* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vision Lecture Notes
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
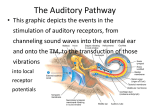
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Color psychology wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Stroop effect wikipedia , lookup
Animal echolocation wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Sensory cue wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup






![Unit 8 Review Sheet[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001686639_1-accaddf9a4bef8f1f5e508cc8efafb82-150x150.png)