* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Central Nervous System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
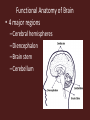
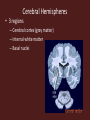
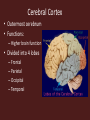
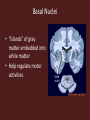
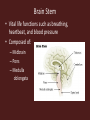
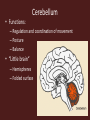
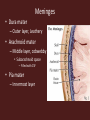
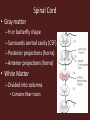
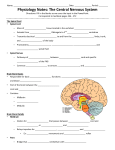
Central Nervous System Development • Embryo – Begins as neural tube • @ 4 weeks – Brain begins to develop – Remaining neural tube becomes spinal cord Functional Anatomy of Brain • 4 major regions –Cerebral hemispheres –Diencephalon –Brain stem –Cerebellum Cerebral Hemispheres • “cerebrum” • Surface has ridges – Gyri- Ridges – Sulci- Shallow grooves – Fissures- Deep grooves Cerebral Hemispheres • 3 regions – Cerebral cortex (gray matter) – Internal white matter – Basal nuclei Cerebral Cortex • Outermost cerebrum • Functions: – Higher brain function • Divided into 4 lobes – Frontal – Parietal – Occipital – Temporal • Frontal Cerebral Lobes – Reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving • Parietal – movement, orientation, recognition, perception of stimuli • Occipital – visual processing • Temporal – perception and recognition of auditory stimuli, memory, and speech Cerebral White Matter • Myelinated axons that connect with other brain regions (tracts) • Corpus Callosum – Largest bundle – Connects left hemisphere to right hemisphere Basal Nuclei • “Islands” of gray matter embedded into white matter • Help regulate motor activities Diencephalon • Composed of two structures – Thalamus • Encloses third ventricle • Relay station for sensory impulses – Hypothalamus • Autonomic functions • Regulates body temperature, water balance, metabolism, limbic system (emotion and behavior), pituitary gland Brain Stem • Vital life functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and blood pressure • Composed of: – Midbrain – Pons – Medulla oblongata Cerebellum • Functions: – Regulation and coordination of movement – Posture – Balance • “Little brain“ – Hemispheres – Folded surface Protection of CNS • Neurons are irreplaceable • Protective features: – Skull & vertebral column • Bone enclosure – Meninges • membranes – Cushioning • Cerebrospinal fluid Meninges • Dura mater – Outer layer, Leathery • Arachnoid mater – Middle layer, cobwebby • Subarachnoid space – Filled with CSF • Pia mater – Innermost layer Cerebrospinal Fluid • Composition similar to blood plasma • Formed from blood by choroid plexus – Choroid plexus • Capillaries in brain ventricles • Protective cushion for brain and spinal cord • Blood brain barrier – Brain environment must be constant – Least permeable capillaries in body – Prevents substances from entering brain tissue Spinal Cord • • • • • 17 inches long (~L2 vertebrae) Continuation of brain stem Pathway to and from brain Protected by meninges 31 pairs of nerves Spinal Cord • Gray matter – H or butterfly shape – Surrounds central cavity (CSF) – Posterior projections (horns) – Anterior projections (horns) • White Matter – Divided into columns • Contains fiber tracts