* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Auditory Sense: Hearing
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Auditory processing disorder wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
Olivocochlear system wikipedia , lookup
Sound from ultrasound wikipedia , lookup
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
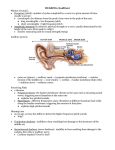
The Auditory Sense: Hearing EQ: What is the process though which we hear and how do we differentiate between sounds? Step 1: Accessory Structures of Hearing • Sounds (A repetitive fluctuation in the pressure of a medium, such as air) are what we hear. • The Pinna, in effect, guides the sound down the Ear Canal to the Tympanic Membrane Focus on the Tympanic Membrane Step 2: Receptor Structures of Hearing • Transduction in the ear takes place in the Cochlea. • The Cochlea can expand and contract in order to differentiate the sound(s) being passed into it. Focus on the Basilar Membrane (corti) Step 3: Sensory Nerves of Hearing • Once the information has been coded during transduction, the information travels up the auditory nerve to the Thalamus. Steps 4/5: Sensory Nerves of Hearing • Once in the Thalamus, the neural impulse is sent to the Primary Auditory Cortex within the temporal lobe • Within this structure, the neural impulse is decoded (Perceived) and decisions based on behavior occur Sensing Loudness: • A loud sound has a higher amplitude • The further the distance between the peak and baseline, the louder the sound (amplitude) • We can measure how loud a sound is in decibels (db) Sensing Pitch: • Pitch refers to the frequency of sound waves measured in hertz • The shorter the wavelength, the higher the frequency (pitch) • The longer the wavelength, the lower the frequency(pitch) Sensing Timbre: • Timbre is the quality of a sound • It is determined by the frequency and amplitudes of a sound • The best quality of timbre comes from naturally heard sounds Deafness: • Deafness can be caused by several issues within the sense of hearing. • While some forms of deafness can be treated, others are permanent Conduction Deafness: • The most common form of deafness • Caused when the three inner bones (Malleus, Incus, Stapes) of the ear fuse • Can be treated through hearing aids Nerve Deafness: • Caused by damage to the auditory nerve or the Cortical Cells • Can be treated through Cochlear implants Temporal Lobe Deafness: • Caused by damage to the temporal lobe • Cannot be treated