers (within hemisphere) Commissural fibers (between hemispheres) • Corpus callosum Projection fibers (cerebral cortex to lower area) • Corona radiata • Internal capsule Gray matter White matter Pons Medulla oblongata Frontal section Decussation (cross-over) of pyramids Association fibers Commissural fibers • Corpus callosum Projection fibers • Corona radiata • Internal capsule Parasagittal section and dissection © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Gray matter Figure 12.8a White fiber tracts of the cerebral hemispheres. Longitudinal fissure Lateral ventricle Basal nuclei • Caudate • Putamen • Globus pallidus Thalamus Third ventricle Superior Association fibers (within hemisphere) Commissural fibers (between hemispheres) • Corpus callosum Projection fibers (cerebral cortex to lower area) • Corona radiata • Internal capsule Gray matter White matter Pons Medulla oblongata Frontal section © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Decussation (cross-over) of pyramids Figure 12.8a White fiber tracts of the cerebral hemispheres. (1 of 2) Longitudinal fissure Lateral ventricle Basal nuclei • Caudate • Putamen • Globus pallidus Thalamus Third ventricle Superior Association fibers (within hemisphere) Commissural fibers (between hemispheres) • Corpus callosum Projection fibers (cerebral cortex to lower area) • Corona radiata • Internal capsule Gray matter White matter Pons Medulla oblongata Frontal section © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Decussation (cross-over) of pyramids Figure 12.8a White fiber tracts of the cerebral hemispheres. (2 of 2) Association fibers (within hemisphere) Commissural fibers (between hemispheres) • Corpus callosum Projection fibers (cerebral cortex to lower area) • Corona radiata • Internal capsule Gray matter White matter Frontal section © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.8b White fiber tracts of the cerebral hemispheres. Association fibers Commissural fibers • Corpus callosum Projection fibers • Corona radiata • Internal capsule Parasagittal section and dissection © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Gray matter Figure 12.9 Basal nuclei. Striatum Caudate nucleus Putamen Thalamus Tail of caudate nucleus Anterior Cerebral cortex Cerebral white matter Corpus callosum Anterior horn of lateral ventricle Head of caudate nucleus Putamen Globus pallidus Thalamus Tail of caudate nucleus Third ventricle Inferior horn of lateral ventricle Posterior © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.9a Basal nuclei. Striatum Caudate nucleus Putamen © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Thalamus Tail of caudate nucleus Figure 12.9b Basal nuclei. Anterior Cerebral cortex Cerebral white matter Corpus callosum Anterior horn of lateral ventricle Head of caudate nucleus Putamen Globus pallidus Thalamus Tail of caudate nucleus Third ventricle Inferior horn of lateral ventricle Posterior © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.9b Basal nuclei. (1 of 2) Anterior Cerebral cortex Cerebral white matter Corpus callosum Anterior horn of lateral ventricle Head of caudate nucleus Putamen Globus pallidus Thalamus Tail of caudate nucleus Third ventricle Inferior horn of lateral ventricle Posterior © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.9b Basal nuclei. (2 of 2) Cerebral cortex Cerebral white matter Corpus callosum Anterior horn of lateral ventricle Head of caudate nucleus Putamen Globus pallidus Thalamus Third ventricle Inferior horn of lateral ventricle © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.10 Midsagittal section of the brain. Cerebral hemisphere Corpus callosum Fornix Septum pellucidum Choroid plexus Interthalamic adhesion (intermediate mass of thalamus) Interventricular foramen Anterior commissure Hypothalamus Optic chiasma Thalamus (encloses third ventricle) Pituitary gland Mammillary body Pons Medulla oblongata Spinal cord Posterior commissure Pineal gland Epithalamus Corpora quadrigemina Cerebral aqueduct Midbrain Arbor vitae (of cerebellum) Fourth ventricle Choroid plexus Cerebellum Corpus callosum Fornix Thalamus Posterior commissure Pineal gland Lateral ventricle (covered by septum pellucidum) Third ventricle Epithalamus Corpora quadrigemina Cerebral aqueduct Anterior commissure Hypothalamus Midbrain Arbor vitae Fourth ventricle Optic chiasma Cerebellum Mammillary body Pons Medulla oblongata © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.10a Midsagittal section of the brain. Cerebral hemisphere Corpus callosum Fornix Choroid plexus Septum pellucidum Interthalamic adhesion (intermediate mass of thalamus) Thalamus (encloses third ventricle) Posterior commissure Pineal gland Interventricular foramen Anterior commissure Hypothalamus Optic chiasma Corpora quadrigemina Midbrain Cerebral aqueduct Pituitary gland Mammillary body Pons Medulla oblongata Spinal cord © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Epithalamus Arbor vitae (of cerebellum) Fourth ventricle Choroid plexus Cerebellum Figure 12.10b Midsagittal section of the brain. Corpus callosum Fornix Thalamus Lateral ventricle (covered by septum pellucidum) Posterior commissure Pineal gland Third ventricle Epithalamus Corpora quadrigemina Cerebral aqueduct Anterior commissure Hypothalamus Arbor vitae Fourth ventricle Optic chiasma Cerebellum Mammillary body Pons Medulla oblongata © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Midbrain Figure 12.11 Selected structures of the diencephalon. Paraventricular nucleus Medial Lateral Lateral dorsal dorsal posterior nucleus nucleus nucleus Pulvinar Anterior nuclei Reticular nucleus Ventral Ventral Ventral posteroanterior lateral lateral Medial geniculate body Lateral geniculate body Ventral nuclei The main thalamic nuclei. (The reticular nuclei that “cap” the thalamus laterally are depicted as curving translucent structures.) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Anterior commissure Preoptic nucleus Anterior hypothalamic nucleus Supraoptic nucleus Suprachiasmatic nucleus Optic chiasma Infundibulum (stalk of the pituitary gland) Fornix Dorsomedial nucleus Posterior hypothalamic nucleus Lateral hypothalamic area Arcuate nucleus Pituitary gland The main hypothalamic nuclei. Ventromedial nucleus Mammillary body Figure 12.11a Selected structures of the diencephalon. Medial Lateral Lateral dorsal dorsal posterior nucleus nucleus nucleus Pulvinar Anterior nuclei Reticular nucleus Ventral Ventral Ventral posteroanterior lateral lateral Medial geniculate body Lateral geniculate body Ventral nuclei The main thalamic nuclei. (The reticular nuclei that “cap” the thalamus laterally are depicted as curving translucent structures.) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.11b Selected structures of the diencephalon. Paraventricular nucleus Anterior commissure Preoptic nucleus Anterior hypothalamic nucleus Supraoptic nucleus Suprachiasmatic nucleus Optic chiasma Infundibulum (stalk of the pituitary gland) Fornix Arcuate nucleus Pituitary gland The main hypothalamic nuclei. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Dorsomedial nucleus Posterior hypothalamic nucleus Lateral hypothalamic area Ventromedial nucleus Mammillary body Figure 12.12 Inferior view of the brain, showing the three parts of the brain stem: midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. Frontal lobe Olfactory bulb (synapse point of cranial nerve I) Optic chiasma Optic nerve (II) Optic tract Mammillary body Midbrain Pons Temporal lobe Medulla oblongata Cerebellum Spinal cord © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.13a–b Three views of the brain stem (green) and the diencephalon (purple). Thalamus Diencephalon Hypothalamus Midbrain View (a) Pons View (c) Brain stem Medulla oblongata View (b) Optic chiasma Diencephalon • Thalamus • Hypothalamus Optic nerve (II) Thalamus Optic tract Mammillary body Infundibulum Pituitary gland Oculomotor nerve (III) Trochlear nerve (IV) Crus cerebri of cerebral peduncles (midbrain) Trigeminal nerve (V) Middle cerebellar peduncle Pons Facial nerve (VII) Abducens nerve (VI) Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) Pyramid Abducens nerve (VI) Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX) Superior colliculus Inferior colliculus Trochlear nerve (IV) Superior cerebellar peduncle Middle cerebellar peduncle Inferior cerebellar peduncle Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) Olive Hypoglossal nerve (XII) Vagus nerve (X) Ventral root of first cervical nerve Accessory nerve (XI) Decussation of pyramids Spinal cord Ventral view © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Left lateral view Figure 12.13a Three views of the brain stem (green) and the diencephalon (purple). Thalamus Hypothalamus Midbrain Pons Diencephalon View (a) View (c) Brain stem Medulla oblongata View (b) Diencephalon • Thalamus • Hypothalamus Optic chiasma Optic nerve (II) Optic tract Mammillary body Oculomotor nerve (III) Trochlear nerve (IV) Crus cerebri of cerebral peduncles (midbrain) Middle cerebellar peduncle Abducens nerve (VI) Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) Pyramid Ventral root of first cervical nerve Decussation of pyramids Spinal cord Trigeminal nerve (V) Pons Facial nerve (VII) Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX) Hypoglossal nerve (XII) Vagus nerve (X) Accessory nerve (XI) Ventral view © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.13b Three views of the brain stem (green) and the diencephalon (purple). Thalamus Hypothalamus Diencephalon Midbrain Pons View (a) View (c) Brain stem Medulla oblongata Optic tract Infundibulum View (b) Thalamus Pituitary gland Crus cerebri of cerebral peduncles (midbrain) Trigeminal nerve (V) Pons Facial nerve (VII) Abducens nerve (VI) Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX) Superior colliculus Inferior colliculus Trochlear nerve (IV) Superior cerebellar peduncle Middle cerebellar peduncle Inferior cerebellar peduncle Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) Olive Hypoglossal nerve (XII) Vagus nerve (X) Accessory nerve (XI) Left lateral view © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.13c Three views of the brain stem (green) and the diencephalon (purple). Thalamus Hypothalamus Diencephalon Midbrain Pons View (a) View (c) Brain stem Medulla oblongata View (b) Thalamus Diencephalon Pineal gland Floor of fourth ventricle Facial nerve (VII) Choroid plexus (fourth ventricle) Dorsal median sulcus Dorsal root of first cervical nerve Dorsal view © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Midbrain • Superior colliculus • Inferior colliculus Corpora quadrigemina of tectum • Trochlear nerve (IV) • Superior cerebellar peduncle Pons • Middle cerebellar peduncle Medulla oblongata • Inferior cerebellar peduncle • Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) • Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX) • Vagus nerve (X) • Accessory nerve (XI) Figure 12.14 Cross sections through different regions of the brain stem. Dorsal Tectum Periaqueductal gray matter Oculomotor nucleus (III) Superior colliculus Cerebral aqueduct Reticular formation Medial lemniscus Red nucleus Substantia nigra Fibers of pyramidal tract Ventral Midbrain Fourth ventricle Trigeminal nerve (V) Medial lemniscus Pons © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Fourth ventricle Reticular formation Pontine nuclei Fibers of pyramidal tract Reticular formation Superior cerebellar peduncle Trigeminal main sensory nucleus Trigeminal motor nucleus Middle cerebellar peduncle Hypoglossal nucleus (XII) Dorsal motor nucleus of vagus (X) Inferior cerebellar peduncle Lateral nuclear group Medial nuclear group Raphe nucleus Medial lemniscus Choroid plexus Crus cerebri of cerebral peduncle Solitary nucleus Vestibular nuclei (VIII) Cochlear nuclei (VIII) Nucleus ambiguus Inferior olivary nucleus Pyramid Medulla oblongata Figure 12.14a Cross sections through different regions of the brain stem. Tectum Periaqueductal gray matter Oculomotor nucleus (III) Medial lemniscus Red nucleus Substantia nigra Fibers of pyramidal tract Dorsal Cerebral aqueduct Reticular formation Ventral Midbrain © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Superior colliculus Crus cerebri of cerebral peduncle Figure 12.14b Cross sections through different regions of the brain stem. Superior cerebellar peduncle Trigeminal main sensory nucleus Trigeminal motor nucleus Middle cerebellar peduncle Trigeminal nerve (V) Medial lemniscus Pons © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Fourth ventricle Reticular formation Pontine nuclei Fibers of pyramidal tract Reticular formation Figure 12.14c Cross sections through different regions of the brain stem. Hypoglossal nucleus (XII) Dorsal motor nucleus of vagus (X) Inferior cerebellar peduncle Lateral nuclear group Medial nuclear group Raphe nucleus Medial lemniscus Fourth ventricle Choroid plexus Medulla oblongata © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Solitary nucleus Vestibular nuclei (VIII) Cochlear nuclei (VIII) Nucleus ambiguus Inferior olivary nucleus Pyramid Figure 12.15 Cerebellum. Anterior lobe Arbor vitae Cerebellar cortex Pons Fourth ventricle Medulla oblongata Posterior lobe Flocculonodular lobe Choroid plexus Anterior lobe Cerebellar cortex Arbor vitae Cerebellar peduncles • Superior • Middle • Inferior Medulla oblongata Posterior lobe Flocculonodular lobe Anterior lobe Primary fissure Posterior lobe Horizontal fissure Vermis © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Vermis Choroid plexus of fourth ventricle Figure 12.15a Cerebellum. Anterior lobe Arbor vitae Cerebellar cortex Pons Fourth ventricle Medulla oblongata © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Posterior lobe Flocculonodular lobe Choroid plexus Figure 12.15b Cerebellum. Anterior lobe Cerebellar cortex Arbor vitae Cerebellar peduncles • Superior • Middle • Inferior Medulla oblongata © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Posterior lobe Flocculonodular lobe Choroid plexus of fourth ventricle Figure 12.15c–d Cerebellum. Anterior lobe Primary fissure Posterior lobe Horizontal fissure Vermis © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Vermis Figure 12.16 The limbic system. Septum pellucidum Diencephalic structures of the limbic system Anterior thalamic nuclei (flanking 3rd ventricle) Hypothalamus Cerebral structures of the limbic system Cingulate gyrus Septal nuclei Amygdaloid body Mammillary body Olfactory bulb © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Corpus callosum Fiber tracts connecting limbic system structures Fornix Anterior commissure Hippocampus • Dentate gyrus • Parahippocampal gyrus Table 12.1 Functions of Major Brain Regions (1 of 4) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Table 12.1 Functions of Major Brain Regions (2 of 4) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Table 12.1 Functions of Major Brain Regions (3 of 4) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Table 12.1 Functions of Major Brain Regions (4 of 4) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.17 The reticular formation. Radiations to cerebral cortex Visual impulses Auditory impulses Reticular formation Ascending general sensory tracts (touch, pain, temperature) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Descending motor projections to spinal cord Figure 12.18 Electroencephalography (EEG) and brain waves. 1-second interval Alpha waves—awake but relaxed Beta waves—awake, alert Theta waves—common in children Delta waves—deep sleep Scalp electrodes are used to record brain wave activity. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Brain waves shown in EEGs fall into four general classes. Figure 12.18a Electroencephalography (EEG) and brain waves. Scalp electrodes are used to record brain wave activity. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.18b Electroencephalography (EEG) and brain waves. 1-second interval Alpha waves—awake but relaxed Beta waves—awake, alert Theta waves—common in children Delta waves—deep sleep Brain waves shown in EEGs fall into four general classes. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.19 Types and stages of sleep. Awake REM: Skeletal muscles (except ocular muscles and diaphragm) are actively inhibited; most dreaming occurs. NREM stage 1: Relaxation begins; EEG shows alpha waves; arousal is easy. NREM stage 2: Irregular EEG with sleep spindles (short highamplitude bursts); arousal is more difficult. NREM stage 3: Sleep deepens; theta and delta waves appear; vital signs decline. Typical EEG patterns NREM stage 4: EEG is dominated by delta waves; arousal is difficult; bed-wetting, night terrors, and sleepwalking may occur. Awake REM Stage 1 NREM Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 1 © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. 2 3 4 5 6 7 Time (hrs) Typical progression of an adult through one night’s sleep stages Figure 12.19a Types and stages of sleep. Awake REM: Skeletal muscles (except ocular muscles and diaphragm) are actively inhibited; most dreaming occurs. NREM stage 1: Relaxation begins; EEG shows alpha waves; arousal is easy. NREM stage 2: Irregular EEG with sleep spindles (short highamplitude bursts); arousal is more difficult. NREM stage 3: Sleep deepens; theta and delta waves appear; vital signs decline. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Typical EEG patterns NREM stage 4: EEG is dominated by delta waves; arousal is difficult; bed-wetting, night terrors, and sleepwalking may occur. Figure 12.19b Types and stages of sleep. Awake REM Stage 1 NREM Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 4 5 7 3 6 Time (hrs) Typical progression of an adult through one night’s sleep stages 1 © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. 2 Figure 12.20 Memory processing. Outside stimuli General and special sensory receptors Afferent inputs Temporary storage (buffer) in cerebral cortex Data permanently lost Data selected for transfer Automatic memory Short-term memory (STM) Forget Forget Data transfer influenced by: Retrieval Excitement Rehearsal Associating new data with stored data Long-term memory (LTM) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Data unretrievable Figure 12.21 Proposed memory circuits. Thalamus Basal forebrain Touch Prefrontal cortex Hearing Taste Vision Sensory input Association cortex Thalamus Medial temporal lobe (hippocampus, etc.) Smell Prefrontal cortex ACh released by basal forebrain Hippocampus Declarative memory circuits Premotor cortex Sensory and motor inputs Association cortex Basal nuclei Dopamine released by substantia nigra Basal nuclei Thalamus Substantia nigra Procedural (skills) memory circuits © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Thalamus Premotor cortex Figure 12.21a Proposed memory circuits. Sensory input Thalamus Basal forebrain Touch Prefrontal cortex Hearing Vision Hippocampus Declarative memory circuits © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Thalamus Taste Smell Association cortex Medial temporal lobe (hippocampus, etc.) ACh released by basal forebrain Prefrontal cortex Figure 12.21b Proposed memory circuits. Premotor cortex Sensory and motor inputs Association cortex Basal nuclei Dopamine released by substantia nigra Basal nuclei Thalamus Substantia nigra Procedural (skills) memory circuits © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Thalamus Premotor cortex Figure 12.22 Meninges: dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. Skin of scalp Periosteum Superior sagittal sinus Subdural space Subarachnoid space © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Bone of skull Dura mater • Periosteal layer • Meningeal layer Arachnoid mater Pia mater Arachnoid villus Blood vessel Falx cerebri (in longitudinal fissure only) Figure 12.23 Dural septa and dural venous sinuses. Superior sagittal sinus Falx cerebri Straight sinus Crista galli of the ethmoid bone Pituitary gland Midsagittal view © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Parietal bone Scalp Occipital lobe Tentorium cerebelli Falx cerebelli Cerebellum Arachnoid mater over medulla oblongata Posterior dissection Dura mater Transverse sinus Temporal bone Figure 12.23a Dural septa and dural venous sinuses. Superior sagittal sinus Falx cerebri Straight sinus Crista galli of the ethmoid bone Pituitary gland Midsagittal view © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Tentorium cerebelli Falx cerebelli Figure 12.23b Dural septa and dural venous sinuses. Superior sagittal sinus Falx cerebri Parietal bone Scalp Occipital lobe Tentorium cerebelli Falx cerebelli Cerebellum Arachnoid mater over medulla oblongata Posterior dissection © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Dura mater Transverse sinus Temporal bone Figure 12.24 Formation, location, and circulation of CSF. Superior sagittal sinus Arachnoid villus Choroid plexus Subarachnoid space Arachnoid mater Meningeal dura mater Periosteal dura mater Right lateral ventricle (deep to cut) Interventricular foramen Third ventricle Choroid plexus of fourth ventricle Cerebral aqueduct Lateral aperture Fourth ventricle Median aperture Central canal of spinal cord Ependymal cells Capillary Connective tissue of pia mater 1 The choroid plexus of each ventricle produces CSF. 2 CSF flows through the ventricles and into the subarachnoid space via the median and lateral apertures. Section of choroid plexus 3 CSF flows through the subarachnoid space. 4 CSF is absorbed into the dural venous sinuses via the arachnoid villi. CSF circulation © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Wastes and unnecessary solutes absorbed Cavity of ventricle CSF formation by choroid plexuses CSF forms as a filtrate containing glucose, oxygen, vitamins, and ions (Na+, Cl–, Mg2+, etc.) Figure 12.24a Formation, location, and circulation of CSF. 4 Superior sagittal sinus Arachnoid villus Choroid plexus Subarachnoid space Arachnoid mater Meningeal dura mater Periosteal dura mater 1 Interventricular foramen Third ventricle Right lateral ventricle (deep to cut) 3 Cerebral aqueduct Lateral aperture Fourth ventricle Median aperture Central canal of spinal cord (a) CSF circulation © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Choroid plexus of fourth ventricle 2 1 The choroid plexus of each Ventricle produces CSF. 2 CSF flows through the ventricles and into the subarachnoid space via the median and lateral apertures. 3 CSF flows through the subarachnoid space. 4 CSF is absorbed into the dural venous sinuses via the arachnoid villi. Figure 12.24b Formation, location, and circulation of CSF. Ependymal cells Capillary Connective tissue of pia mater Wastes and unnecessary solutes absorbed Section of choroid plexus Cavity of ventricle CSF formation by choroid plexuses © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. CSF forms as a filtrate containing glucose, oxygen, vitamins, and ions (Na+, Cl–, Mg2+, etc.) Figure 12.25 Hydrocephalus in a newborn. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.26 Gross structure of the spinal cord, dorsal view. Cranial dura mater Terminus of medulla oblongata of brain Cervical spinal nerves Sectioned pedicles of cervical vertebrae Spinal nerve rootlets Cervical enlargement Dorsal median sulcus of spinal cord Dura and arachnoid mater Cervical spinal cord. Thoracic spinal nerves Lumbar enlargement Spinal cord Vertebral arch Denticulate ligament Denticulate ligament Dorsal median sulcus Conus medullaris Cauda equina Lumbar spinal nerves Arachnoid mater Dorsal root Spinal dura mater Filum terminale Thoracic spinal cord, showing denticulate ligaments. Sacral spinal nerves Spinal cord Cauda equina First lumbar vertebral arch (cut across) Conus medullaris The spinal cord and its nerve roots, with the bony vertebral arches removed. The dura mater and arachnoid mater are cut open and reflected laterally. Spinous process of second lumbar vertebra Filum terminale © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Inferior end of spinal cord, showing conus medullaris, cauda equina, and filum terminale. Figure 12.26a Gross structure of the spinal cord, dorsal view. Cervical enlargement Dura and arachnoid mater Lumbar enlargement Conus medullaris Cauda equina Filum terminale © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Cervical spinal nerves Thoracic spinal nerves Lumbar spinal nerves Sacral spinal nerves The spinal cord and its nerve roots, with the bony vertebral arches removed. The dura mater and arachnoid mater are cut open and reflected laterally. Figure 12.26b Gross structure of the spinal cord, dorsal view. Cranial dura mater Terminus of medulla oblongata of brain Sectioned pedicles of cervical vertebrae Spinal nerve rootlets Dorsal median sulcus of spinal cord Cervical spinal cord. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.26c Gross structure of the spinal cord, dorsal view. Spinal cord Vertebral arch Denticulate ligament Denticulate ligament Dorsal median sulcus Arachnoid mater Dorsal root Spinal dura mater Thoracic spinal cord, showing denticulate ligaments. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.26d Gross structure of the spinal cord, dorsal view. Spinal cord Cauda equina First lumbar vertebral arch (cut across) Conus medullaris Spinous process of second lumbar vertebra Filum terminale Inferior end of spinal cord, showing conus medullaris, cauda equina, and filum terminale. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.27 Diagram of a lumbar tap. T12 L5 Ligamentum flavum Lumbar puncture needle entering subarachnoid space L4 Supraspinous ligament Filum terminale L5 S1 Intervertebral disc © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Arachnoid mater Dura mater Cauda equina in subarachnoid space Figure 12.28 Anatomy of the spinal cord. Epidural space (contains fat) Subdural space Subarachnoid space (contains CSF) Pia mater Arachnoid mater Dura mater Spinal meninges Bone of vertebra Dorsal root ganglion Body of vertebra Cross section of spinal cord and vertebra Dorsal median sulcus Dorsal funiculus White columns Ventral funiculus Lateral funiculus Gray commissure Dorsal horn Ventral horn Lateral horn Gray matter Dorsal root ganglion Spinal nerve Dorsal root (fans out into dorsal rootlets) Central canal Ventral median fissure Pia mater Ventral root (derived from several ventral rootlets) Arachnoid mater Spinal dura mater The spinal cord and its meningeal coverings © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.28a Anatomy of the spinal cord. Epidural space (contains fat) Subdural space Subarachnoid space (contains CSF) Pia mater Arachnoid mater Dura mater Spinal meninges Bone of vertebra Dorsal root ganglion Body of vertebra Cross section of spinal cord and vertebra © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.28b Anatomy of the spinal cord. Dorsal funiculus White columns Ventral funiculus Lateral funiculus Dorsal median sulcus Gray commissure Dorsal horn Gray Ventral horn matter Lateral horn Dorsal root ganglion Spinal nerve Dorsal root (fans out into dorsal rootlets) Central canal Ventral median fissure Pia mater Ventral root (derived from several ventral rootlets) Arachnoid mater Spinal dura mater The spinal cord and its meningeal coverings © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.29 Organization of the gray matter of the spinal cord. Dorsal root (sensory) Dorsal horn (interneurons) Dorsal root ganglion SS VS Somatic sensory neuron VM Visceral sensory neuron SM Visceral motor neuron Somatic motor neuron Spinal nerve Ventral horn (motor neurons) Ventral root (motor) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. SS Interneurons receiving input from somatic sensory neurons VS Interneurons receiving input from visceral sensory neurons VM Visceral motor (autonomic) neurons SM Somatic motor neurons Figure 12.30 Major ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) tracts of the spinal cord, cross-sectional view. Ascending tracts Dorsal Fasciculus gracilis white Fasciculus cuneatus column Dorsal spinocerebellar tract Ventral spinocerebellar tract Lateral spinothalamic tract Ventral spinothalamic tract Descending tracts Ventral white commissure Lateral reticulospinal tract Lateral corticospinal tract Rubrospinal tract Medial reticulospinal tract Ventral corticospinal tract Vestibulospinal tract Tectospinal tract © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.31 Pathways of selected ascending spinal cord tracts. Primary somatosensory cortex Axons of third-order neurons Thalamus Cerebrum Midbrain Cerebellum Pons Dorsal spinocerebellar tract (axons of second-order neurons) Lateral spinothalamic tract (axons of second-order neurons) Medial lemniscus (tract) (axons of second-order neurons) Nucleus gracilis Nucleus cuneatus Medulla oblongata Fasciculus cuneatus (axon of first-order sensory neuron) Pain receptors Joint stretch receptor (proprioceptor) Axon of first-order neuron Muscle spindle (proprioceptor) Cervical spinal cord Axons of first-order neurons Fasciculus gracilis (axon of first-order sensory neuron) Temperature receptors Lumbar spinal cord Touch receptor Spinocerebellar pathway Dorsal column–medial lemniscal pathway © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Spinothalamic pathway Figure 12.31a Pathways of selected ascending spinal cord tracts. Primary somatosensory cortex Axons of third-order neurons Thalamus Cerebrum Midbrain Cerebellum Pons Dorsal spinocerebellar tract (axons of second-order neurons) Medial lemniscus (tract) (axons of second-order neurons) Nucleus gracilis Nucleus cuneatus Medulla oblongata Fasciculus cuneatus (axon of first-order sensory neuron) Joint stretch receptor (proprioceptor) Axon of first-order neuron Muscle spindle (proprioceptor) Cervical spinal cord Fasciculus gracilis (axon of first-order sensory neuron) Lumbar spinal cord Touch receptor Spinocerebellar pathway Dorsal column–medial lemniscal pathway © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.31a Pathways of selected ascending spinal cord tracts. (1 of 2) Primary somatosensory cortex Axons of third-order neurons Thalamus Cerebrum Midbrain Cerebellum Pons Spinocerebellar pathway Dorsal column–medial lemniscal pathway © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.31a Pathways of selected ascending spinal cord tracts. (2 of 2) Dorsal spinocerebellar tract (axons of second-order neurons) Medial lemniscus (tract) (axons of second-order neurons) Nucleus gracilis Nucleus cuneatus Medulla oblongata Fasciculus cuneatus (axon of first-order sensory neuron) Axon of first-order neuron Muscle spindle (proprioceptor) Joint stretch receptor (proprioceptor) Cervical spinal cord Fasciculus gracilis (axon of first-order sensory neuron) Lumbar spinal cord Touch receptor Spinocerebellar pathway Dorsal column–medial lemniscal pathway © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.31b Pathways of selected ascending spinal cord tracts. Primary somatosensory cortex Axons of third-order neurons Thalamus Cerebrum Midbrain Cerebellum Pons Lateral spinothalamic tract (axons of second-order neurons) Medulla oblongata Pain receptors Cervical spinal cord Axons of first-order neurons Temperature receptors Lumbar spinal cord Spinothalamic pathway © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.31b Pathways of selected ascending spinal cord tracts. (1 of 2) Primary somatosensory cortex Axons of third-order neurons Thalamus Cerebrum Midbrain Cerebellum Pons © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Spinothalamic pathway Figure 12.31b Pathways of selected ascending spinal cord tracts. (2 of 2) Lateral spinothalamic tract (axons of second-order neurons) Medulla oblongata Pain receptors Cervical spinal cord Axons of first-order neurons Temperature receptors Lumbar spinal cord Spinothalamic pathway © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Table 12.2 Major Ascending (Sensory) Pathways and Spinal Cord Tracts (1 of 3) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Table 12.2 Major Ascending (Sensory) Pathways and Spinal Cord Tracts (2 of 3) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Table 12.2 Major Ascending (Sensory) Pathways and Spinal Cord Tracts (3 of 3) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.32 Three descending pathways by which the brain influences movement. Pyramidal cells (upper motor neurons) Primary motor cortex Internal capsule Cerebrum Red nucleus Midbrain Cerebral peduncle Cerebellum Pons Rubrospinal tract Ventral corticospinal tract Medulla oblongata Pyramids Decussation of pyramids Lateral corticospinal tract Cervical spinal cord Skeletal muscle Lumbar spinal cord Somatic motor neurons (lower motor neurons) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Pyramidal (lateral and ventral corticospinal) pathways Rubrospinal tract Figure 12.32a Three descending pathways by which the brain influences movement. Pyramidal cells (upper motor neurons) Primary motor cortex Internal capsule Cerebrum Midbrain Cerebral peduncle Cerebellum Pons Ventral corticospinal tract Medulla oblongata Pyramids Decussation of pyramids Lateral corticospinal tract Cervical spinal cord Skeletal muscle Lumbar spinal cord Somatic motor neurons (lower motor neurons) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Pyramidal (lateral and ventral corticospinal) pathways Figure 12.32a Three descending pathways by which the brain influences movement. (1 of 2) Pyramidal cells (upper motor neurons) Primary motor cortex Internal capsule Cerebrum Midbrain Cerebral peduncle Cerebellum Pons Pyramidal (lateral and ventral corticospinal) pathways © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.32a Three descending pathways by which the brain influences movement. (2 of 2) Ventral corticospinal tract Medulla oblongata Pyramids Decussation of pyramids Lateral corticospinal tract Cervical spinal cord Skeletal muscle Lumbar spinal cord Somatic motor neurons (lower motor neurons) Pyramidal (lateral and ventral corticospinal) pathways © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.32b Three descending pathways by which the brain influences movement. Cerebrum Red nucleus Midbrain Cerebellum Pons Rubrospinal tract Medulla oblongata Cervical spinal cord Lumbar spinal cord © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Rubrospinal tract Figure 12.32b Three descending pathways by which the brain influences movement. (1 of 2) Cerebrum Red nucleus Midbrain Cerebellum Pons © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Rubrospinal tract Figure 12.32b Three descending pathways by which the brain influences movement. (2 of 2) Rubrospinal tract Medulla oblongata Cervical spinal cord Lumbar spinal cord Rubrospinal tract © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Table 12.3 Major Descending (Motor) Pathways and Spinal Cord Tracts (1 of 2) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Table 12.3 Major Descending (Motor) Pathways and Spinal Cord Tracts (2 of 2) © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.33 Development of the neural tube from embryonic ectoderm. Head Neural fold forming Surface ectoderm Neural plate Tail 1 The neural plate forms from surface ectoderm. It then invaginates, forming the neural groove flanked by neural folds. Neural crest Neural groove 2 Neural fold cells migrate to form the neural crest, which will form much of the PNS and many other structures. Head Surface ectoderm Neural tube Tail © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 The neural groove becomes the neural tube, which will form CNS structures. Figure 12.33 Development of the neural tube from embryonic ectoderm. (1 of 3) Head Neural fold forming Surface ectoderm Neural plate Tail 1 The neural plate forms from surface ectoderm. It then invaginates, forming the neural groove flanked by neural folds. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.33 Development of the neural tube from embryonic ectoderm. (2 of 3) Neural crest Neural groove 2 Neural fold cells migrate to form the neural crest, which will form much of the PNS and many other structures. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.33 Development of the neural tube from embryonic ectoderm. (3 of 3) Head Surface ectoderm Neural tube Tail 3 The neural groove becomes the neural tube, which will form CNS structures. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 12.34 Structure of the embryonic spinal cord. Dorsal root ganglion: sensory neurons from neural crest Alar plate: interneurons White matter Basal plate: motor neurons Neural tube cells © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Central cavity Figure 12.35 Newborn with a lumbar myelomeningocele. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.