* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download auditory association cortex
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Animal echolocation wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Sensory cue wikipedia , lookup
Music psychology wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
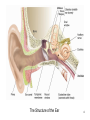
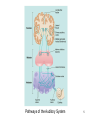
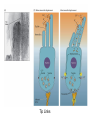
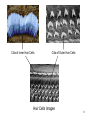
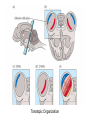
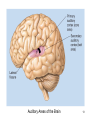
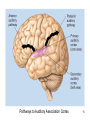
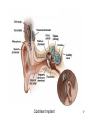
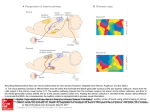
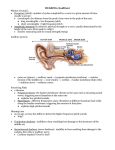
Psychology 304: Brain and Behaviour Lecture 29 1 Announcement Please note that course evaluations are available online. If you have not received an e-mail directing you to the evaluations for this course, you may provide your evaluation at: https://eval.olt.ubc.ca/arts. Your feedback is extremely valuable—both to the Psychology Department and to me. 2 From last class …. 3 The Structure of the Ear 4 Pathways of the Auditory System 5 Miscellaneous Points 1. Tip links. 2. Function of outer hair cells. 3. Duplex (duplicity) theory of pitch perception, duplex theory of sound localization, tonotopic organization. 6 Tip Links 7 Cilia of Inner Hair Cells Cilia of Outer Hair Cells Hair Cells Images 8 Tonotopic Organization 9 The Auditory System 1. What are the major areas of the brain that are associated with the perception of sound? 2. What is the neurological basis of deafness? 10 By the end of today’s class, you should be able to: 1. identify the locations and functions of the primary cortex, secondary cortex, and association areas for the auditory system. 2. discuss the three primary causes of deafness. 3. explain how cochlear implants restore auditory ability. 11 What are the major areas of the brain that are associated with the perception of sound? • The majority of thalamic neurons that receive sound information subsequently project the information to the primary auditory cortex. Thereafter, information is projected to the secondary auditory cortex (SII) and association areas. 12 Auditory Areas of the Brain 13 • Current theory suggests two large areas of auditory association cortex: the prefrontal cortex and the posterior parietal cortex. • The anterior auditory pathway leading to the prefrontal cortex is thought to be involved in identifying sounds; the posterior auditory pathway is thought to be involved in locating sounds. 14 Pathways to Auditory Association Cortex 15 What is the neurological basis of deafness? • Although impaired hearing is a common human disability, complete deafness is rare. • There are three common classes of hearing impairments: conductive deafness (outer or middle ear damage), sensorineural deafness (inner ear damage), and central deafness (cortical damage). • Cochlear implants can improve the hearing of those who have sensorineural deafness. 16 Cochlear Implant 17 Cochlear Implant 18 The Auditory System 1. What are the major areas of the brain that are associated with the perception of sound? 2. What is the neurological basis of deafness? 19